
A rectangular sheet of fixed perimeter with sides having their lengths in the ratio \[8:15\] is converted into an open rectangular box by folding after removing squares of equal areas from all four corners. If the total area of removed squares is 100, the resulting box has maximum volume. Then the length of the sides of the rectangular sheet are:
THIS QUESTION HAS MULTIPLE CORRECT OPTIONS
A. 24
B. 32
C. 45
D. 60
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: First of all, find the length, breadth and height of the rectangular open box when four squares are removed from the corners. Find the length of the side by equating the area of 4 squares to 100. Then find the volume of the rectangular open box and use a second derivative test to reach the solution of the given problem.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to solve this problem for the determination of lengths of the sides of the rectangular sheet, we will check the maximum change of volume in the rectangular shape and then find the value of the sides of the rectangular sheet.
Given that the sides of the rectangle are in ratio of \[8:15\].
Let the sides of the rectangle be \[8k\] and \[15k\] as the given ratio of sides of rectangles is \[8:15\].
And let the side length of the square be \[x\]. Now we have to four squares from each of the corner from the rectangular sheet as shown in the below figure:
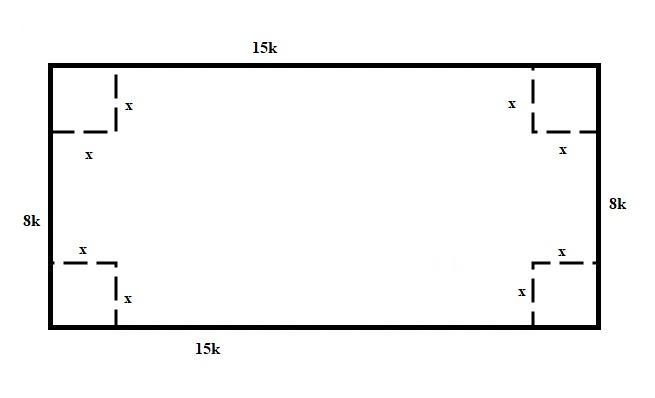
Now the remaining sheet is converted into a rectangular open box.
So, length of the box = \[15k - 2x\]
Breadth of the box = \[8k - 2x\]
Height of the box = \[x\]
Given that the total area of the four squares is 100.
So, we have
\[
\Rightarrow 4\left( {{x^2}} \right) = 100 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} = \dfrac{{100}}{4} = 25 \\
\therefore x = \sqrt {25} = 5 \\
\]
We know that the volume of a rectangular box with length \[l\], breadth \[b\] and height \[h\] is given by \[lbh\].
Let the volume of the rectangular open box be \[v\]. So, we have
\[
\Rightarrow v = \left( {15k - 2x} \right)\left( {8k - 2x} \right)x \\
\Rightarrow v = \left( {120{k^2} - 46kx + 4{x^2}} \right)x \\
\Rightarrow v = 4{x^3} - 46k{x^2} + 120x{k^2} \\
\]
We know that for maximum or minimum value the value of the first derivative must be equal to zero.
So, for maximum or minimum volume of the rectangular box we have
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dv}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left[ {4{x^3} - 46k{x^2} + 120x{k^2}} \right] = 0 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dv}}{{dx}} = 12{x^2} - 92kx + 120{k^2} = 0 \\
\]
The volume of the rectangular box would be minimum or maximum at \[x = 5\]. So, we have
\[
\Rightarrow 12{\left( 5 \right)^2} - 92k\left( 5 \right) + 120{k^2} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 300 - 460k + 120{k^2} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 20\left( {6{k^2} - 23k + 15} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 6{k^2} - 18k - 5k + 15 = \dfrac{0}{{20}} \\
\Rightarrow 6k\left( {k - 3} \right) - 5\left( {k - 3} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow \left( {6k - 5} \right)\left( {k - 3} \right) = 0 \\
\therefore k = 3,\dfrac{5}{6} \\
\]
We know that, the least value is obtained for the value of \[x\] at which \[\dfrac{{{d^2}v}}{{d{x^2}}} > 0\] and the greatest value is obtained for the value of \[x\] at which \[\dfrac{{{d^2}v}}{{d{x^2}}} < 0\].
Now, consider the second derivative of the volume of the rectangular open box
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}v}}{{d{x^2}}} = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {\dfrac{{dv}}{{dx}}} \right) = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {12{x^2} - 92kx + 120{k^2}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}v}}{{d{x^2}}} = 24x - 92k \\
\]
Now at \[x = 5,k = \dfrac{5}{6}\]
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}v}}{{d{x^2}}} = 24\left( 5 \right) - 92\left( {\dfrac{5}{6}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}v}}{{d{x^2}}} = 120 - 76.67 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}v}}{{d{x^2}}} = 43.33 > 0 \\
\]
So, at \[k = \dfrac{5}{6}\] the rectangular open box has a minimum value.
