
A road is 8m wide. Two poles measuring 10m and 16m are fixed on two sides across the road. Find distance between their upper ends $(AC)$.


Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint : In above question we need to find the length of AC.
For that we will assume this figure. As a combination of two figures. Below one is a rectangle with sides ABDE and above one is the right triangle AEC.
We have all the dimensions of the rectangle, we will find dimensions of triangles.
Formulas/Properties used
1. Pythagorean Theorem -
According to this theorem ${(Hypotenuse)^2} = $ sum of square of legs
${(AB)^2} = {(AC)^2} + {(BC)^2}$
2. Property of rectangle – Opposite sides of rectangle are equal and parallel to each other. And its vertices make an angle of $90^\circ $.
Complete step by step solution :
Let’s divide the given figure in two parts.
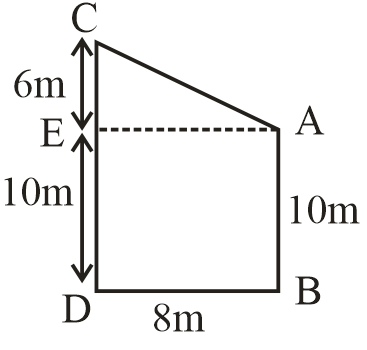
Two parts of given figure one is $\Delta ACE$ and other one is rectangle ABDE
Here in $\Delta ACE$
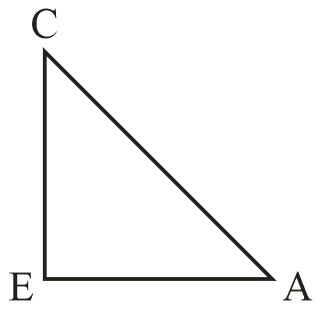
$EA = 8m$
$CE = CD = ED$
$ = (16 - 10)m$
$CE = 6m$
In rectangle ABDE
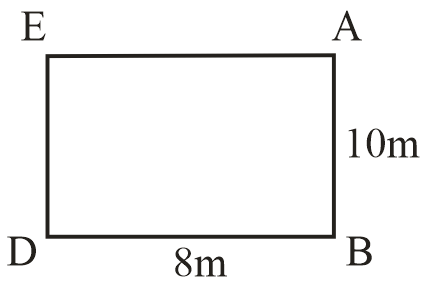
If $AB = 10m$ given
$ED = 10m$ (opposite sides of rectangle are equal)
$DB = 8m$ (given)
$EA = 8m$ (opposite sides of rectangle)
$\Delta ACE$ is a right angled triangle, so by using Pythagora's theorem.
${(Hypotenuse)^2} = {(Base)^2} + {(Perpendicular)^2}$
${(AC)^2} = {(CE)^2} + {(AE)^2}$
${(AC)^2} = {(6)^2} + {(8)^2}$
${(AC)^2} = 36 + 64$
${(AC)^2} = 100$
$AC = \sqrt {100} $
$AC = 10m$
Therefore distance between upper ends of given figure is $AC = 10m$
Note: While using Pythagoras theorem do not make the mistake of adding the values of both the legs first and then squaring the result. It is incorrect .
For that we will assume this figure. As a combination of two figures. Below one is a rectangle with sides ABDE and above one is the right triangle AEC.
We have all the dimensions of the rectangle, we will find dimensions of triangles.
Formulas/Properties used
1. Pythagorean Theorem -
According to this theorem ${(Hypotenuse)^2} = $ sum of square of legs
${(AB)^2} = {(AC)^2} + {(BC)^2}$
2. Property of rectangle – Opposite sides of rectangle are equal and parallel to each other. And its vertices make an angle of $90^\circ $.
Complete step by step solution :
Let’s divide the given figure in two parts.

Two parts of given figure one is $\Delta ACE$ and other one is rectangle ABDE
Here in $\Delta ACE$

$EA = 8m$
$CE = CD = ED$
$ = (16 - 10)m$
$CE = 6m$
In rectangle ABDE

If $AB = 10m$ given
$ED = 10m$ (opposite sides of rectangle are equal)
$DB = 8m$ (given)
$EA = 8m$ (opposite sides of rectangle)
$\Delta ACE$ is a right angled triangle, so by using Pythagora's theorem.
${(Hypotenuse)^2} = {(Base)^2} + {(Perpendicular)^2}$
${(AC)^2} = {(CE)^2} + {(AE)^2}$
${(AC)^2} = {(6)^2} + {(8)^2}$
${(AC)^2} = 36 + 64$
${(AC)^2} = 100$
$AC = \sqrt {100} $
$AC = 10m$
Therefore distance between upper ends of given figure is $AC = 10m$
Note: While using Pythagoras theorem do not make the mistake of adding the values of both the legs first and then squaring the result. It is incorrect .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




