
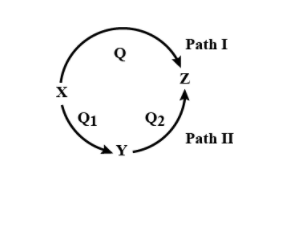
A reaction proceeds through two paths I and II to convert \[X \to Z\]. What is the correct relationship between, Q, \[{Q_1}\], and \[{Q_2}\] (Q represents a change in internal energy, here)?
A. \[Q = {Q_1} \times {Q_2}\]
B. \[Q = {Q_1} + {Q_2}\]
C. \[Q = {Q_2} - {Q_1}\]
D. \[Q = \dfrac{{{Q_1}}}{{{Q_2}}}\]

Answer
568.2k+ views
Hint: We know that the Internal energy is a state function. In the question above, Q is the change in internal energy. We all know that,
\[\delta Q = \;\delta U + \delta W\].
Complete step by step answer:
We can define Internal Energy as the energy that is random and disordered motion of the molecule. To make it clear, we should know that the change in internal energy for a reaction is always the same whether it occurs in one step or the reaction either occurs in two steps or is in multiple steps that is in a series of steps. So in the above reaction, if X is converted to Z in single step, then the internal energy that is Q released and when the change happens through two step that is X to and then Y to Z, then the internal energy release while change from X to Y that is \[{Q_1}\] and the internal energy released from change while Y to Z that is Q will definitely be equal to the energy while direct conversion of X to Z. so \[{Q_1}\] that is released while conversion of X to Y and \[{Q_2}\] that is released while conversion from Y to Z will be equal to Q that is released from conversion of X to Z.
Internal energy (Q) is a state function.
\[ \Rightarrow {Q_{XZ}} = {Q_{XY}} + {Q_{YZ}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow Q = Q1 + Q2\]
Therefore, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: The internal energies released in a multi-step reaction will be equal to when the reaction happens in just one step. The enthalpy of reaction is defined as the internal energy of the system.
\[\delta Q = \;\delta U + \delta W\].
Complete step by step answer:
We can define Internal Energy as the energy that is random and disordered motion of the molecule. To make it clear, we should know that the change in internal energy for a reaction is always the same whether it occurs in one step or the reaction either occurs in two steps or is in multiple steps that is in a series of steps. So in the above reaction, if X is converted to Z in single step, then the internal energy that is Q released and when the change happens through two step that is X to and then Y to Z, then the internal energy release while change from X to Y that is \[{Q_1}\] and the internal energy released from change while Y to Z that is Q will definitely be equal to the energy while direct conversion of X to Z. so \[{Q_1}\] that is released while conversion of X to Y and \[{Q_2}\] that is released while conversion from Y to Z will be equal to Q that is released from conversion of X to Z.
Internal energy (Q) is a state function.
\[ \Rightarrow {Q_{XZ}} = {Q_{XY}} + {Q_{YZ}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow Q = Q1 + Q2\]
Therefore, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: The internal energies released in a multi-step reaction will be equal to when the reaction happens in just one step. The enthalpy of reaction is defined as the internal energy of the system.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




