
A rock is launched upward at ${45^o}$. A bee moves along the trajectory of the rock at a constant speed equal to the initial speed of the rock. What is the magnitude of acceleration (in m${s^{ - 2}}$) of the bee at the top point of the trajectory? For the rock, neglect the air resistance.
(A) 20
(B) 30
(C) 40
(D) 50
Answer
545.1k+ views
Hint : In a projectile motion a body moves simultaneously in the direction of horizontal and vertical. Here in question it is projected with${45^o}$. We first find out the acceleration due to gravity of rock which is $\dfrac{{{{\left( {v{{\cos }^o}} \right)}^2}}}{r}$ =g, where v is the final velocity, r is the radius of curvature and g is the gravity=10$m{s^{ - 2}}$ . From there we will get $\dfrac{{{v^2}}}{r}$ for stone and it will be the same for bees too.
Complete Step by step solution:
Step 1:
Projectile motion is a form of motion experienced by an object or particle (a projectile) that is projected near the Earth's surface and moves along a curved path under the action of gravity only (in particular, the effects of air resistance are assumed to be negligible).
When a particle is projected obliquely near the earth’s surface, it moves simultaneously in the direction of horizontal and vertical. The motion of such a particle is called Projectile Motion. In the below diagram, where a particle is projected at an angle$\theta $ =${45^o}$ with an initial velocity u.
We have a diagram below for the better understanding of the question. Stone moves along tangentially hence along the cos$\theta $ component.
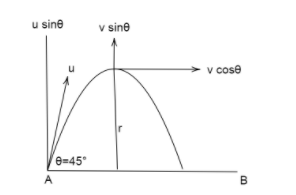
Step 2:
We are given a bee moves along the trajectory of the rock at a constant speed equal to the initial speed of the rock
And we have to find the magnitude of acceleration (in m${s^{ - 2}}$) of the bee at the top point of the trajectory.
So, the acceleration due to gravity of rock at the top point is $\dfrac{{{{\left( {v{{\cos }^o}} \right)}^2}}}{r}$=g, where v is the final velocity, r is the radius of curvature and g is the gravity=10$m{s^{ - 2}}$
From here we can write it as $\dfrac{{{v^2}}}{r}$=$\dfrac{g}{{\cos \theta }}$ ……. (1)
We are given$\theta $=${45^o}$ and cos${45^o}$=$\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$ ($\therefore {\cos ^2}{45^o} = \dfrac{1}{2}$ )
Putting in equation (1) the value of ${\cos ^2}{45^o}$ and g we will get $\dfrac{{{v^2}}}{r}$=20m${s^{ - 2}}$
The bee and rock will have same radius of curvature r hence the magnitude of acceleration (in m${s^{ - 2}}$) of the bee at the top point of the trajectory is 20$m{s^{ - 2}}$
Option A is correct.
Note:
In projectile motion the maximum horizontal range can be obtained when an object is thrown at an angle of ${45^o}$ and here the range will be maximum for the stone. For maximum horizontal range ${R_m} = \dfrac{{{v^2}}}{g}$ , g is the gravity constant and v is velocity.
Complete Step by step solution:
Step 1:
Projectile motion is a form of motion experienced by an object or particle (a projectile) that is projected near the Earth's surface and moves along a curved path under the action of gravity only (in particular, the effects of air resistance are assumed to be negligible).
When a particle is projected obliquely near the earth’s surface, it moves simultaneously in the direction of horizontal and vertical. The motion of such a particle is called Projectile Motion. In the below diagram, where a particle is projected at an angle$\theta $ =${45^o}$ with an initial velocity u.
We have a diagram below for the better understanding of the question. Stone moves along tangentially hence along the cos$\theta $ component.

Step 2:
We are given a bee moves along the trajectory of the rock at a constant speed equal to the initial speed of the rock
And we have to find the magnitude of acceleration (in m${s^{ - 2}}$) of the bee at the top point of the trajectory.
So, the acceleration due to gravity of rock at the top point is $\dfrac{{{{\left( {v{{\cos }^o}} \right)}^2}}}{r}$=g, where v is the final velocity, r is the radius of curvature and g is the gravity=10$m{s^{ - 2}}$
From here we can write it as $\dfrac{{{v^2}}}{r}$=$\dfrac{g}{{\cos \theta }}$ ……. (1)
We are given$\theta $=${45^o}$ and cos${45^o}$=$\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$ ($\therefore {\cos ^2}{45^o} = \dfrac{1}{2}$ )
Putting in equation (1) the value of ${\cos ^2}{45^o}$ and g we will get $\dfrac{{{v^2}}}{r}$=20m${s^{ - 2}}$
The bee and rock will have same radius of curvature r hence the magnitude of acceleration (in m${s^{ - 2}}$) of the bee at the top point of the trajectory is 20$m{s^{ - 2}}$
Option A is correct.
Note:
In projectile motion the maximum horizontal range can be obtained when an object is thrown at an angle of ${45^o}$ and here the range will be maximum for the stone. For maximum horizontal range ${R_m} = \dfrac{{{v^2}}}{g}$ , g is the gravity constant and v is velocity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




