
A ray of light is incident on a glass sphere of refractive index $\dfrac{3}{2}$ . What should be the angle of incidence so that the ray which enters the sphere does not come out of the sphere?
a. ${\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}} \right)$
b. ${60^ \circ }$
c. ${90^ \circ }$
d. ${30^ \circ }$
Answer
497.7k+ views
Hint: We want to determine the angle of incidence of a ray of light on a sphere of glass with refractive index $\dfrac{3}{2}$ so as to ensure that the ray of light does not come out of the sphere and by using Snell’s Law we will get the answer.
Formula used:
$\mu = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
For the light to not come out of the sphere, $e$ must be greater than or equal to \[{90^ \circ }\].
Consider a ray of light $AB$ incident on the glass sphere at point $B$ at an angle $i$ . The angle of refraction is $r$ .
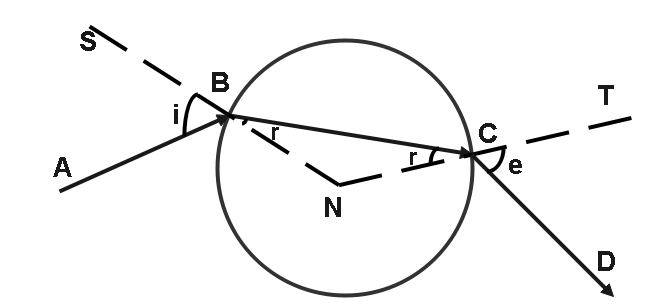
The refracted ray $BC$ comes out of the sphere at point at point $C$ and emerges from the sphere as ray $CD$ , with an angle of emergence $e$ .
Here we can see that $NS$ and $NT$ are the normal at the point of incidence and the point of emergence respectively and that $NB$ and $NC$ are radii of the sphere.
$ \Rightarrow \angle NBC = r = \angle NCB$
Also,
$\mu = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}}$
Where,
$\mu $ is known as the refractive index,
\[i\] is known as the angle of incidence and
$r$ is known as the angle of refraction.
And
$\mu = \dfrac{{\sin e}}{{\sin r}}$
$ \Rightarrow \sin i = \sin e \\
\Rightarrow i = e $
This means that, when a ray of light is incident on a sphere, the angle of incidence and the angle of emergence are always equal. If the ray of light should not come out of the sphere it means that the angle of emergence has to be at least ${90^ \circ }$ .
$\therefore $ The angle of incidence is ${90^ \circ }$ .
Hence, option (c) is the correct option.
Note: However, the angle of incidence cannot be more than ${90^ \circ }$ and if the angle of incidence is ${90^ \circ }$ , the ray of light will just brush past the sphere and will not enter the sphere. Refractive index is basically the speed of light in a medium with respect to air. Since we have speeds in both numerator and denominator, their units cancel out and thus the refractive index is unit less.
Additional information: The phenomenon happening here is known as refraction of light, this happens due to different speeds of light in different mediums. The medium in which the speed of light is more is known as rarer and in which it is less is known as denser medium.
Formula used:
$\mu = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
For the light to not come out of the sphere, $e$ must be greater than or equal to \[{90^ \circ }\].
Consider a ray of light $AB$ incident on the glass sphere at point $B$ at an angle $i$ . The angle of refraction is $r$ .

The refracted ray $BC$ comes out of the sphere at point at point $C$ and emerges from the sphere as ray $CD$ , with an angle of emergence $e$ .
Here we can see that $NS$ and $NT$ are the normal at the point of incidence and the point of emergence respectively and that $NB$ and $NC$ are radii of the sphere.
$ \Rightarrow \angle NBC = r = \angle NCB$
Also,
$\mu = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}}$
Where,
$\mu $ is known as the refractive index,
\[i\] is known as the angle of incidence and
$r$ is known as the angle of refraction.
And
$\mu = \dfrac{{\sin e}}{{\sin r}}$
$ \Rightarrow \sin i = \sin e \\
\Rightarrow i = e $
This means that, when a ray of light is incident on a sphere, the angle of incidence and the angle of emergence are always equal. If the ray of light should not come out of the sphere it means that the angle of emergence has to be at least ${90^ \circ }$ .
$\therefore $ The angle of incidence is ${90^ \circ }$ .
Hence, option (c) is the correct option.
Note: However, the angle of incidence cannot be more than ${90^ \circ }$ and if the angle of incidence is ${90^ \circ }$ , the ray of light will just brush past the sphere and will not enter the sphere. Refractive index is basically the speed of light in a medium with respect to air. Since we have speeds in both numerator and denominator, their units cancel out and thus the refractive index is unit less.
Additional information: The phenomenon happening here is known as refraction of light, this happens due to different speeds of light in different mediums. The medium in which the speed of light is more is known as rarer and in which it is less is known as denser medium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




