
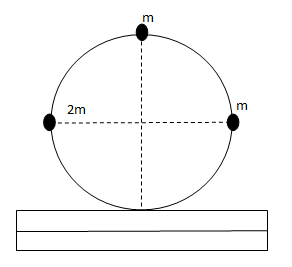
A ring of mass \[m\] and radius \[R\] has three particles attached to the ring as shown in the figure. The centre of the ring has a speed \[{v_0}\]. If the kinetic energy of the system is \[xm{v_0}^2\]. Find x (Slipping is absent)

Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: The kinetic energy of the system is given and we are asked to find the value of x. To find the value of x we have to calculate the kinetic energy of the system. For this, first find the kinetic energy of each particle and then kinetic energy of the ring and equate the kinetic energy of the system obtained with the given value.
Complete step by step answer:
Given, velocity of centre is \[{v_0}\]
As the velocity of the centre is \[{v_0}\], so each point on the ring will move with the same velocity that is \[{v_0}\]. So, all three particles attached to the ring will also move with the same velocity \[{v_0}\]. Let us assume the ring is moving towards right or rotating in clockwise direction.
Let us draw a diagram,
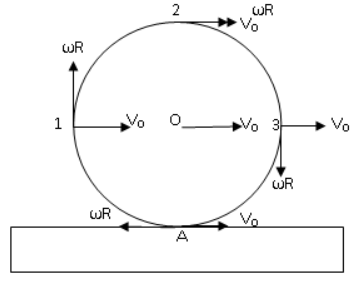
Let O be the centre and A be the point of contact between ring and block, \[\omega \] be the angular velocity of the ring and R be the radius of the ring. It is given that the slipping is absent, if slipping is absent then at the point of contact the velocity will be zero. That is at point A velocity is zero and this is possible only when
\[\omega R = {v_0}\] (i)
Now, let us find the kinetic energy of each particle.
For particle 1, let \[{v_1}\] be its velocity. We observe that \[{v_1}\] is the resultant velocity of \[{v_0}\] and \[\omega R\]and angle between them is \[{90^ \circ }\]. So, \[{v_1}\] can be written as,
\[{v_1} = \sqrt {{v_0}^2 + {{\left( {\omega R} \right)}^2} + 2{v_0}\omega R\cos {{90}^ \circ }} \]
We have, \[\omega R = {v_0}\] , that is
\[{v_1} = \sqrt {{v_0}^2 + {v_0}^2} \\\
\Rightarrow {v_1} = \sqrt 2 {v_0} \\\]
Kinetic energy of particle 1 with mass \[2m\] is,
\[{\left( {K.E} \right)_1} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {2m} \right){v_1}^2 \\\
\Rightarrow {\left( {K.E} \right)_1} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {2m} \right){\left( {\sqrt 2 {v_0}} \right)^2} \\\
\Rightarrow {\left( {K.E} \right)_1} = 2m{v_0}^2 \\\]
For particle 2, let \[{v_2}\] be its velocity. We observe that \[{v_2}\]is the resultant velocity of \[{v_0}\] and \[\omega R\]and angle between them is \[{0^ \circ }\]. So, \[{v_2}\]can be written as,
\[{v_2} = \sqrt {{v_0}^2 + {{\left( {\omega R} \right)}^2} + 2{v_0}\omega R\cos {0^ \circ }} \]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_2} = \sqrt {{v_0}^2 + {v_0}^2 + 2{v_0}{v_0}} \] [putting \[\omega R = {v_0}\] ]
\[\Rightarrow {v_2} = \sqrt 4 {v_0} \\\
\Rightarrow {v_2} = 2{v_0} \\\]
Kinetic energy of particle 2 with mass \[m\] is,
\[{\left( {K.E} \right)_2} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( m \right){v_2}^2 \\\
\Rightarrow {\left( {K.E} \right)_2} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( m \right){\left( {2{v_0}} \right)^2} \\\
\Rightarrow {\left( {K.E} \right)_2} = 2m{v_0}^2 \\\]
For particle 3, let \[{v_3}\] be its velocity. We observe that \[{v_3}\] is the resultant velocity of \[{v_0}\] and \[\omega R\]and angle between them is \[{90^ \circ }\]. So, \[{v_3}\] can be written as,
\[{v_3} = \sqrt {{v_0}^2 + {{\left( {\omega R} \right)}^2} + 2{v_0}\omega R\cos {{90}^ \circ }} \]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_3} = \sqrt {{v_0}^2 + {v_0}^2} \] [putting \[\omega R = {v_0}\] ]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_3} = \sqrt 2 {v_0}\]
Kinetic energy of particle 3 with mass \[m\] is,
\[{\left( {K.E} \right)_3} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( m \right){v_3}^2 \\\
\Rightarrow {\left( {K.E} \right)_3} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( m \right){\left( {\sqrt 2 {v_0}} \right)^2} \\\
\Rightarrow {\left( {K.E} \right)_3} = m{v_0}^2 \\\]
Therefore, total kinetic energy of the particles
\[{\left( {K.E} \right)_p} = {\left( {K.E} \right)_1} + {\left( {K.E} \right)_2} + {\left( {K.E} \right)_3} \\\
\Rightarrow {\left( {K.E} \right)_p} = 2m{v_0}^2 + 2m{v_0}^2 + m{v_0}^2 \\\
\Rightarrow {\left( {K.E} \right)_p} = 5m{v_0}^2 \\\]
Kinetic energy of ring is, \[{\left( {K.E} \right)_R} = {\left( {K.E} \right)_r} + {\left( {K.E} \right)_t}\] , where \[{\left( {K.E} \right)_r}\] is the rotational kinetic energy and \[{\left( {K.E} \right)_t}\]is the translational kinetic energy of the ring.
