
A round balloon of radius r subtends an angle $\alpha $ at the eye of the observer, while the angle of elevation of its centre is $\beta $. Prove that the height of the centre of the balloon is $r\sin \beta \csc \dfrac{\alpha }{2}$.
Answer
607.8k+ views
- Hint: We will be using the concept of trigonometry and height and distance to solve the problem. We will first start by drawing the diagram as per the data given in the questions then we will use the angle of elevation to apply the trigonometric ratios to prove that the height of the balloon is $r\sin \beta \csc \dfrac{\alpha }{2}$.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Now we have been given a round balloon of radius r which subtends an angle \[\alpha \] at the eye of the observer. Also the angle of elevation of its centre is \[\beta \]. We draw the diagram corresponding to this situation.
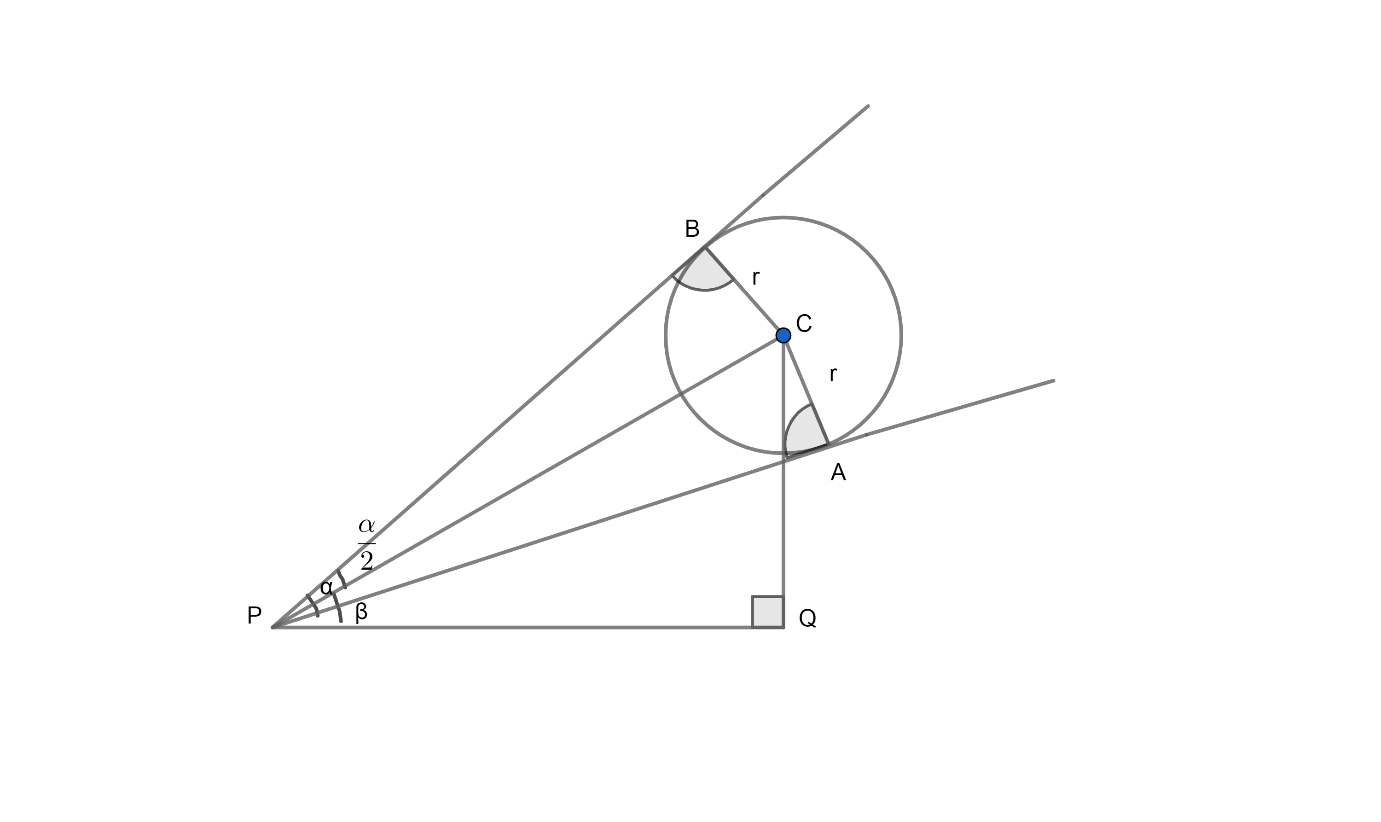
Let the eye of the observer be at P. Now, we have to find the height of the centre of the balloon from the ground and prove it to be equal to $r\sin \left( \beta \right)\csc \left( \dfrac{\alpha }{2} \right)$.
Now, we can see from the figure that,
In $\Delta PBC\ and\ \Delta PCA$,
$\begin{align}
& PC=PC \\
& BC=AC\left( radii \right) \\
& \angle PBA=\angle PAC\left( 90{}^\circ each \right) \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, $\Delta PBC\cong \Delta PCA$ by RHS.
Therefore, we have by correspondence part of congruent triangles that,
$\begin{align}
& \angle BPC=\angle CPA \\
& \angle BPA=\alpha \\
& \Rightarrow \angle BPC=\angle CPA=\dfrac{\alpha }{2} \\
\end{align}$
Now, in $\Delta PCA$ we will apply $\sin \theta $ to find PAC. Therefore,
$\begin{align}
& \sin \left( \dfrac{\alpha }{2} \right)=\dfrac{r}{PC} \\
& PC=r\csc \left( \dfrac{\alpha }{2} \right)............\left( 1 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, in $\Delta PCQ$ we have $\angle CPQ=\beta $. Therefore, we will apply $\sin \theta $ to get the height of the centre from ground.
$=\sin \left( \beta \right)=\dfrac{P}{H}$
Where P is perpendicular and H is Hypotenuse.
$=\sin \left( \beta \right)=\dfrac{CQ}{PC}$
Now, we have from (1) the value of $PC=r\csc \left( \dfrac{\alpha }{2} \right)$. Therefore,
$\begin{align}
& \sin \left( \beta \right)=\dfrac{CQ}{r\csc \left( \dfrac{\alpha }{2} \right)} \\
& CQ=r\sin \left( \beta \right)\csc \left( \dfrac{\alpha }{2} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, we have proved that the distance of the centre from ground is $r\sin \left( \beta \right)\csc \left( \dfrac{\alpha }{2} \right)$.
Note: To solve these types of questions it is advised to draw a diagram clearly showing all the values given also it is important to note that we have first applied the $\sin \theta $ in the $\Delta PCA$ to find the value of PC then we have used this value to prove the result given to us. It is also important to remember the following identities to solve these questions easily.
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{\cos \theta }=\sec \theta \\
& \dfrac{1}{\sin \theta }=\csc \theta \\
& \tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta } \\
\end{align}$
Complete step-by-step solution -
Now we have been given a round balloon of radius r which subtends an angle \[\alpha \] at the eye of the observer. Also the angle of elevation of its centre is \[\beta \]. We draw the diagram corresponding to this situation.