Now at \[x = 5,k = 3\]
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}v}}{{d{x^2}}} = 24\left( 5 \right) - 92\left( 3 \right) \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}v}}{{d{x^2}}} = 120 - 276 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}v}}{{d{x^2}}} = - 156 < 0 \\
\]
So, at \[k = 3\] the rectangular open box has maximum value.
Hence, the sides of the rectangle are \[8k = 8\left( 3 \right) = 24\] and \[15k = 15\left( 3 \right) = 45\].
Thus, the correct options are A. 24 and C. 45
Note:
For the least and greatest value of any function is obtained by equating its first derivative to zero. The least value is obtained for the value of \[x\] at which \[\dfrac{{{d^2}f\left( x \right)}}{{d{x^2}}} > 0\] and the greatest value is obtained for the value of \[x\] at which \[\dfrac{{{d^2}f\left( x \right)}}{{d{x^2}}} < 0\].
Complete step by step answer:
We have to solve this problem for the determination of lengths of the sides of the rectangular sheet, we will check the maximum change of volume in the rectangular shape and then find the value of the sides of the rectangular sheet.
Given that the sides of the rectangle are in ratio of \[8:15\].
Let the sides of the rectangle be \[8k\] and \[15k\] as the given ratio of sides of rectangles is \[8:15\].
And let the side length of the square be \[x\]. Now we have to four squares from each of the corner from the rectangular sheet as shown in the below figure:

Now the remaining sheet is converted into a rectangular open box.
So, length of the box = \[15k - 2x\]
Breadth of the box = \[8k - 2x\]
Height of the box = \[x\]
Given that the total area of the four squares is 100.
So, we have
\[
\Rightarrow 4\left( {{x^2}} \right) = 100 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} = \dfrac{{100}}{4} = 25 \\
\therefore x = \sqrt {25} = 5 \\
\]
We know that the volume of a rectangular box with length \[l\], breadth \[b\] and height \[h\] is given by \[lbh\].
Let the volume of the rectangular open box be \[v\]. So, we have
\[
\Rightarrow v = \left( {15k - 2x} \right)\left( {8k - 2x} \right)x \\
\Rightarrow v = \left( {120{k^2} - 46kx + 4{x^2}} \right)x \\
\Rightarrow v = 4{x^3} - 46k{x^2} + 120x{k^2} \\
\]
We know that for maximum or minimum value the value of the first derivative must be equal to zero.
So, for maximum or minimum volume of the rectangular box we have
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dv}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left[ {4{x^3} - 46k{x^2} + 120x{k^2}} \right] = 0 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dv}}{{dx}} = 12{x^2} - 92kx + 120{k^2} = 0 \\
\]
The volume of the rectangular box would be minimum or maximum at \[x = 5\]. So, we have
\[
\Rightarrow 12{\left( 5 \right)^2} - 92k\left( 5 \right) + 120{k^2} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 300 - 460k + 120{k^2} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 20\left( {6{k^2} - 23k + 15} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 6{k^2} - 18k - 5k + 15 = \dfrac{0}{{20}} \\
\Rightarrow 6k\left( {k - 3} \right) - 5\left( {k - 3} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow \left( {6k - 5} \right)\left( {k - 3} \right) = 0 \\
\therefore k = 3,\dfrac{5}{6} \\
\]
We know that, the least value is obtained for the value of \[x\] at which \[\dfrac{{{d^2}v}}{{d{x^2}}} > 0\] and the greatest value is obtained for the value of \[x\] at which \[\dfrac{{{d^2}v}}{{d{x^2}}} < 0\].
Now, consider the second derivative of the volume of the rectangular open box
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}v}}{{d{x^2}}} = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {\dfrac{{dv}}{{dx}}} \right) = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {12{x^2} - 92kx + 120{k^2}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}v}}{{d{x^2}}} = 24x - 92k \\
\]
Now at \[x = 5,k = \dfrac{5}{6}\]
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}v}}{{d{x^2}}} = 24\left( 5 \right) - 92\left( {\dfrac{5}{6}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}v}}{{d{x^2}}} = 120 - 76.67 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}v}}{{d{x^2}}} = 43.33 > 0 \\
\]
So, at \[k = \dfrac{5}{6}\] the rectangular open box has a minimum value.
Now at \[x = 5,k = 3\]
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}v}}{{d{x^2}}} = 24\left( 5 \right) - 92\left( 3 \right) \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}v}}{{d{x^2}}} = 120 - 276 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}v}}{{d{x^2}}} = - 156 < 0 \\
\]
So, at \[k = 3\] the rectangular open box has maximum value.
Hence, the sides of the rectangle are \[8k = 8\left( 3 \right) = 24\] and \[15k = 15\left( 3 \right) = 45\].
Thus, the correct options are A. 24 and C. 45
Note:
For the least and greatest value of any function is obtained by equating its first derivative to zero. The least value is obtained for the value of \[x\] at which \[\dfrac{{{d^2}f\left( x \right)}}{{d{x^2}}} > 0\] and the greatest value is obtained for the value of \[x\] at which \[\dfrac{{{d^2}f\left( x \right)}}{{d{x^2}}} < 0\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




