
A satellite is orbiting around the earth in an orbit in equatorial plane of radius $2{{R}_{e}}$ (where ${{R}_{e}}$ is the radius of the earth). Find the area on the Earth that this satellite covers for communication purposes in its complete revolution.
A. $4\pi {{R}_{e}}^{2}$
B. $2\pi \sqrt{3}{{R}_{e}}^{2}$
C. $2\pi \left( 2-\sqrt{3} \right){{R}_{e}}^{2}$
D. $2\pi \left( 4+\sqrt{3} \right){{R}_{e}}^{2}$
Answer
534k+ views
Hint: On making a neat diagram of the situation given, you will see that there are two patches at north as well as south end that are not covered by the satellite. So, we could simply subtract this area from the total area of Earth to find the answer. You could use the solid angle subtended by these patches at the earth’s center to find the area of the patches.
Formula used:
Solid angle,
$\Omega =2\pi \left( 1-\cos \theta \right)$
Complete answer:
In the question, we are said that a satellite is orbiting around the earth in orbit that is double the Earth’s radius. We are supposed to find the area on the Earth that the satellite covers in one complete revolution for communication purposes.
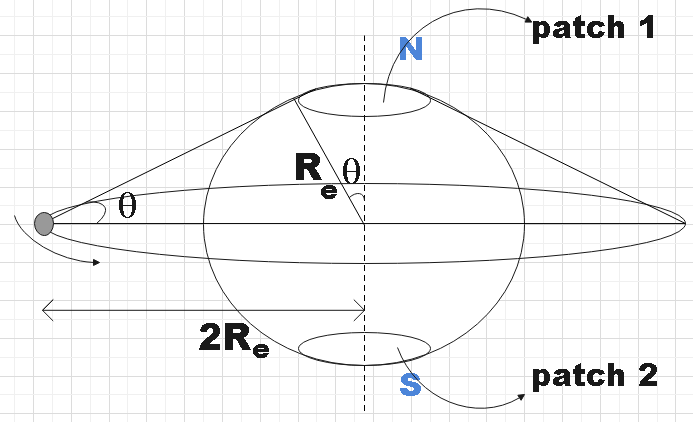
Clearly, we see that there are two patches that are left uncovered by the satellite during its revolution around earth. So, we have to subtract this area from the earth’s total area to get the answer.
We see that,
$\sin \theta =\dfrac{{{R}_{e}}}{2{{R}_{e}}}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \theta =\dfrac{\pi }{6}$ ………………………………………….. (1)
Now, we could find the solid angle subtended by a patch on Earth’s centre as,
$\Omega =2\pi \left( 1-\cos \theta \right)$
$\Rightarrow \Omega =\pi \left( 2-\sqrt{3} \right)steradian$
Now area of a patch would be,
${{A}_{p}}=\Omega {{R}_{e}}^{2}=\pi \left( 2-\sqrt{3} \right){{R}_{e}}^{2}$ ………………………………… (2)
Now, the required area could be given by,
${{A}_{C}}=4\pi {{R}_{e}}^{2}-2{{A}_{p}}$
$\Rightarrow {{A}_{C}}=4\pi {{R}_{e}}^{2}-2\pi \left( 2-\sqrt{3} \right){{R}_{e}}^{2}$
$\therefore {{A}_{C}}=2\sqrt{3}\pi {{R}_{e}}^{2}$
Therefore, we found the area of the earth covered by the satellite for communication purpose to be,
${{A}_{C}}=2\sqrt{3}\pi {{R}_{e}}^{2}$
Option B is correct.
Note:
Solid angle by definition is the measure of the amount of the field of view from a certain point that an object under consideration covers. In other words, we could define it as the measure of how large a particular object appears when viewed from that point. It is normally represented by Greek letter $\Omega $.
Formula used:
Solid angle,
$\Omega =2\pi \left( 1-\cos \theta \right)$
Complete answer:
In the question, we are said that a satellite is orbiting around the earth in orbit that is double the Earth’s radius. We are supposed to find the area on the Earth that the satellite covers in one complete revolution for communication purposes.

Clearly, we see that there are two patches that are left uncovered by the satellite during its revolution around earth. So, we have to subtract this area from the earth’s total area to get the answer.
We see that,
$\sin \theta =\dfrac{{{R}_{e}}}{2{{R}_{e}}}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \theta =\dfrac{\pi }{6}$ ………………………………………….. (1)
Now, we could find the solid angle subtended by a patch on Earth’s centre as,
$\Omega =2\pi \left( 1-\cos \theta \right)$
$\Rightarrow \Omega =\pi \left( 2-\sqrt{3} \right)steradian$
Now area of a patch would be,
${{A}_{p}}=\Omega {{R}_{e}}^{2}=\pi \left( 2-\sqrt{3} \right){{R}_{e}}^{2}$ ………………………………… (2)
Now, the required area could be given by,
${{A}_{C}}=4\pi {{R}_{e}}^{2}-2{{A}_{p}}$
$\Rightarrow {{A}_{C}}=4\pi {{R}_{e}}^{2}-2\pi \left( 2-\sqrt{3} \right){{R}_{e}}^{2}$
$\therefore {{A}_{C}}=2\sqrt{3}\pi {{R}_{e}}^{2}$
Therefore, we found the area of the earth covered by the satellite for communication purpose to be,
${{A}_{C}}=2\sqrt{3}\pi {{R}_{e}}^{2}$
Option B is correct.
Note:
Solid angle by definition is the measure of the amount of the field of view from a certain point that an object under consideration covers. In other words, we could define it as the measure of how large a particular object appears when viewed from that point. It is normally represented by Greek letter $\Omega $.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