Let the eye of the observer be at P. Now, we have to find the height of the centre of the balloon from the ground and prove it to be equal to $r\sin \left( \beta \right)\csc \left( \dfrac{\alpha }{2} \right)$.
Now, we can see from the figure that,
In $\Delta PBC\ and\ \Delta PCA$,
$\begin{align}
& PC=PC \\
& BC=AC\left( radii \right) \\
& \angle PBA=\angle PAC\left( 90{}^\circ each \right) \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, $\Delta PBC\cong \Delta PCA$ by RHS.
Therefore, we have by correspondence part of congruent triangles that,
$\begin{align}
& \angle BPC=\angle CPA \\
& \angle BPA=\alpha \\
& \Rightarrow \angle BPC=\angle CPA=\dfrac{\alpha }{2} \\
\end{align}$
Now, in $\Delta PCA$ we will apply $\sin \theta $ to find PAC. Therefore,
$\begin{align}
& \sin \left( \dfrac{\alpha }{2} \right)=\dfrac{r}{PC} \\
& PC=r\csc \left( \dfrac{\alpha }{2} \right)............\left( 1 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, in $\Delta PCQ$ we have $\angle CPQ=\beta $. Therefore, we will apply $\sin \theta $ to get the height of the centre from ground.
$=\sin \left( \beta \right)=\dfrac{P}{H}$
Where P is perpendicular and H is Hypotenuse.
$=\sin \left( \beta \right)=\dfrac{CQ}{PC}$
Now, we have from (1) the value of $PC=r\csc \left( \dfrac{\alpha }{2} \right)$. Therefore,
$\begin{align}
& \sin \left( \beta \right)=\dfrac{CQ}{r\csc \left( \dfrac{\alpha }{2} \right)} \\
& CQ=r\sin \left( \beta \right)\csc \left( \dfrac{\alpha }{2} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, we have proved that the distance of the centre from ground is $r\sin \left( \beta \right)\csc \left( \dfrac{\alpha }{2} \right)$.
Note: To solve these types of questions it is advised to draw a diagram clearly showing all the values given also it is important to note that we have first applied the $\sin \theta $ in the $\Delta PCA$ to find the value of PC then we have used this value to prove the result given to us. It is also important to remember the following identities to solve these questions easily.
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{\cos \theta }=\sec \theta \\
& \dfrac{1}{\sin \theta }=\csc \theta \\
& \tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta } \\
\end{align}$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

The Equation xxx + 2 is Satisfied when x is Equal to Class 10 Maths

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What is Contraception List its four different methods class 10 biology CBSE