Now, the rotational kinetic energy of the ring is,
\[{\left( {K.E} \right)_r} = \dfrac{1}{2}I{\omega ^2}\] (ii)
Here , \[I\] is the moment of inertia of the ring.
We have the formula for moment of inertia of a ring about an axis passing through its centre as,
\[I = m{R^2}\] (iii)
\[m\]is the mass of the ring.
Now, putting the value of \[I\]from equation (iii) and \[\omega = \dfrac{{{v_0}}}{R}\] from equation (i) in equation (ii), we get
\[{\left( {K.E} \right)_r} = \dfrac{1}{2}m{R^2}{\left( {\dfrac{{{v_0}}}{R}} \right)^2} = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v_0}^2\]
And translational kinetic energy of the ring is
\[{\left( {K.E} \right)_t} = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v_0}^2\]
Therefore, kinetic energy of the ring
\[{\left( {K.E} \right)_R} = {\left( {K.E} \right)_r} + {\left( {K.E} \right)_t} = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v_0}^2 + \dfrac{1}{2}m{v_0}^2 = m{v_0}^2\]
Now, kinetic energy of the system is,
\[K.E = {\left( {K.E} \right)_R} + {\left( {K.E} \right)_p}\]
Putting the values of \[{\left( {K.E} \right)_R}\] and \[{\left( {K.E} \right)_p}\] we have,
\[K.E = 5m{v_0}^2 + m{v_0}^2 \\\
\Rightarrow K.E = 6m{v_0}^2 \\\]
We are given that kinetic energy of the system is \[xm{v_0}^2\]
So, comparing this value with our calculated value we get,
\[xm{v_0}^2 = 6m{v_0}^2 \\\
\Rightarrow x = 6 \\\]
Thus, the value of \[x\] is \[6\]
Note:
In such types of questions where there is more than one particle, first try to find the energies of each particle. And look carefully for all the clues given in the question, like here we were given slipping is absent which makes the problem simple as that means the velocity of the contact point is zero. So, for such questions apply all the conditions given in the questions this will simplify the problem.
Complete step by step answer:
Given, velocity of centre is \[{v_0}\]
As the velocity of the centre is \[{v_0}\], so each point on the ring will move with the same velocity that is \[{v_0}\]. So, all three particles attached to the ring will also move with the same velocity \[{v_0}\]. Let us assume the ring is moving towards right or rotating in clockwise direction.
Let us draw a diagram,

Let O be the centre and A be the point of contact between ring and block, \[\omega \] be the angular velocity of the ring and R be the radius of the ring. It is given that the slipping is absent, if slipping is absent then at the point of contact the velocity will be zero. That is at point A velocity is zero and this is possible only when
\[\omega R = {v_0}\] (i)
Now, let us find the kinetic energy of each particle.
