
A rectangular hyperbola whose centre is $ C $ is cut by any circle of radius $ r $ in four points $ P,Q,R $ And $ S $ . Then if $ C{P^2} + C{Q^2} + C{R^2} + C{S^2} = k{r^2} $ , find the value of $ k $ .
Answer
543.6k+ views
Hint: In this question we need to find the value of $ k $ . Therefore, here we will consider a circle and a hyperbola with a common centre. Then substitute the values of $ x $ and $ y $ from the equation of hyperbola into the equation of the circle, to determine the common point. Then , we will consider the equations as a quadratic equation in $ {x^2} $ and $ {y^2} $ and taking the common centre is $ C\left( {0,0} \right) $ then, $ P,Q,R,S $ be $ \left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right),\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right),\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right),\left( {{x_4},{y_4}} \right) $ respectively. And, finally substituting the values and evaluating it we will get the required solution.
Complete step by step solution:
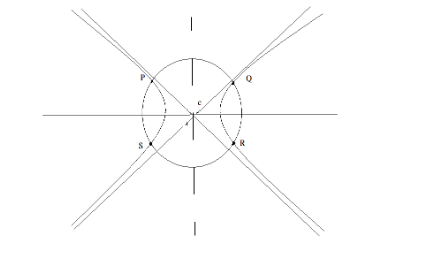
Now, we know that the equation of rectangular hyperbola is $ xy = {c^2} $ .
And also, the equation of the circle is $ {x^2} + {y^2} = {r^2} $ .
Let both the hyperbola and the circle have a common centre $ C\left( {0,0} \right) $ .
From the equation of hyperbola, we have,
$ y = \dfrac{{{c^2}}}{x} $ and $ x = \dfrac{{{c^2}}}{y} $
Now, we need to find the common points of hyperbola and the circle.
So, let us substitute the value of $ y $ from equation of hyperbola into the equation of circle, we get,
$ {x^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{{{c^2}}}{x}} \right)^2} = {r^2} $
$ {x^2} + \dfrac{{{c^4}}}{{{x^2}}} = {r^2} $
$ {\left( {{x^2}} \right)^2} - \left( {{r^2}} \right){x^2} + {c^4} = 0 $
Let it be equation (1)
Now, let us take equation (1) as a quadratic equation in $ {x^2} $ .
Thus, the sum of roots of the equation is,
$ {\left( {{x_1}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{x_2}} \right)^2} = {r^2} $ or $ {\left( {{x_3}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{x_4}} \right)^2} = {r^2} $
Let it be equation (2)
Now, let us substitute the value of $ x $ from equation of hyperbola into equation of circle, we get,
$ {y^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{{{c^2}}}{y}} \right)^2} = {r^2} $
$ {x^2} + \dfrac{{{c^4}}}{{{y^2}}} = {r^2} $
$ {\left( {{y^2}} \right)^2} - \left( {{r^2}} \right){y^2} + {c^4} = 0 $
Let it be equation (3)
Now, let us take equation (3) as a quadratic equation in $ {y^2} $ ,
Thus, the sum of roots of the equation is,
$ {\left( {{y_1}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{y_2}} \right)^2} = {r^2} $ or $ {\left( {{y_3}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{y_4}} \right)^2} = {r^2} $
Let this be equation (4)
If the common centre is $ C\left( {0,0} \right) $ then, $ P,Q,R,S $ be $ \left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right),\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right),\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right),\left( {{x_4},{y_4}} \right) $ respectively.
Hence, $ C{P^2} = {x_1}^2 + {y_1}^2 $
$ C{Q^2} = {x_2}^2 + {y_2}^2 $
$ C{R^2} = {x_3}^2 + {y_3}^2 $
$ C{S^2} = {x_4}^2 + {y_4}^2 $
Now, $ C{P^2} + C{Q^2} + C{R^2} + C{S^2} = {x_1}^2 + {y_1}^2 + {x_2}^2 + {y_2}^2 + {x_3}^2 + {y_3}^2 + {x_4}^2 + {y_4}^2 $
By rearranging the terms, we have,
$ C{P^2} + C{Q^2} + C{R^2} + C{S^2} = {x_1}^2 + {x_2}^2 + {x_3}^2 + {x_4}^2 + {y_1}^2 + {y_2}^2 + {y_3}^2 + {y_4}^2 $
Let this be equation (5)
Substituting the values from equation (2) and equation (4) into equation (5), we get,
$
\Rightarrow C{P^2} + C{Q^2} + C{R^2} + C{S^2} = {r^2} + {r^2} + {r^2} + {r^2} \\
\Rightarrow C{P^2} + C{Q^2} + C{R^2} + C{S^2} = 4{r^2} \;
$
Hence, comparing $ C{P^2} + C{Q^2} + C{R^2} + C{S^2} = 4{r^2} $ with $ C{P^2} + C{Q^2} + C{R^2} + C{S^2} = k{r^2} $ , we have,
$ k = 4 $
Hence, the value of $ k $ is $ 4 $ .
