
A ring of radius $r = 25cm$ made of lead wire is rotated about a stationary vertical axis passing through its center and perpendicular to the plane of the ring. The angular speed in $rps$ at which the ring ruptures is $(20 + x)$. The value of $x$ is:
Answer
595.2k+ views
- Hint: You can start by assuming a small section on the ring $\theta $ . Then draw a well-labelled diagram including all the forces acting on the ring. Then compare the inwards and outwards forces on the ring that will give you this equation ${F_C} = 2T\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2}$. Then use the equation $F = ma$ and compare the two equations of force to get this equation $m{\omega ^2}R = T\theta $. Then use the equation $\because \rho = \dfrac{m}{V}$ and obtain the value of $m$ and substitute this value into $m{\omega ^2}R = T\theta $ to reach the solution.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the given situation the ring will only break if the tension on the ring will be equal to the breaking stress of the wire.
Let’s consider a small section of the ring $\theta $ (Assuming $\theta $ is very small)
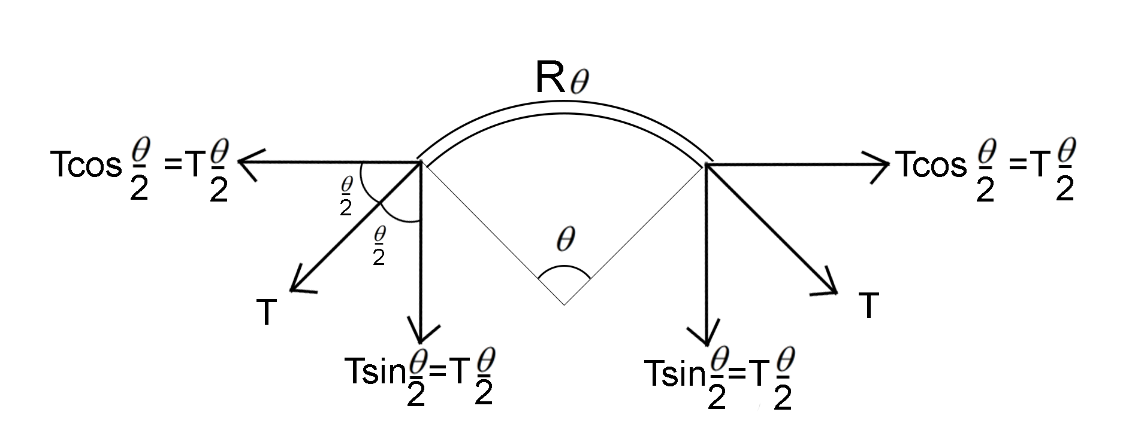
Now, we know
In vertical direction the ring experiences an upwards force equal to the downwards force that the two ends experience
${F_C} = 2T\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2}$
${F_C} = T\theta $( $\because \theta $ is small)(Equation 1)
We know that acceleration of a rotating body is
$a = {\omega ^2}R$
And force is given by
$F = ma$
$F = m{\omega ^2}R$ (Equation 2)
Comparing equation 1 and 2, we get
$m{\omega ^2}R = T\theta $
$\because \rho = \dfrac{m}{V}$
$\therefore \rho V{\omega ^2}R = T\theta $ (Equation 3)
We know that
$V = l \times A$
Here $V = $ Volume
$l = $ Length
$A = $ Area of cross-section
$V = R\theta (2\pi {R^2})$
Using this value of $V$in equation 3, we get
$\rho \theta \pi {R^4}{\omega ^2} = T\theta $
$ \Rightarrow T = \rho \pi {R^4}{\omega ^2}$
We know that stress is
$Stress = \dfrac{{Force}}{{Area}}$
Let $\sigma $ be the breaking stress of the lead wire, so
$F = \sigma \pi {R^2}$
We know that for the ring to rupture
$\rho \pi {R^4}{\omega ^2} \geqslant \sigma \pi {R^2}$
So at the minimum for the ring to break
$\rho \pi {R^4}{\omega ^2} = \sigma \pi {R^2}$
$\omega = \sqrt {\dfrac{\sigma }{{\rho {R^2}}}} $
We know that the frequency ( $f$ or also called $rps$ ) is given by
$f = \dfrac{\omega }{{2\pi }}$
$f = \dfrac{1}{{2\pi R}}\sqrt {\dfrac{\sigma }{\rho }} $
We know that
$\sigma = 1.5 \times {10^7}N{m^{ - 2}}$
And $\rho = 11.3$
$\therefore f = 23rps$
Given, $f = 20 + x$
$23 = 20 + x$
$x = 3$
Hence, the value of $x$ is $3$ .
Note: The concept of stress used in this question is a very important concept. From a bridge to your smartphone every object is quality controlled based on a number of standards. This quality testing is very important because we don’t want our possessions to break during daily use and last us a long time.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the given situation the ring will only break if the tension on the ring will be equal to the breaking stress of the wire.
Let’s consider a small section of the ring $\theta $ (Assuming $\theta $ is very small)

Now, we know
In vertical direction the ring experiences an upwards force equal to the downwards force that the two ends experience
${F_C} = 2T\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2}$
${F_C} = T\theta $( $\because \theta $ is small)(Equation 1)
We know that acceleration of a rotating body is
$a = {\omega ^2}R$
And force is given by
$F = ma$
$F = m{\omega ^2}R$ (Equation 2)
Comparing equation 1 and 2, we get
$m{\omega ^2}R = T\theta $
$\because \rho = \dfrac{m}{V}$
$\therefore \rho V{\omega ^2}R = T\theta $ (Equation 3)
We know that
$V = l \times A$
Here $V = $ Volume
$l = $ Length
$A = $ Area of cross-section
$V = R\theta (2\pi {R^2})$
Using this value of $V$in equation 3, we get
$\rho \theta \pi {R^4}{\omega ^2} = T\theta $
$ \Rightarrow T = \rho \pi {R^4}{\omega ^2}$
We know that stress is
$Stress = \dfrac{{Force}}{{Area}}$
Let $\sigma $ be the breaking stress of the lead wire, so
$F = \sigma \pi {R^2}$
We know that for the ring to rupture
$\rho \pi {R^4}{\omega ^2} \geqslant \sigma \pi {R^2}$
So at the minimum for the ring to break
$\rho \pi {R^4}{\omega ^2} = \sigma \pi {R^2}$
$\omega = \sqrt {\dfrac{\sigma }{{\rho {R^2}}}} $
We know that the frequency ( $f$ or also called $rps$ ) is given by
$f = \dfrac{\omega }{{2\pi }}$
$f = \dfrac{1}{{2\pi R}}\sqrt {\dfrac{\sigma }{\rho }} $
We know that
$\sigma = 1.5 \times {10^7}N{m^{ - 2}}$
And $\rho = 11.3$
$\therefore f = 23rps$
Given, $f = 20 + x$
$23 = 20 + x$
$x = 3$
Hence, the value of $x$ is $3$ .
Note: The concept of stress used in this question is a very important concept. From a bridge to your smartphone every object is quality controlled based on a number of standards. This quality testing is very important because we don’t want our possessions to break during daily use and last us a long time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




