
A reaction rate constant is given by: $ k=1.2\times {{10}^{14}}{{e}^{-\dfrac{2500}{RT}}}{{s}^{-1}}. $ T means:
(A) log k versus log T will give a straight line with a slope as $ 25000. $
(B) log k versus log T will give a straight line with a slope as $ -25000. $
(C) log k versus T will give a straight line with a slope as $ -25000. $
(D) log k versus $ 1/T $ will give a straight line.
Answer
512.1k+ views
Hint : We know that the rate constant is also known by the name proportionality constant which gives the relationship between molar concentration of the reactants and chemical reaction. Chemical kinetics deals with the study of rate of chemical reaction and factors affecting rate of reaction.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
To know about rate constant and half-life, we should understand the rate law expression. Rate constant (k) is defined as the rate of the reaction when the concentration of the one or more than one reacting species approaches to or equal to unity. Rate constant is also called a velocity constant and specific rate constant. The rate constant depends on the temperature but it is independent of the concentration. The temperature dependence of the rate constant can be seen by the Arrhenius equation. Rate constant can be easily calculated with the help of Arrhenius equation.
This equation gives us the formula for the temperature dependence of reaction rates. The Arrhenius equation has many applications but the main and very important application of the Arrhenius equation is it is useful in determination of rate of chemical reaction and for the calculation of energy of activation. The unit of rate constant also depends on the order of reaction where order of reaction can be defined as the Sum of the exponents which gives us the overall order of a reaction. The order of a complex reaction is given by the order of the slowest step in the sequence of various steps involved in that reaction.
$ k=1.2\times {{10}^{14}}{{e}^{-\dfrac{2500}{RT}}}{{s}^{-1}}. $
From k it can be seen that, log k versus $ 1/T $ will give a straight line as:
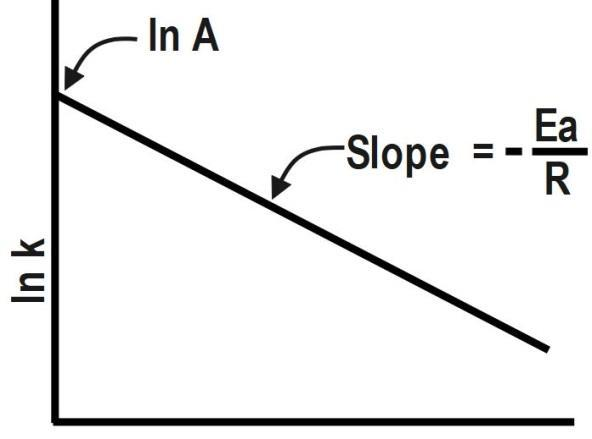
Therefore, the correct answer is option D.
Note :
Remember that the order of reaction tells the relationship between the rate of a chemical reaction and the concentration of the species taking part in it. In order to calculate the reaction order the rate expression of the reaction is very necessary.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
To know about rate constant and half-life, we should understand the rate law expression. Rate constant (k) is defined as the rate of the reaction when the concentration of the one or more than one reacting species approaches to or equal to unity. Rate constant is also called a velocity constant and specific rate constant. The rate constant depends on the temperature but it is independent of the concentration. The temperature dependence of the rate constant can be seen by the Arrhenius equation. Rate constant can be easily calculated with the help of Arrhenius equation.
This equation gives us the formula for the temperature dependence of reaction rates. The Arrhenius equation has many applications but the main and very important application of the Arrhenius equation is it is useful in determination of rate of chemical reaction and for the calculation of energy of activation. The unit of rate constant also depends on the order of reaction where order of reaction can be defined as the Sum of the exponents which gives us the overall order of a reaction. The order of a complex reaction is given by the order of the slowest step in the sequence of various steps involved in that reaction.
$ k=1.2\times {{10}^{14}}{{e}^{-\dfrac{2500}{RT}}}{{s}^{-1}}. $
From k it can be seen that, log k versus $ 1/T $ will give a straight line as:

Therefore, the correct answer is option D.
Note :
Remember that the order of reaction tells the relationship between the rate of a chemical reaction and the concentration of the species taking part in it. In order to calculate the reaction order the rate expression of the reaction is very necessary.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