So, the correct answer is “4”.
Note: In this question it is important to note that the hyperbola whose asymptotes are at right angles at each other is called rectangular hyperbola. For a quadratic equation $ a{x^2} + bx + c = 0 $ , the sum of the roots of the equation is $ \dfrac{{ - b}}{a} $ and the product of the roots of the equation is $ \dfrac{c}{a} $ .
Complete step by step solution:

Now, we know that the equation of rectangular hyperbola is $ xy = {c^2} $ .
And also, the equation of the circle is $ {x^2} + {y^2} = {r^2} $ .
Let both the hyperbola and the circle have a common centre $ C\left( {0,0} \right) $ .
From the equation of hyperbola, we have,
$ y = \dfrac{{{c^2}}}{x} $ and $ x = \dfrac{{{c^2}}}{y} $
Now, we need to find the common points of hyperbola and the circle.
So, let us substitute the value of $ y $ from equation of hyperbola into the equation of circle, we get,
$ {x^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{{{c^2}}}{x}} \right)^2} = {r^2} $
$ {x^2} + \dfrac{{{c^4}}}{{{x^2}}} = {r^2} $
$ {\left( {{x^2}} \right)^2} - \left( {{r^2}} \right){x^2} + {c^4} = 0 $
Let it be equation (1)
Now, let us take equation (1) as a quadratic equation in $ {x^2} $ .
Thus, the sum of roots of the equation is,
$ {\left( {{x_1}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{x_2}} \right)^2} = {r^2} $ or $ {\left( {{x_3}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{x_4}} \right)^2} = {r^2} $
Let it be equation (2)
Now, let us substitute the value of $ x $ from equation of hyperbola into equation of circle, we get,
$ {y^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{{{c^2}}}{y}} \right)^2} = {r^2} $
$ {x^2} + \dfrac{{{c^4}}}{{{y^2}}} = {r^2} $
$ {\left( {{y^2}} \right)^2} - \left( {{r^2}} \right){y^2} + {c^4} = 0 $
Let it be equation (3)
Now, let us take equation (3) as a quadratic equation in $ {y^2} $ ,
Thus, the sum of roots of the equation is,
$ {\left( {{y_1}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{y_2}} \right)^2} = {r^2} $ or $ {\left( {{y_3}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{y_4}} \right)^2} = {r^2} $
Let this be equation (4)
If the common centre is $ C\left( {0,0} \right) $ then, $ P,Q,R,S $ be $ \left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right),\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right),\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right),\left( {{x_4},{y_4}} \right) $ respectively.
Hence, $ C{P^2} = {x_1}^2 + {y_1}^2 $
$ C{Q^2} = {x_2}^2 + {y_2}^2 $
$ C{R^2} = {x_3}^2 + {y_3}^2 $
$ C{S^2} = {x_4}^2 + {y_4}^2 $
Now, $ C{P^2} + C{Q^2} + C{R^2} + C{S^2} = {x_1}^2 + {y_1}^2 + {x_2}^2 + {y_2}^2 + {x_3}^2 + {y_3}^2 + {x_4}^2 + {y_4}^2 $
By rearranging the terms, we have,
$ C{P^2} + C{Q^2} + C{R^2} + C{S^2} = {x_1}^2 + {x_2}^2 + {x_3}^2 + {x_4}^2 + {y_1}^2 + {y_2}^2 + {y_3}^2 + {y_4}^2 $
Let this be equation (5)
Substituting the values from equation (2) and equation (4) into equation (5), we get,
$
\Rightarrow C{P^2} + C{Q^2} + C{R^2} + C{S^2} = {r^2} + {r^2} + {r^2} + {r^2} \\
\Rightarrow C{P^2} + C{Q^2} + C{R^2} + C{S^2} = 4{r^2} \;
$
Hence, comparing $ C{P^2} + C{Q^2} + C{R^2} + C{S^2} = 4{r^2} $ with $ C{P^2} + C{Q^2} + C{R^2} + C{S^2} = k{r^2} $ , we have,
$ k = 4 $
Hence, the value of $ k $ is $ 4 $ .
So, the correct answer is “4”.
Note: In this question it is important to note that the hyperbola whose asymptotes are at right angles at each other is called rectangular hyperbola. For a quadratic equation $ a{x^2} + bx + c = 0 $ , the sum of the roots of the equation is $ \dfrac{{ - b}}{a} $ and the product of the roots of the equation is $ \dfrac{c}{a} $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




