
A right triangle has a hypotenuse of length \[p\] cm and one side of length \[q\] cm. If \[p - q = 1\] , find the length of the third side of the triangle if \[p = 5\] and \[q = 4\]
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, to calculate the third side of a right-angled triangle we use the Pythagoras theorem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
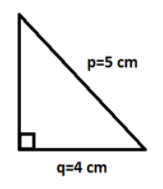
In the question, it is given that the hypotenuse is of length \[p\] cm and one side is of length \[q\] cm.
So, Hypotenuse \[ = p\] cm and Base \[ = q\] cm as shown in the figure.
So, now we will use Pythagoras theorem.
Pythagoras theorem states that “In a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides.“ The sides of this triangle have been named as Perpendicular, Base and Hypotenuse.
So, \[Hypotenus{e^2} = Bas{e^2} + Perpendicula{r^2}\]
\[{p^2} = {q^2} + Perpendicula{r^2}\]
\[Perpendicula{r^2} = {p^2} - {q^2}\]
Now, we will put \[p = 5\] and \[q = 4\] in the above formed equation, we get
\[Perpendicula{r^2} = {5^2} - {4^2}\]
Or, \[Perpendicula{r^2} = 25 - 16\]
Or, \[Perpendicula{r^2} = 9\]
Therefore, \[Perpendicular = 3\]
Thus, the length of the third side of the triangle is equal to \[3\] cm.
Note: Keep in mind the Pythagoras theorem. The Pythagorean equation relates the sides of a right triangle in a simple way, so that if the lengths of any two sides are known the length of the third side can be found. Another corollary of the theorem is that in any right triangle, the hypotenuse is greater than any one of the other sides, but less than their sum.
Complete step-by-step answer:

In the question, it is given that the hypotenuse is of length \[p\] cm and one side is of length \[q\] cm.
So, Hypotenuse \[ = p\] cm and Base \[ = q\] cm as shown in the figure.
So, now we will use Pythagoras theorem.
Pythagoras theorem states that “In a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides.“ The sides of this triangle have been named as Perpendicular, Base and Hypotenuse.
So, \[Hypotenus{e^2} = Bas{e^2} + Perpendicula{r^2}\]
\[{p^2} = {q^2} + Perpendicula{r^2}\]
\[Perpendicula{r^2} = {p^2} - {q^2}\]
Now, we will put \[p = 5\] and \[q = 4\] in the above formed equation, we get
\[Perpendicula{r^2} = {5^2} - {4^2}\]
Or, \[Perpendicula{r^2} = 25 - 16\]
Or, \[Perpendicula{r^2} = 9\]
Therefore, \[Perpendicular = 3\]
Thus, the length of the third side of the triangle is equal to \[3\] cm.
Note: Keep in mind the Pythagoras theorem. The Pythagorean equation relates the sides of a right triangle in a simple way, so that if the lengths of any two sides are known the length of the third side can be found. Another corollary of the theorem is that in any right triangle, the hypotenuse is greater than any one of the other sides, but less than their sum.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What type of cell is found in the Seminiferous tub class 10 biology CBSE

What are the public facilities provided by the government? Also explain each facility




