
A right circular cone is divided by plane parallel to its base into a small cone of volume \[{V_1} \] at the top and frustum of volume \[{V_2} \] at the bottom. If \[{V_1}:{V_2} = 1:3 \] . Find the ratio of the height of the altitude of the cone and that of the frustum.
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: In this question, we will first find the volume of the small cone and the frustum, then we will find the ratio of these two volumes to find the ratio of the height of the altitude of the cone and that of the frustum.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let the volume of the larger cone be V
Now it is said that the cone is divided by the plane parallel to its base, where
The volume of small cone is \[{V_1} \]
The volume of the frustum is \[{V_2} \]
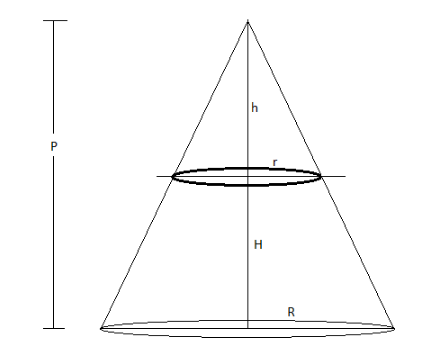
It is given that the ratio of the volume of the small cone and the frustum is
\[ \dfrac{{{V_1}}}{{{V_2}}} = \dfrac{1}{3} - - (i) \]
Now since we know that the volume of a cone is \[{V_{cone}} = \dfrac{1}{3} \pi {r^2}h \] and the volume of frustum is \[{V_{frustum}} = \dfrac{ \pi }{3}H \left( {{R^2} + {r^2} + Rr} \right) \] , hence we can write equation (i) as
\[
\dfrac{{{V_1}}}{{{V_2}}} = \dfrac{1}{3} \\
\dfrac{{{V_1}}}{{{V_2}}} = \dfrac{{ \dfrac{1}{3} \pi {r^2}h}}{{ \dfrac{ \pi }{3}H \left( {{R^2} + {r^2} + Rr} \right)}} - - (ii) \;
\]
Now as we know when we cut a cone by a plane then its larger cone and the smaller cone will be similar by angle-angle similarity theorem with same semi vertical angle and one of the angles being 90 degrees.
We know when two triangles are similar then their sides are also proportional, hence we can write from the diagram
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{r}{R} = \dfrac{h}{P} - - (iii) \]
Where \[P = h + H - - (iv) \]
Now divide both side of the equation (iv) by h, hence we can write
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{P}{h} = 1 + \dfrac{H}{h} - - (v) \]
Let us assume
\[ \dfrac{R}{r} = x \]
Hence by comparing equation (iii) and (v), we can write
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{R}{r} = 1 + \dfrac{H}{h} - - (vi) \ \
\Rightarrow \dfrac{H}{h} = x - 1 \;
\]
Now we divide numerator and the denominator of equation (ii) by \[{r^2} \]
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{V_1}}}{{{V_2}}} = \dfrac{h}{{H \left( { \dfrac{{{R^2}}}{{{r^2}}} + 1 + \dfrac{R}{r}} \right)}} = \dfrac{1}{3} \ \
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{V_1}}}{{{V_2}}} = \dfrac{1}{{ \dfrac{H}{h} \left( { \dfrac{{{R^2}}}{{{r^2}}} + 1 + \dfrac{R}{r}} \right)}} = \dfrac{1}{3} \ \
\]
Now, since \[ \dfrac{R}{r} = x \] and \[ \dfrac{H}{h} = x - 1 \] , hence we can further write this equation as
\[ \dfrac{1}{{ \left( {x - 1} \right) \left( {{x^2} + x + 1} \right)}} = \dfrac{1}{3} \]
By cross multiplying
\[ \left( {x - 1} \right) \left( {{x^2} + x + 1} \right) = 3 \]
By further solving this
\[
\Rightarrow x \left( {{x^2} + x + 1} \right) - \left( {{x^2} + x + 1} \right) = 3 \\
\Rightarrow {x^3} - 1 = 3 \\
\Rightarrow {x^3} = 4 \\
\Rightarrow x = {4^{ \dfrac{1}{3}}} \;
\]
Hence by substituting the value of x in equation (vi) we get
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{R}{r} = 1 + \dfrac{H}{h} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{H}{h} = {4^{ \dfrac{1}{3}}} - 1 \;
\]
Hence the ratio of the height of the altitude of the cone and that of the frustum \[ = \dfrac{{{4^{ \dfrac{1}{3}}} - 1}}{1} \]
So, the correct answer is “\[ = \dfrac{{{4^{ \dfrac{1}{3}}} - 1}}{1} \] ”.
