
A rectangular bar 2 cm in breadth, 1 cm in depth and 100 cm in length is supported at its ends and a load of 2 kg is applied at its middle. If Young’s modulus of the material of the bar is $20 \times {10^{11}}{\text{dyne c}}{{\text{m}}^{{\text{ - 2}}}}$, the depression in the bar is
A) $0.2450cm$
B) $0.3675cm$
C) $0.1225cm$
D) $0.9800cm$
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: Young’s modulus is the ratio of longitudinal stress over strain. Assume the rectangular bar to be similar to a beam being bent under the force of weight. Then apply the same formula for the deformation of the beam to the given system and solve for the required answer.
Formula used:
$\delta = \dfrac{{w{l^3}}}{{4Yb{d^3}}}$
Complete answer:
When a beam is bent, a strain is produced which is longitudinal thus, the elastic modulus involved is Young’s modulus.
Consider a beam rigidly supported at both its ends in a horizontal manner, as shown in the figure below:
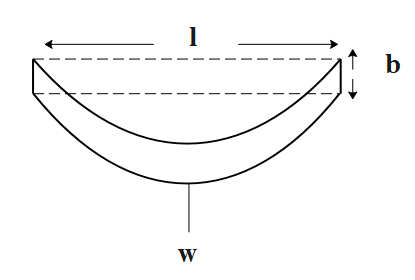
It has a weight ‘w’ suspended at its middle portion. Let its length be ‘l’, breadth be ‘d’ and its depth be ‘d’. Let the Young’s modulus of the material be represented by ‘Y’.
Then the depression attained by this beam will be given mathematically as,
$\delta = \dfrac{{w{l^3}}}{{4b{d^3}Y}}$ --(1)
Now, given length of rod, $l = 100cm$
Breadth of rod, $b = 2cm$
Depth of rod, $d = 1cm$
Young’s modulus of the rod, $Y = 20 \times {10^{11}}{\text{dyne c}}{{\text{m}}^{{\text{ - 2}}}}$
Substituting the given values in equation (1) we get,
$\delta = \dfrac{{w{l^3}}}{{4b{d^3}Y}} = \dfrac{{2 \times {{\left( {100} \right)}^3}}}{{4 \times 2 \times {{\left( 1 \right)}^3}20 \times {{10}^{11}}}} = 0.1225cm$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
When the force acts on the rod, every point along the rod faces the curvature due to this deforming force. This curvature is such that the internal stress is completely balanced by the external bending. So, the curvature is not constant, in other words it is a function of distance from the sides. Young’s modulus is defined as the measure of the ability of a material to withstand changes in the length when under tension or compression. It is also referred to as modulus of elasticity.
Formula used:
$\delta = \dfrac{{w{l^3}}}{{4Yb{d^3}}}$
Complete answer:
When a beam is bent, a strain is produced which is longitudinal thus, the elastic modulus involved is Young’s modulus.
Consider a beam rigidly supported at both its ends in a horizontal manner, as shown in the figure below:

It has a weight ‘w’ suspended at its middle portion. Let its length be ‘l’, breadth be ‘d’ and its depth be ‘d’. Let the Young’s modulus of the material be represented by ‘Y’.
Then the depression attained by this beam will be given mathematically as,
$\delta = \dfrac{{w{l^3}}}{{4b{d^3}Y}}$ --(1)
Now, given length of rod, $l = 100cm$
Breadth of rod, $b = 2cm$
Depth of rod, $d = 1cm$
Young’s modulus of the rod, $Y = 20 \times {10^{11}}{\text{dyne c}}{{\text{m}}^{{\text{ - 2}}}}$
Substituting the given values in equation (1) we get,
$\delta = \dfrac{{w{l^3}}}{{4b{d^3}Y}} = \dfrac{{2 \times {{\left( {100} \right)}^3}}}{{4 \times 2 \times {{\left( 1 \right)}^3}20 \times {{10}^{11}}}} = 0.1225cm$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
When the force acts on the rod, every point along the rod faces the curvature due to this deforming force. This curvature is such that the internal stress is completely balanced by the external bending. So, the curvature is not constant, in other words it is a function of distance from the sides. Young’s modulus is defined as the measure of the ability of a material to withstand changes in the length when under tension or compression. It is also referred to as modulus of elasticity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




