
A resultant of two vectors makes ${{30}^{o}}$ with one vector and ${{45}^{o}}$ with the other. Find the two vectors if the resultant has the magnitude 15. [Hint: law of sines $\dfrac{P}{\sin \alpha }=\dfrac{Q}{\sin \beta }=\dfrac{R}{\sin \theta '}$, by geometry$\theta =\alpha +\beta $]
Answer
532.8k+ views
Hint: Two unknown vectors are added such that the magnitude of resultant is 15. Using angle sum property wherein the sum of all angles in a triangle is equal to 180 degrees, we can calculate the angle between the two vectors and then use the sine law to calculate the magnitude of each vector.
Formulas used:
$30+45+x=180$
$\dfrac{A}{\sin 45}=\dfrac{B}{\sin 30}=\dfrac{C}{\sin 105}$
Complete answer:
The triangle law of vector addition states that when two vectors are added such that they represent two sides of a triangle taken in the same order then their resultant is the third side taken in the opposite order. Therefore,
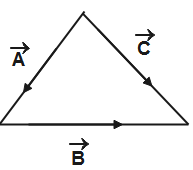
$\overrightarrow{C}=\overrightarrow{A}+\overrightarrow{B}$
Given that the resultant of two vectors make ${{30}^{o}}$ and ${{45}^{o}}$. Let the resultant vector be $\overrightarrow{C}$ then,

Applying the angle sum property, the third angle of the triangle or the angle between the vectors will be-
$\begin{align}
& 30+45+x=180 \\
& \Rightarrow x=180-75 \\
& \therefore x=105 \\
\end{align}$
Given, $\left| \overrightarrow{C} \right|=15$
The magnitude of a vector is the length of that vector or the part represented by a physical unit.
Now, applying the sines law, we get,
$\dfrac{A}{\sin 45}=\dfrac{B}{\sin 30}=\dfrac{C}{\sin 105}$
Using the above equation we calculate the magnitude of first vector as-
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{A}{\sin 45}=\dfrac{C}{\sin 105} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{A}{\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}}=\dfrac{15}{\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+1}{2\sqrt{2}}} \\
& \therefore A=\dfrac{30}{\sqrt{3}+1} \\
\end{align}$
The value of one of the vectors is $\dfrac{30}{\sqrt{3}+1}$
Similarly, the magnitude of the second vector will be-
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{B}{\sin 30}=\dfrac{C}{\sin 105} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{B}{\dfrac{1}{2}}=\dfrac{15}{\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+1}{2\sqrt{2}}} \\
& \therefore B=\dfrac{15\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{3}+1} \\
\end{align}$
The value of the other vector is $\dfrac{15\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{3}+1}$.
Therefore, the magnitude of two vectors are $\dfrac{30}{\sqrt{3}+1}$ and $\dfrac{15\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{3}+1}$.
Note: Vector is a quantity that has magnitude as well as direction. The direction in space is described in terms of units vectors. The most common unit vectors used are along the x, y and z direction. Addition of vectors is commutative and associative while multiplication is neither commutative nor associative.
Formulas used:
$30+45+x=180$
$\dfrac{A}{\sin 45}=\dfrac{B}{\sin 30}=\dfrac{C}{\sin 105}$
Complete answer:
The triangle law of vector addition states that when two vectors are added such that they represent two sides of a triangle taken in the same order then their resultant is the third side taken in the opposite order. Therefore,

$\overrightarrow{C}=\overrightarrow{A}+\overrightarrow{B}$
Given that the resultant of two vectors make ${{30}^{o}}$ and ${{45}^{o}}$. Let the resultant vector be $\overrightarrow{C}$ then,

Applying the angle sum property, the third angle of the triangle or the angle between the vectors will be-
$\begin{align}
& 30+45+x=180 \\
& \Rightarrow x=180-75 \\
& \therefore x=105 \\
\end{align}$
Given, $\left| \overrightarrow{C} \right|=15$
The magnitude of a vector is the length of that vector or the part represented by a physical unit.
Now, applying the sines law, we get,
$\dfrac{A}{\sin 45}=\dfrac{B}{\sin 30}=\dfrac{C}{\sin 105}$
Using the above equation we calculate the magnitude of first vector as-
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{A}{\sin 45}=\dfrac{C}{\sin 105} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{A}{\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}}=\dfrac{15}{\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+1}{2\sqrt{2}}} \\
& \therefore A=\dfrac{30}{\sqrt{3}+1} \\
\end{align}$
The value of one of the vectors is $\dfrac{30}{\sqrt{3}+1}$
Similarly, the magnitude of the second vector will be-
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{B}{\sin 30}=\dfrac{C}{\sin 105} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{B}{\dfrac{1}{2}}=\dfrac{15}{\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+1}{2\sqrt{2}}} \\
& \therefore B=\dfrac{15\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{3}+1} \\
\end{align}$
The value of the other vector is $\dfrac{15\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{3}+1}$.
Therefore, the magnitude of two vectors are $\dfrac{30}{\sqrt{3}+1}$ and $\dfrac{15\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{3}+1}$.
Note: Vector is a quantity that has magnitude as well as direction. The direction in space is described in terms of units vectors. The most common unit vectors used are along the x, y and z direction. Addition of vectors is commutative and associative while multiplication is neither commutative nor associative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




