
A resonance tube is old and has a jagged end. It is still used in the laboratory to determine velocity of sound in air. A tuning fork of frequency 512 Hz produces first resonance when the tube is filled with water to a mark 11 cm below a reference mark, near the open end of the tube. The experiment is repeated with another fork of frequency 256 Hz which produces first resonance when water reaches a mark 27 cm below the reference mark. The velocity of sound in air, obtained in the experiment, is close to:
A. $328m/s$
B. $322m/s$
C. $341m/s$
D. $335m/s$
Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint:
1. Velocity of sound is constant in a given medium.
2. First resonance frequency occurs for air column length, $l = \dfrac{\lambda }{4}$ in ideal scenarios.
3. End correction must be added to the path length of first resonance frequency.
Formula Used:
1. Distance between two consecutive nodes $ = \dfrac{\lambda }{2}$ …… (a)
2. Distance between Antinode and next successive node $ = \dfrac{\lambda }{4}$ ……. (b)
3.First resonance frequency with air column of length ${l_{air}} + e = \dfrac{\lambda }{4}$ ……. (c)
where $e$ is end correction
4. Constant speed of sound wave with $f$ be frequency of tuning fork and $\lambda $ be wavelength of sound wave $v = \lambda f$ $ \Rightarrow \lambda = \dfrac{v}{f}$ …… (d)
Figure 1 shows rough sketch for first resonance air column:
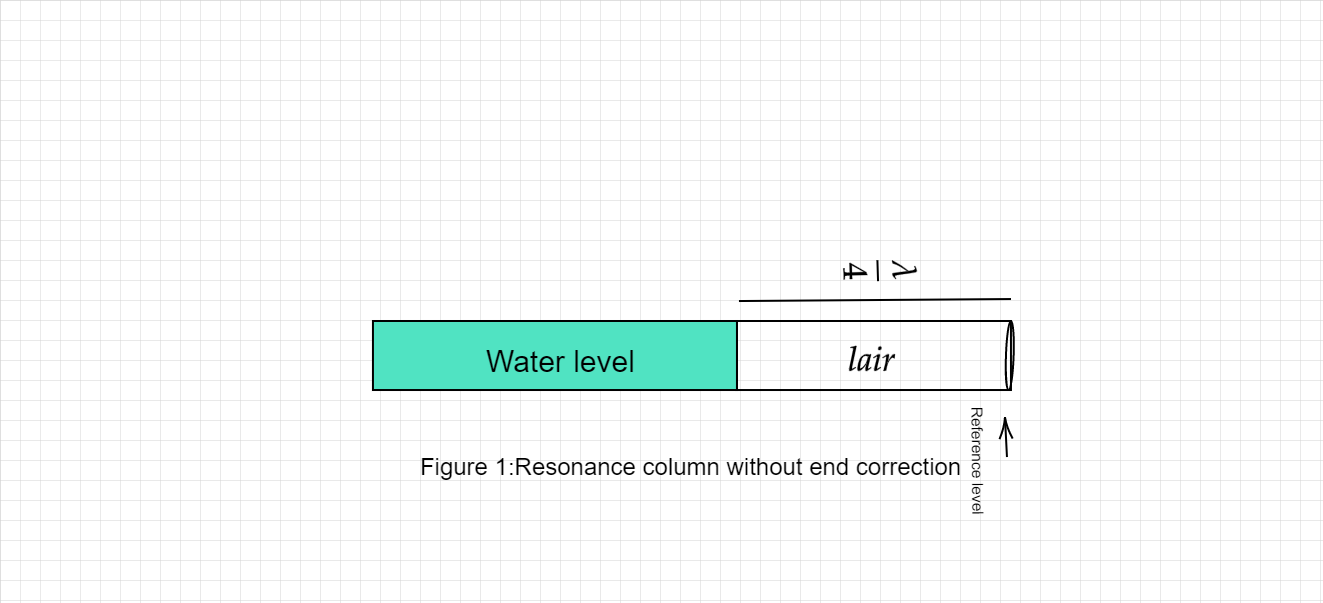
Complete step by step answer:
Given,
Two tuning forks of frequencies ${f_1}$ and ${f_2}$ be 512 Hz and 256 Hz respectively.
Corresponding to each frequency’s paths, the lengths of the first resonance air column are 11cm and 27 cm respectively.
