
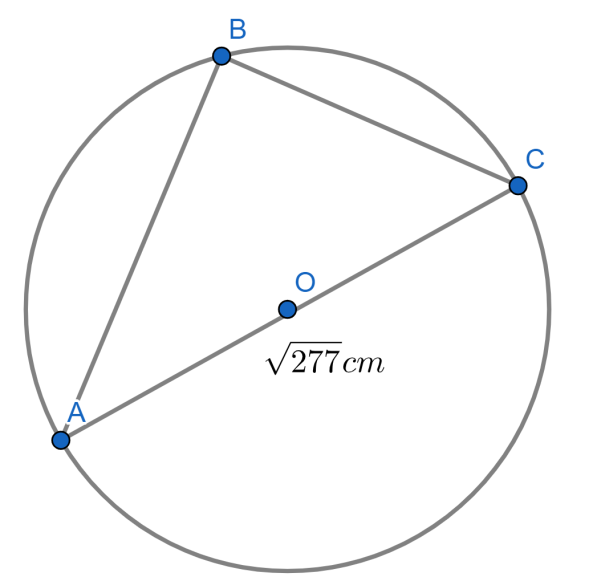
A right triangle $ABC$ is inscribed in a circle with center $O$, as shown in the following diagram. $A$ and $C$ are endpoints of a diameter, and $B$ is a point that lies on the circumference. $AC$ measures $\sqrt{277}cm$ , and side $BC$ measures $5cm$ less than $AB$ ?
What is the area of the region located around the right angled triangle $ABC$ only above $AC$ ?

Answer
546k+ views
Hint: In this question we have been asked to find the area of the region located around the right angle triangle $ABC$ only above $AC$ . So we will derive the area of the semicircle using the formula $\pi \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}}{8}$ and then we will find the area of the triangle by using the formula $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( height \right)\left( base \right)$ and Pythagoras theorem.
Complete step by step solution:
Now considering from the question we need to find the area of region located around the right angled triangle $ABC$ only above $AC$ using the given information that the length of $AC$ is $\sqrt{277}cm$ and $BC$ is $5cm$ is less than $AB$ .
The area of the asked region is given by subtracting the area of the triangle from the area of the semicircle.
We know that the length of the diameter $AC$ is given as $\sqrt{277}cm$ , then the area of the semicircle will be given by the formula $\pi \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}}{8}$ . So the area of this triangle will be $\Rightarrow \pi \dfrac{277}{8}=108.82c{{m}^{2}}$.
As the given triangle is right angle triangle then by using the Pythagoras theorem the square of the length of the hypotenuse is given by the sum of the squares of the adjacent sides.
Hence we will have $A{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}$ that is
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 277=A{{B}^{2}}+{{\left( AB-5 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 277=2A{{B}^{2}}+25-10AB \\
& \Rightarrow 252=2A{{B}^{2}}-10AB \\
& \Rightarrow 2A{{B}^{2}}-10AB-252=0 \\
& \Rightarrow A{{B}^{2}}-5AB-126=0 \\
\end{align}$.
The roots of the quadratic expression in the form of $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$ is given by the formula $\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}$ .
Therefore the length of $AB$ will be given as
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{5\pm \sqrt{25+4\left( 126 \right)}}{2}=\dfrac{5\pm \sqrt{529}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{5\pm 23}{2}=14,-11 \\
\end{align}$
Length can never be negative so the length of $AB$ will be $14cm$.
Then the length of $BC$ will be $9cm$ .
The area of a right angle triangle is given by the formula $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( height \right)\left( base \right)$ .
Hence the area of the given triangle will be $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( BC \right)\left( AB \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 14 \right)\left( 9 \right)\Rightarrow 63c{{m}^{2}}$.
Therefore the area of the given region will be $108.82- 63 = 45.82c{{m}^{2}}$.
Note: While answering questions of this type we should be sure with our calculations. The concept that we apply is very basic. So if we perform the calculations accurately and understand the question correctly then we can solve it in a short span of time ending up with the correct result. Similarly we can find the area of the whole circle except the right angle triangle which will be given as $\Rightarrow \pi \dfrac{277}{4}-\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 14 \right)\left( 9 \right)=217.64-63\Rightarrow 154.64c{{m}^{2}}$ .
Complete step by step solution:
Now considering from the question we need to find the area of region located around the right angled triangle $ABC$ only above $AC$ using the given information that the length of $AC$ is $\sqrt{277}cm$ and $BC$ is $5cm$ is less than $AB$ .
The area of the asked region is given by subtracting the area of the triangle from the area of the semicircle.
We know that the length of the diameter $AC$ is given as $\sqrt{277}cm$ , then the area of the semicircle will be given by the formula $\pi \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}}{8}$ . So the area of this triangle will be $\Rightarrow \pi \dfrac{277}{8}=108.82c{{m}^{2}}$.
As the given triangle is right angle triangle then by using the Pythagoras theorem the square of the length of the hypotenuse is given by the sum of the squares of the adjacent sides.
Hence we will have $A{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}$ that is
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 277=A{{B}^{2}}+{{\left( AB-5 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 277=2A{{B}^{2}}+25-10AB \\
& \Rightarrow 252=2A{{B}^{2}}-10AB \\
& \Rightarrow 2A{{B}^{2}}-10AB-252=0 \\
& \Rightarrow A{{B}^{2}}-5AB-126=0 \\
\end{align}$.
The roots of the quadratic expression in the form of $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$ is given by the formula $\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}$ .
Therefore the length of $AB$ will be given as
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{5\pm \sqrt{25+4\left( 126 \right)}}{2}=\dfrac{5\pm \sqrt{529}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{5\pm 23}{2}=14,-11 \\
\end{align}$
Length can never be negative so the length of $AB$ will be $14cm$.
Then the length of $BC$ will be $9cm$ .
The area of a right angle triangle is given by the formula $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( height \right)\left( base \right)$ .
Hence the area of the given triangle will be $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( BC \right)\left( AB \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 14 \right)\left( 9 \right)\Rightarrow 63c{{m}^{2}}$.
Therefore the area of the given region will be $108.82- 63 = 45.82c{{m}^{2}}$.
Note: While answering questions of this type we should be sure with our calculations. The concept that we apply is very basic. So if we perform the calculations accurately and understand the question correctly then we can solve it in a short span of time ending up with the correct result. Similarly we can find the area of the whole circle except the right angle triangle which will be given as $\Rightarrow \pi \dfrac{277}{4}-\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 14 \right)\left( 9 \right)=217.64-63\Rightarrow 154.64c{{m}^{2}}$ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




