
A resistor R and $2\mu F$ capacitor in series is connected through a switch $200V$ direct supply. Across the capacitor is a neon bulb that lights up at $120V$. Calculate the value of R to make the bulb light up $5\sec $ after the switch has been closed.
${\log _{10}}2.5 = 0.4$
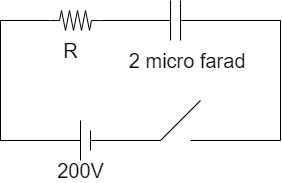

Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint:-A capacitor is a device that is used to store energy. It is made up of two or more conductors that are separated by an insulator. When a capacitor is connected in a circuit with a resistor, the resistance tries to oppose the flow of current in the capacitor. This will charge or discharge a capacitor.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Step I:
Since the circuit has a resistor and capacitor connected, it is called a RC-circuit. The time constant of a RC-circuit helps to determine how long it will take to a capacitor to charge to a certain voltage. It is denoted by the symbol tau$\tau $. The formula is
$\tau = RC$
R is the resistor and C is the capacitor.
Step II:
The voltage V is related to the capacitor by the equation
${V_c} = {V_s}(1 - {e^{\dfrac{{ - t}}{\tau }}})$
${V_c}$ is the voltage of capacitor
${V_s}$ is the supply voltage
$e$ is an irrational number
$t$ is the time
$\tau $ is the time constant
Step III:
Substituting the values in the given formula,
${V_c} = 200(1 - {e^{\dfrac{{ - t}}{\tau }}})$
$\Rightarrow 120 = 200(1 - {e^{\dfrac{{ - t}}{\tau }}})$
$\Rightarrow 1 - {e^{\dfrac{{ - t}}{\tau }}} = \dfrac{{120}}{{200}}$
$\Rightarrow 1 - {e^{\dfrac{{ - t}}{\tau }}} = \dfrac{3}{5}$
\[\Rightarrow {e^{\dfrac{{ - t}}{\tau }}} = 1 - \dfrac{3}{5} = \dfrac{2}{5}\]
$\Rightarrow {e^{\dfrac{t}{\tau }}} = \dfrac{5}{2}$
$\Rightarrow {e^{\dfrac{t}{\tau }}} = 2.5$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{t}{\tau } = {\log _e}2.5$
Step IV:
$\dfrac{t}{{RC}} = 2.303{\log _{10}}2.5$
Substitute the value given in the question,
$\dfrac{t}{{RC}} = 2.303 \times 0.4$
Given $C = 2\mu F = 2 \times {10^{ - 6}}F$and $t = 5\sec $
$\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{5}{{2.303 \times 0.4 \times 2 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}}$
$\Rightarrow R = 2.73 \times {10^6}\Omega $
The value of R to make the bulb after the switch is closed is $2.73 \times {10^6}\Omega $.
Note:- It is to be noted that the plates of the capacitor carry equal and opposite charges. So the net charge on the capacitor is always zero. The higher the voltage, the greater is the amount of energy stored in the capacitor. But when the capacitor discharges the potential difference between the plates disappears by transferring the energy to the circuit connected to the capacitor.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Step I:
Since the circuit has a resistor and capacitor connected, it is called a RC-circuit. The time constant of a RC-circuit helps to determine how long it will take to a capacitor to charge to a certain voltage. It is denoted by the symbol tau$\tau $. The formula is
$\tau = RC$
R is the resistor and C is the capacitor.
Step II:
The voltage V is related to the capacitor by the equation
${V_c} = {V_s}(1 - {e^{\dfrac{{ - t}}{\tau }}})$
${V_c}$ is the voltage of capacitor
${V_s}$ is the supply voltage
$e$ is an irrational number
$t$ is the time
$\tau $ is the time constant
Step III:
Substituting the values in the given formula,
${V_c} = 200(1 - {e^{\dfrac{{ - t}}{\tau }}})$
$\Rightarrow 120 = 200(1 - {e^{\dfrac{{ - t}}{\tau }}})$
$\Rightarrow 1 - {e^{\dfrac{{ - t}}{\tau }}} = \dfrac{{120}}{{200}}$
$\Rightarrow 1 - {e^{\dfrac{{ - t}}{\tau }}} = \dfrac{3}{5}$
\[\Rightarrow {e^{\dfrac{{ - t}}{\tau }}} = 1 - \dfrac{3}{5} = \dfrac{2}{5}\]
$\Rightarrow {e^{\dfrac{t}{\tau }}} = \dfrac{5}{2}$
$\Rightarrow {e^{\dfrac{t}{\tau }}} = 2.5$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{t}{\tau } = {\log _e}2.5$
Step IV:
$\dfrac{t}{{RC}} = 2.303{\log _{10}}2.5$
Substitute the value given in the question,
$\dfrac{t}{{RC}} = 2.303 \times 0.4$
Given $C = 2\mu F = 2 \times {10^{ - 6}}F$and $t = 5\sec $
$\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{5}{{2.303 \times 0.4 \times 2 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}}$
$\Rightarrow R = 2.73 \times {10^6}\Omega $
The value of R to make the bulb after the switch is closed is $2.73 \times {10^6}\Omega $.
Note:- It is to be noted that the plates of the capacitor carry equal and opposite charges. So the net charge on the capacitor is always zero. The higher the voltage, the greater is the amount of energy stored in the capacitor. But when the capacitor discharges the potential difference between the plates disappears by transferring the energy to the circuit connected to the capacitor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