Note: A right circular cone is a three-dimensional mathematical structure which is formed by rotating the two dimensional mathematical shape along a particular point. When a cone is cut along the horizontal axis (or parallel to the base) then, a small cone can be seen in the upper cut section with decreased radius and the height.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let the volume of the larger cone be V
Now it is said that the cone is divided by the plane parallel to its base, where
The volume of small cone is \[{V_1} \]
The volume of the frustum is \[{V_2} \]

It is given that the ratio of the volume of the small cone and the frustum is
\[ \dfrac{{{V_1}}}{{{V_2}}} = \dfrac{1}{3} - - (i) \]
Now since we know that the volume of a cone is \[{V_{cone}} = \dfrac{1}{3} \pi {r^2}h \] and the volume of frustum is \[{V_{frustum}} = \dfrac{ \pi }{3}H \left( {{R^2} + {r^2} + Rr} \right) \] , hence we can write equation (i) as
\[
\dfrac{{{V_1}}}{{{V_2}}} = \dfrac{1}{3} \\
\dfrac{{{V_1}}}{{{V_2}}} = \dfrac{{ \dfrac{1}{3} \pi {r^2}h}}{{ \dfrac{ \pi }{3}H \left( {{R^2} + {r^2} + Rr} \right)}} - - (ii) \;
\]
Now as we know when we cut a cone by a plane then its larger cone and the smaller cone will be similar by angle-angle similarity theorem with same semi vertical angle and one of the angles being 90 degrees.
We know when two triangles are similar then their sides are also proportional, hence we can write from the diagram
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{r}{R} = \dfrac{h}{P} - - (iii) \]
Where \[P = h + H - - (iv) \]
Now divide both side of the equation (iv) by h, hence we can write
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{P}{h} = 1 + \dfrac{H}{h} - - (v) \]
Let us assume
\[ \dfrac{R}{r} = x \]
Hence by comparing equation (iii) and (v), we can write
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{R}{r} = 1 + \dfrac{H}{h} - - (vi) \ \
\Rightarrow \dfrac{H}{h} = x - 1 \;
\]
Now we divide numerator and the denominator of equation (ii) by \[{r^2} \]
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{V_1}}}{{{V_2}}} = \dfrac{h}{{H \left( { \dfrac{{{R^2}}}{{{r^2}}} + 1 + \dfrac{R}{r}} \right)}} = \dfrac{1}{3} \ \
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{V_1}}}{{{V_2}}} = \dfrac{1}{{ \dfrac{H}{h} \left( { \dfrac{{{R^2}}}{{{r^2}}} + 1 + \dfrac{R}{r}} \right)}} = \dfrac{1}{3} \ \
\]
Now, since \[ \dfrac{R}{r} = x \] and \[ \dfrac{H}{h} = x - 1 \] , hence we can further write this equation as
\[ \dfrac{1}{{ \left( {x - 1} \right) \left( {{x^2} + x + 1} \right)}} = \dfrac{1}{3} \]
By cross multiplying
\[ \left( {x - 1} \right) \left( {{x^2} + x + 1} \right) = 3 \]
By further solving this
\[
\Rightarrow x \left( {{x^2} + x + 1} \right) - \left( {{x^2} + x + 1} \right) = 3 \\
\Rightarrow {x^3} - 1 = 3 \\
\Rightarrow {x^3} = 4 \\
\Rightarrow x = {4^{ \dfrac{1}{3}}} \;
\]
Hence by substituting the value of x in equation (vi) we get
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{R}{r} = 1 + \dfrac{H}{h} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{H}{h} = {4^{ \dfrac{1}{3}}} - 1 \;
\]
Hence the ratio of the height of the altitude of the cone and that of the frustum \[ = \dfrac{{{4^{ \dfrac{1}{3}}} - 1}}{1} \]
So, the correct answer is “\[ = \dfrac{{{4^{ \dfrac{1}{3}}} - 1}}{1} \] ”.
Note: A right circular cone is a three-dimensional mathematical structure which is formed by rotating the two dimensional mathematical shape along a particular point. When a cone is cut along the horizontal axis (or parallel to the base) then, a small cone can be seen in the upper cut section with decreased radius and the height.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




