
A rectangular coil of copper wires is rotated in a magnetic field. The direction of the induced current changes once in each:
A. Two revolution
B. One revolution
C. Half revolution
D. One fourth revolution
Answer
506.4k+ views
Hint: This question utilizes the concept of induced currents. We know that current can be induced in a conducting loop when it is exposed to a changing magnetic field. Here, the flux through the rectangular loop is constantly changing, hence current is induced in the rectangular coil.
Rules used:
Fleming's Right hand rule: It states that when the thumb, the index finger and the middle finger of the Right hand is kept mutually perpendicular to each other, the thumb gives the direction of motion, the index finger gives the direction of magnetic field and the middle finger gives the direction of the induced current.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the given question, a rectangular coil of copper wires is rotating in a constant magnetic field. Let there be a magnetic field $B$ given off by a magnet. Let there be a rectangular coil $DEFG$ which is placed in the magnetic field $B$. Let there be a axis passing through the middle of coil $DEFG$ about which it is rotated as shown below
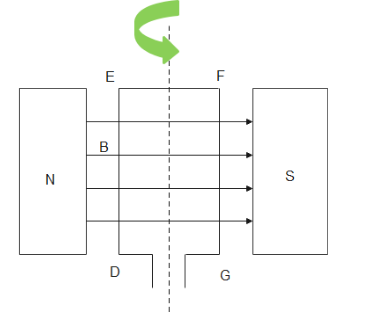
Applying Fleming's Right hand rule and putting the directions for part $DE$ , we find that the current is induced in direction $DEFGD$ .
After half rotation, from the below figure
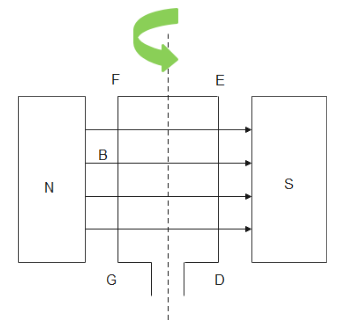
Again, applying Fleming's Right Hand Rule for $GF$ , we find the direction of induced current to be $GFEDG$. Therefore, we can infer that current reverses its direction after every half rotation.
Thus, the correct answer is option C.
Note: Fleming's Right hand rule is only used for finding the induced current when a conductor is placed in a magnetic field(mostly in coils) whereas Fleming's Left hand rule is used to find the direction of force when a current carrying wire is placed in a magnetic field. They should not be confused with each other.
Rules used:
Fleming's Right hand rule: It states that when the thumb, the index finger and the middle finger of the Right hand is kept mutually perpendicular to each other, the thumb gives the direction of motion, the index finger gives the direction of magnetic field and the middle finger gives the direction of the induced current.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the given question, a rectangular coil of copper wires is rotating in a constant magnetic field. Let there be a magnetic field $B$ given off by a magnet. Let there be a rectangular coil $DEFG$ which is placed in the magnetic field $B$. Let there be a axis passing through the middle of coil $DEFG$ about which it is rotated as shown below

Applying Fleming's Right hand rule and putting the directions for part $DE$ , we find that the current is induced in direction $DEFGD$ .
After half rotation, from the below figure

Again, applying Fleming's Right Hand Rule for $GF$ , we find the direction of induced current to be $GFEDG$. Therefore, we can infer that current reverses its direction after every half rotation.
Thus, the correct answer is option C.
Note: Fleming's Right hand rule is only used for finding the induced current when a conductor is placed in a magnetic field(mostly in coils) whereas Fleming's Left hand rule is used to find the direction of force when a current carrying wire is placed in a magnetic field. They should not be confused with each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




