
A ring of radius $R$ is rolling purely on the outer surface of a pipe of radius $4\;R$. At some instant, the centre of the ring has a constant speed $v$. Then, the acceleration of the point on the ring which is in contact with the surface of the pipe is
\[\begin{align}
& A.\dfrac{4{{v}^{2}}}{5R} \\
& B.\dfrac{3{{v}^{2}}}{5R} \\
& C.\dfrac{{{v}^{2}}}{4R} \\
& D.0 \\
\end{align}\]
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: We know that acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes with respect to time. Here we have two rings placed on one another. Since both are moving with a velocity $v$, we can find the acceleration at any point of contact between the two rings.
Formula used: $a=\dfrac{v}{t}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
Consider the system of rings with radius $R$ and $4\; R$ placed as shown in the figure. Let the linear velocity of the system be $v$. And angular velocity $\omega$, we know that $\omega=\dfrac{v}{r}$ where $r$ is the radius of the system.
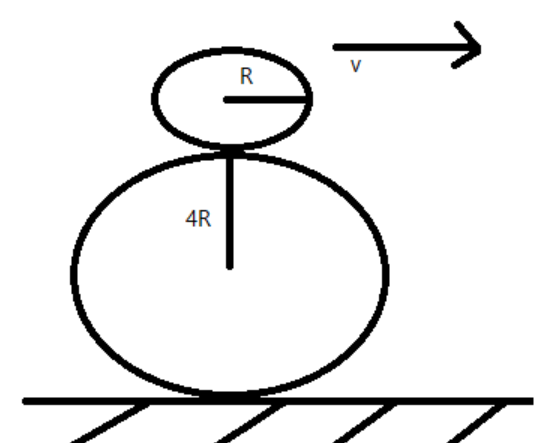
If we consider the completer system to be a ring of radius $5\; R$ then the angular acceleration acting on the center of mass of the system is given as $a_{cm}=\dfrac{v^{2}}{5R}$ in the negative y-direction.
Let us now assume that the small and big ring is in contact and that they don’t slip away. Then the acceleration at the point of contact between the two rings is given as $=\omega^{2}R=\dfrac{v^{2}}{R}$ this is acting in the positive y-direction.
Clearly, the two accelerations act at the same point and are in opposite directions. Thus we can subtract the two to find the net acceleration. Then the net acceleration is given as $a_{net}=a_{cm}-a$
On substituting the values, we get $\implies a_{net}=\dfrac{v^{2}}{5R}-\dfrac{v^{2}}{R}=\dfrac{4v^{2}}{5R}$
Thus the acceleration at the point of contact of the is $\dfrac{4v^{2}}{5R}$
Hence the answer is \[A.\dfrac{4{{v}^{2}}}{5R}\]
Note: Here, since the body rolls, it will have angular acceleration and angular velocity. Since the linear velocity is given, we can calculate the angular velocity. Also, there are two types of acceleration here in the opposite direction. Hence we subtract the two to find the net acceleration on the system.
Formula used: $a=\dfrac{v}{t}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
Consider the system of rings with radius $R$ and $4\; R$ placed as shown in the figure. Let the linear velocity of the system be $v$. And angular velocity $\omega$, we know that $\omega=\dfrac{v}{r}$ where $r$ is the radius of the system.

If we consider the completer system to be a ring of radius $5\; R$ then the angular acceleration acting on the center of mass of the system is given as $a_{cm}=\dfrac{v^{2}}{5R}$ in the negative y-direction.
Let us now assume that the small and big ring is in contact and that they don’t slip away. Then the acceleration at the point of contact between the two rings is given as $=\omega^{2}R=\dfrac{v^{2}}{R}$ this is acting in the positive y-direction.
Clearly, the two accelerations act at the same point and are in opposite directions. Thus we can subtract the two to find the net acceleration. Then the net acceleration is given as $a_{net}=a_{cm}-a$
On substituting the values, we get $\implies a_{net}=\dfrac{v^{2}}{5R}-\dfrac{v^{2}}{R}=\dfrac{4v^{2}}{5R}$
Thus the acceleration at the point of contact of the is $\dfrac{4v^{2}}{5R}$
Hence the answer is \[A.\dfrac{4{{v}^{2}}}{5R}\]
Note: Here, since the body rolls, it will have angular acceleration and angular velocity. Since the linear velocity is given, we can calculate the angular velocity. Also, there are two types of acceleration here in the opposite direction. Hence we subtract the two to find the net acceleration on the system.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