Let, end correction be $e$
Step 1 of 4:
Using equation (c) and (b) for frequency ${f_1}$=512 Hz we get
$\dfrac{{{\lambda _1}}}{4} = {l_{1,air}} + e$ …… (1)
Given ${l_{air}} = 11cm$,
Putting substitutions from equation (1) and (d) we get,
$\dfrac{v}{{4 \times {f_1}}} = 11cm + e$ …… (2)
Step 2 of 4:
Similarly, using equation (c) and (b) for frequency ${f_2}$ =256 Hz we get
$\dfrac{{{\lambda _2}}}{4} = {l_{2,}}_{air} + e$ …… (3)
Putting substitutions from equation (1) and (d) we get,
$\dfrac{v}{{4 \times {f_2}}} = 27cm + e$ …… (4)
Step 3 of 4:
Subtracting equation (2) from equation (4) we get,
$\dfrac{v}{{4 \times {f_2}}} - \dfrac{v}{{4 \times {f_1}}} = 27cm + e - 11cm + e$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{v}{4}\left( {\dfrac{1}{{{f_2}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{f_1}}}} \right) = 16 \times {10^{ - 2}}m$ …… (5)
Step 4 of 4:
Putting values of ${f_1}$ and ${f_2}$ in equation (5) we get,
$v = 328m/s$
Correct Answer: A.$328m/s$
Additional Information: At the opening of a vessel there always lies an antinode. There lies a node at the interface between air and fluid since the fluid boundary acts as a closed vessel because at that point no displacement is possible.
Note: End correction should always be considered while solving sound wave problems in a vessel or tube.
1. Velocity of sound is constant in a given medium.
2. First resonance frequency occurs for air column length, $l = \dfrac{\lambda }{4}$ in ideal scenarios.
3. End correction must be added to the path length of first resonance frequency.
Formula Used:
1. Distance between two consecutive nodes $ = \dfrac{\lambda }{2}$ …… (a)
2. Distance between Antinode and next successive node $ = \dfrac{\lambda }{4}$ ……. (b)
3.First resonance frequency with air column of length ${l_{air}} + e = \dfrac{\lambda }{4}$ ……. (c)
where $e$ is end correction
4. Constant speed of sound wave with $f$ be frequency of tuning fork and $\lambda $ be wavelength of sound wave $v = \lambda f$ $ \Rightarrow \lambda = \dfrac{v}{f}$ …… (d)
Figure 1 shows rough sketch for first resonance air column:

Complete step by step answer:
Given,
Two tuning forks of frequencies ${f_1}$ and ${f_2}$ be 512 Hz and 256 Hz respectively.
Corresponding to each frequency’s paths, the lengths of the first resonance air column are 11cm and 27 cm respectively.
Let, end correction be $e$
Step 1 of 4:
Using equation (c) and (b) for frequency ${f_1}$=512 Hz we get
$\dfrac{{{\lambda _1}}}{4} = {l_{1,air}} + e$ …… (1)
Given ${l_{air}} = 11cm$,
Putting substitutions from equation (1) and (d) we get,
$\dfrac{v}{{4 \times {f_1}}} = 11cm + e$ …… (2)
Step 2 of 4:
Similarly, using equation (c) and (b) for frequency ${f_2}$ =256 Hz we get
$\dfrac{{{\lambda _2}}}{4} = {l_{2,}}_{air} + e$ …… (3)
Putting substitutions from equation (1) and (d) we get,
$\dfrac{v}{{4 \times {f_2}}} = 27cm + e$ …… (4)
Step 3 of 4:
Subtracting equation (2) from equation (4) we get,
$\dfrac{v}{{4 \times {f_2}}} - \dfrac{v}{{4 \times {f_1}}} = 27cm + e - 11cm + e$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{v}{4}\left( {\dfrac{1}{{{f_2}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{f_1}}}} \right) = 16 \times {10^{ - 2}}m$ …… (5)
Step 4 of 4:
Putting values of ${f_1}$ and ${f_2}$ in equation (5) we get,
$v = 328m/s$
Correct Answer: A.$328m/s$
Additional Information: At the opening of a vessel there always lies an antinode. There lies a node at the interface between air and fluid since the fluid boundary acts as a closed vessel because at that point no displacement is possible.
Note: End correction should always be considered while solving sound wave problems in a vessel or tube.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