For particle 1, let \[{v_1}\] be its velocity. We observe that \[{v_1}\] is the resultant velocity of \[{v_0}\] and \[\omega R\]and angle between them is \[{90^ \circ }\]. So, \[{v_1}\] can be written as,
\[{v_1} = \sqrt {{v_0}^2 + {{\left( {\omega R} \right)}^2} + 2{v_0}\omega R\cos {{90}^ \circ }} \]
We have, \[\omega R = {v_0}\] , that is
\[{v_1} = \sqrt {{v_0}^2 + {v_0}^2} \\\
\Rightarrow {v_1} = \sqrt 2 {v_0} \\\]
Kinetic energy of particle 1 with mass \[2m\] is,
\[{\left( {K.E} \right)_1} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {2m} \right){v_1}^2 \\\
\Rightarrow {\left( {K.E} \right)_1} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {2m} \right){\left( {\sqrt 2 {v_0}} \right)^2} \\\
\Rightarrow {\left( {K.E} \right)_1} = 2m{v_0}^2 \\\]
For particle 2, let \[{v_2}\] be its velocity. We observe that \[{v_2}\]is the resultant velocity of \[{v_0}\] and \[\omega R\]and angle between them is \[{0^ \circ }\]. So, \[{v_2}\]can be written as,
\[{v_2} = \sqrt {{v_0}^2 + {{\left( {\omega R} \right)}^2} + 2{v_0}\omega R\cos {0^ \circ }} \]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_2} = \sqrt {{v_0}^2 + {v_0}^2 + 2{v_0}{v_0}} \] [putting \[\omega R = {v_0}\] ]
\[\Rightarrow {v_2} = \sqrt 4 {v_0} \\\
\Rightarrow {v_2} = 2{v_0} \\\]
Kinetic energy of particle 2 with mass \[m\] is,
\[{\left( {K.E} \right)_2} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( m \right){v_2}^2 \\\
\Rightarrow {\left( {K.E} \right)_2} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( m \right){\left( {2{v_0}} \right)^2} \\\
\Rightarrow {\left( {K.E} \right)_2} = 2m{v_0}^2 \\\]
For particle 3, let \[{v_3}\] be its velocity. We observe that \[{v_3}\] is the resultant velocity of \[{v_0}\] and \[\omega R\]and angle between them is \[{90^ \circ }\]. So, \[{v_3}\] can be written as,
\[{v_3} = \sqrt {{v_0}^2 + {{\left( {\omega R} \right)}^2} + 2{v_0}\omega R\cos {{90}^ \circ }} \]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_3} = \sqrt {{v_0}^2 + {v_0}^2} \] [putting \[\omega R = {v_0}\] ]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_3} = \sqrt 2 {v_0}\]
Kinetic energy of particle 3 with mass \[m\] is,
\[{\left( {K.E} \right)_3} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( m \right){v_3}^2 \\\
\Rightarrow {\left( {K.E} \right)_3} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( m \right){\left( {\sqrt 2 {v_0}} \right)^2} \\\
\Rightarrow {\left( {K.E} \right)_3} = m{v_0}^2 \\\]
Therefore, total kinetic energy of the particles
\[{\left( {K.E} \right)_p} = {\left( {K.E} \right)_1} + {\left( {K.E} \right)_2} + {\left( {K.E} \right)_3} \\\
\Rightarrow {\left( {K.E} \right)_p} = 2m{v_0}^2 + 2m{v_0}^2 + m{v_0}^2 \\\
\Rightarrow {\left( {K.E} \right)_p} = 5m{v_0}^2 \\\]
Kinetic energy of ring is, \[{\left( {K.E} \right)_R} = {\left( {K.E} \right)_r} + {\left( {K.E} \right)_t}\] , where \[{\left( {K.E} \right)_r}\] is the rotational kinetic energy and \[{\left( {K.E} \right)_t}\]is the translational kinetic energy of the ring.
Now, the rotational kinetic energy of the ring is,
\[{\left( {K.E} \right)_r} = \dfrac{1}{2}I{\omega ^2}\] (ii)
Here , \[I\] is the moment of inertia of the ring.
We have the formula for moment of inertia of a ring about an axis passing through its centre as,
\[I = m{R^2}\] (iii)
\[m\]is the mass of the ring.
Now, putting the value of \[I\]from equation (iii) and \[\omega = \dfrac{{{v_0}}}{R}\] from equation (i) in equation (ii), we get
\[{\left( {K.E} \right)_r} = \dfrac{1}{2}m{R^2}{\left( {\dfrac{{{v_0}}}{R}} \right)^2} = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v_0}^2\]
And translational kinetic energy of the ring is
\[{\left( {K.E} \right)_t} = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v_0}^2\]
Therefore, kinetic energy of the ring
\[{\left( {K.E} \right)_R} = {\left( {K.E} \right)_r} + {\left( {K.E} \right)_t} = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v_0}^2 + \dfrac{1}{2}m{v_0}^2 = m{v_0}^2\]
Now, kinetic energy of the system is,
\[K.E = {\left( {K.E} \right)_R} + {\left( {K.E} \right)_p}\]
Putting the values of \[{\left( {K.E} \right)_R}\] and \[{\left( {K.E} \right)_p}\] we have,
\[K.E = 5m{v_0}^2 + m{v_0}^2 \\\
\Rightarrow K.E = 6m{v_0}^2 \\\]
We are given that kinetic energy of the system is \[xm{v_0}^2\]
So, comparing this value with our calculated value we get,
\[xm{v_0}^2 = 6m{v_0}^2 \\\
\Rightarrow x = 6 \\\]
Thus, the value of \[x\] is \[6\]
Note:
In such types of questions where there is more than one particle, first try to find the energies of each particle. And look carefully for all the clues given in the question, like here we were given slipping is absent which makes the problem simple as that means the velocity of the contact point is zero. So, for such questions apply all the conditions given in the questions this will simplify the problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




