
A rocket of height h meters is fired vertically upwards. Its velocity at time t seconds is (2t + 3 ) meters per second. If the angle of elevation of the top of the rocket from a point on the ground after 1 second of firing is $\dfrac{\pi }{6}$ and after 3 seconds it is $\dfrac{\pi }{3}$then the distance at the point from the rocket is
A) $14\sqrt 3 meters$
B) $7\sqrt 3 meters$
C) $2\sqrt 3 meters$
D) Cannot be found without the value of h.
Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint:
By integrating the given velocity we get the displacement and substituting the values of t we get the values of BC and BD and using the given angle of elevation we can find the distance at the point from which the rocket is projected.
Complete step by step solution:
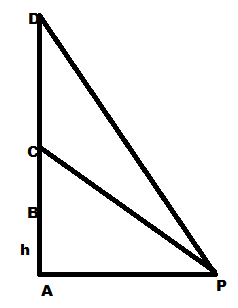
We are given that the velocity of the rocket is (2t + 3 ) meters per second
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} = 2t + 3$
Now to find the displacement x we need to integrate the velocity
$
\Rightarrow dx = \left( {2t + 3} \right)dt \\
\Rightarrow \int {dx = \int {\left( {2t + 3} \right)dt} } \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{2{t^2}}}{2} + 3t + c = {t^2} + 3t + c \\
$
Now we have the displacement
The displacement BC is made when t = 1
$ \Rightarrow BC = {1^2} + 3(1) + c = 4 + c$
The displacement BD is made when t = 3
$ \Rightarrow BD = {3^2} + 3(3) + c = 18 + c$
Now at t = 1 the angle of elevation is $\dfrac{\pi }{6}$
Therefore $\tan \dfrac{\pi }{6} = \dfrac{{h + 4 + c}}{{AP}}$ …………(1)
Now at t = 3 the angle of elevation is $\dfrac{\pi }{3}$
Therefore $\tan \dfrac{\pi }{3} = \dfrac{{h + 18 + c}}{{AP}}$ …………..(2)
Subtracting (2) – (1)
$
\Rightarrow \tan \dfrac{\pi }{3} - \tan \dfrac{\pi }{6} = \dfrac{{h + 18 + c - h - 4 - c}}{{AP}} \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt 3 - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{14}}{{AP}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{14}}{{AP}} \\
\Rightarrow AP = 14 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} = 7\sqrt 3 meters \\
$
Hence we get the distance of the rocket to be $7\sqrt 3 meters$. The correct option is (B).
Note:
Height is the measurement of an object in the vertical direction and distance is the measurement of an object from a particular point in the horizontal direction.
So if we know the height of the object and the linear distance, we can easily find out the angle by trigonometric formula. It is given by tan = Height / distance . The angle of elevation of the sun that is better known as altitude angle, can also be found by the same method.
By integrating the given velocity we get the displacement and substituting the values of t we get the values of BC and BD and using the given angle of elevation we can find the distance at the point from which the rocket is projected.
Complete step by step solution:

We are given that the velocity of the rocket is (2t + 3 ) meters per second
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} = 2t + 3$
Now to find the displacement x we need to integrate the velocity
$
\Rightarrow dx = \left( {2t + 3} \right)dt \\
\Rightarrow \int {dx = \int {\left( {2t + 3} \right)dt} } \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{2{t^2}}}{2} + 3t + c = {t^2} + 3t + c \\
$
Now we have the displacement
The displacement BC is made when t = 1
$ \Rightarrow BC = {1^2} + 3(1) + c = 4 + c$
The displacement BD is made when t = 3
$ \Rightarrow BD = {3^2} + 3(3) + c = 18 + c$
Now at t = 1 the angle of elevation is $\dfrac{\pi }{6}$
Therefore $\tan \dfrac{\pi }{6} = \dfrac{{h + 4 + c}}{{AP}}$ …………(1)
Now at t = 3 the angle of elevation is $\dfrac{\pi }{3}$
Therefore $\tan \dfrac{\pi }{3} = \dfrac{{h + 18 + c}}{{AP}}$ …………..(2)
Subtracting (2) – (1)
$
\Rightarrow \tan \dfrac{\pi }{3} - \tan \dfrac{\pi }{6} = \dfrac{{h + 18 + c - h - 4 - c}}{{AP}} \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt 3 - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{14}}{{AP}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{14}}{{AP}} \\
\Rightarrow AP = 14 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} = 7\sqrt 3 meters \\
$
Hence we get the distance of the rocket to be $7\sqrt 3 meters$. The correct option is (B).
Note:
Height is the measurement of an object in the vertical direction and distance is the measurement of an object from a particular point in the horizontal direction.
So if we know the height of the object and the linear distance, we can easily find out the angle by trigonometric formula. It is given by tan = Height / distance . The angle of elevation of the sun that is better known as altitude angle, can also be found by the same method.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




