
What is a reflex action? Describe the steps involved in reflex action.
Answer
588.3k+ views
Hint: A reflex action is a type of animal behaviour which is responsible for involuntary and sudden response to a stimulus in case of a dangerous situation. The spinal cord plays a major role in the reflex arc.
Complete answer:
A reflex action is an involuntary, sudden and instantaneous movement in response to a stimulus against a dangerous situation. Example- Sudden jerky withdrawal of hand on contact with a hot pan. A reflex occurs due to the activity of neural pathways called reflex arcs which act upon an impulse before the impulse reaches the brain. Reflex arc may be defined as the path taken by the nerve impulses in a reflex. There are two types of reflexes: natural reflexes and conditioned reflexes.
A reflex action involves following steps:
Stimulus $\rightarrow$ Receptor organ $\rightarrow$ Afferent nerve fibre $\rightarrow$ Central Nervous system (spinal cord) $\rightarrow$ Efferent nerve fibre $\rightarrow$ Effector organ $\rightarrow$ Response.
Additional information:
- Nerves from various parts of the body bundle up in the spinal cord before they enter the brain. Reflex arcs are formed in the spinal cord. The components of the reflex arc are:
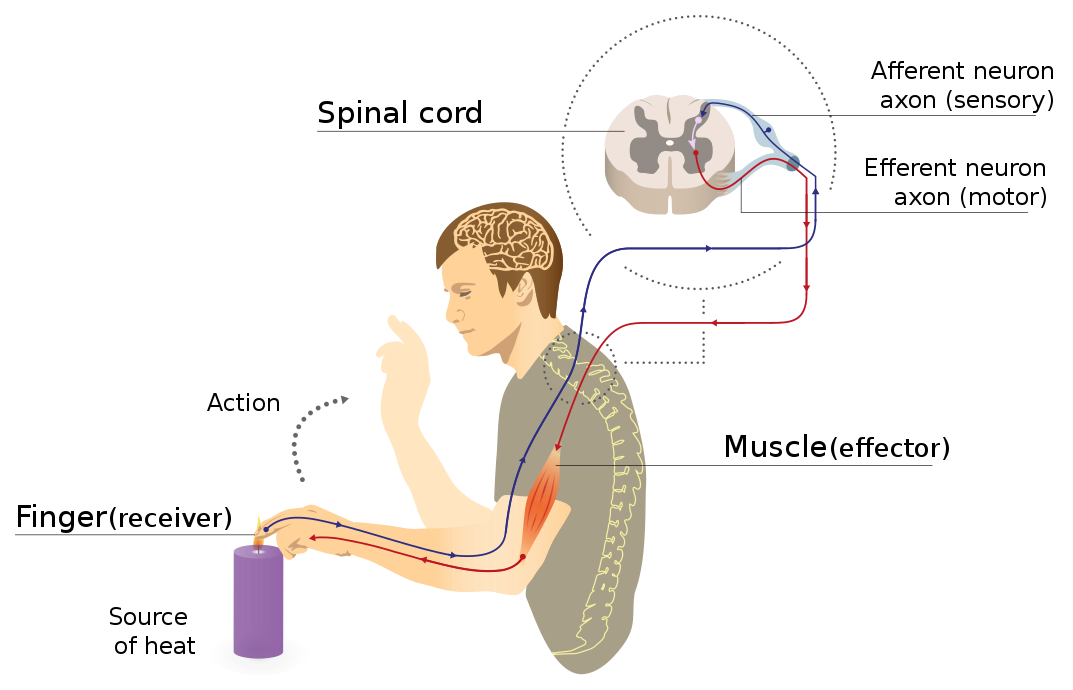
- Receptor organ: These are mainly the sense organs that senses the danger.
- Sensory/Afferent neurons: They pick up the signals from the sensory organ and transport the impulse through interconnected networks of neurons.
- Central nervous system: The spinal cord sends the necessary signal (such as withdrawal of hand etc) to the affected muscle through the motor neuron.
- Receptor/Afferent neuron: Carries the response from the spinal cord to the affected muscle.
- Response: This leads to the withdrawal of the muscle or the organ away from the danger.
Note: Reflexes can be either natural in which no previous experience or learning is required or it can be conditioned which develops during lifetime due to a particular experience or learning.
Complete answer:
A reflex action is an involuntary, sudden and instantaneous movement in response to a stimulus against a dangerous situation. Example- Sudden jerky withdrawal of hand on contact with a hot pan. A reflex occurs due to the activity of neural pathways called reflex arcs which act upon an impulse before the impulse reaches the brain. Reflex arc may be defined as the path taken by the nerve impulses in a reflex. There are two types of reflexes: natural reflexes and conditioned reflexes.
A reflex action involves following steps:
Stimulus $\rightarrow$ Receptor organ $\rightarrow$ Afferent nerve fibre $\rightarrow$ Central Nervous system (spinal cord) $\rightarrow$ Efferent nerve fibre $\rightarrow$ Effector organ $\rightarrow$ Response.
Additional information:
- Nerves from various parts of the body bundle up in the spinal cord before they enter the brain. Reflex arcs are formed in the spinal cord. The components of the reflex arc are:

- Receptor organ: These are mainly the sense organs that senses the danger.
- Sensory/Afferent neurons: They pick up the signals from the sensory organ and transport the impulse through interconnected networks of neurons.
- Central nervous system: The spinal cord sends the necessary signal (such as withdrawal of hand etc) to the affected muscle through the motor neuron.
- Receptor/Afferent neuron: Carries the response from the spinal cord to the affected muscle.
- Response: This leads to the withdrawal of the muscle or the organ away from the danger.
Note: Reflexes can be either natural in which no previous experience or learning is required or it can be conditioned which develops during lifetime due to a particular experience or learning.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




