
A ray of light, incident on an equilateral glass prism \[\left( {{\mu _{\text{g}}} = \sqrt 3 } \right)\] moves parallel to the baseline of the prism inside it. Find the angle of incidence for the ray.
Answer
604.8k+ views
Hint: To find the angle of incident ray we draw an appropriate figure depicting all the given information in the question and apply Snell’s law of refraction of light using the data from the figure. It is known that the refractive index of air \[\left( {{\mu _{\text{a}}} = 1} \right)\].
Formula Used:
Snell’s Law : ${\mu _{\text{1}}}{\text{Sin}}{\theta _1} = {\mu _2}{\text{Sin}}{\theta _2}$,
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
Given Data,
Refractive index of glass of prism \[\left( {{\mu _{\text{g}}} = \sqrt 3 } \right)\]
It is an equilateral prism, i.e. all the angles in the figure are equal. The angle of the prism is 60°.
Snell’s Law : ${\mu _{\text{1}}}{\text{Sin}}{\theta _1} = {\mu _2}{\text{Sin}}{\theta _2}$,
Where the refractive index of the medium incident ray comes from is ${\mu _{\text{1}}}$ and ${\theta _1}$ is the angle of incidence.${\mu _2}$ is the refractive index of the medium refracted ray goes into and ${\theta _2}$ is the angle of refraction.
We draw a figure of a prism with an angle 60°. The incident ray of light falls on the prism and gets refracted. We show the angle of incidence by drawing a perpendicular dotted line to the side of the prism the incident ray falls, joining the center of the prism O.
The angle between the dotted line and the incident ray is called the angle of incidence “i” and the angle between the dotted line and the refracted ray on the inside of the prism is called the angle of refraction “r”.
It is as follows:
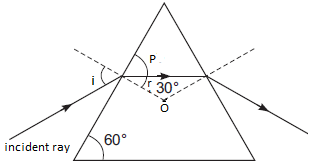
From the figure,
The angle of the prism is 60°
The sum of the angles ∠P and ∠r should be equal to 90° as they form an angle on the side of the prism perpendicular to the dotted line.
(Angle on a straight line is 180°, a perpendicular line divides it into two equal halves.)
⟹∠P + ∠r = 90° --- (1)
Now from the figure we can say the angle P is corresponding to the angle of the prism. Therefore using the property of corresponding angle we get ∠P = 60°.
Using this in equation (1) we get,
⟹∠P + ∠r = 90°
⟹60° + ∠r = 90°
⟹∠r = 30° -- (2)
Therefore the angle of refraction is 30°.
Snell’s law gives us the relation between the angles of incidence and refraction when a ray of light passes from one medium to the other such as air, water and glass etc.
Refractive index of a medium is defined as the ratio of velocity of light in vacuum to the velocity of light in the specific medium.
Applying Snell’s law using the figure
${\mu _{\text{1}}}{\text{Sin}}{\theta _1} = {\mu _2}{\text{Sin}}{\theta _2}$
Here angle of incidence is i, angle of refraction is ∠r = 30°,${\mu _{\text{1}}}$ is refractive index of air\[\left( {{\mu _{\text{a}}} = 1} \right)\] and ${\mu _2}$ is the refractive index of glass\[\left( {{\mu _{\text{g}}} = \sqrt 3 } \right)\]given.
Therefore according to Snell’s law:
$
\Rightarrow {\mu _{\text{a}}}{\text{Sin}}\left( {\text{i}} \right) = {\mu _{\text{g}}}{\text{Sin}}\left( {\text{r}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow 1 \times {\text{Sin}}\left( {\text{i}} \right) = \sqrt 3 \times {\text{Sin}}\left( {30^\circ } \right) \\
$
From the trigonometric table of Sin function we know ${\text{Sin}}\left( {30^\circ } \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}$.
Therefore,
$
\Rightarrow 1 \times {\text{Sin}}\left( {\text{i}} \right) = \sqrt 3 \times \dfrac{1}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{Sin}}\left( {\text{i}} \right) = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{i = Si}}{{\text{n}}^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow {\text{i = 60}}^\circ \\
$
From the trigonometric table of Sin function we get, ${\text{Si}}{{\text{n}}^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right) = 60^\circ $
Hence the angle of incidence of the ray is 60°.
Note – In order to answer this type of question the key is to know the properties of a prism like corresponding angles and minimum deviation.
Corresponding angles are the angles which are in the same relative position on two parallel lines intersecting the same traversal. Corresponding angles are congruent.
At minimum deviation, if the refracted ray inside the prism becomes parallel to the base of the prism the angle of refraction becomes $\angle {\text{r = }}\dfrac{{\angle {\text{A}}}}{2}$, where A is the angle of the prism.
The angle of refraction depends on the refractive index of a medium, the greater the refractive index the smaller the angle of refraction, i.e. the refracted ray is closer to the normal.
Formula Used:
Snell’s Law : ${\mu _{\text{1}}}{\text{Sin}}{\theta _1} = {\mu _2}{\text{Sin}}{\theta _2}$,
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
Given Data,
Refractive index of glass of prism \[\left( {{\mu _{\text{g}}} = \sqrt 3 } \right)\]
It is an equilateral prism, i.e. all the angles in the figure are equal. The angle of the prism is 60°.
Snell’s Law : ${\mu _{\text{1}}}{\text{Sin}}{\theta _1} = {\mu _2}{\text{Sin}}{\theta _2}$,
Where the refractive index of the medium incident ray comes from is ${\mu _{\text{1}}}$ and ${\theta _1}$ is the angle of incidence.${\mu _2}$ is the refractive index of the medium refracted ray goes into and ${\theta _2}$ is the angle of refraction.
We draw a figure of a prism with an angle 60°. The incident ray of light falls on the prism and gets refracted. We show the angle of incidence by drawing a perpendicular dotted line to the side of the prism the incident ray falls, joining the center of the prism O.
The angle between the dotted line and the incident ray is called the angle of incidence “i” and the angle between the dotted line and the refracted ray on the inside of the prism is called the angle of refraction “r”.
It is as follows:

From the figure,
The angle of the prism is 60°
The sum of the angles ∠P and ∠r should be equal to 90° as they form an angle on the side of the prism perpendicular to the dotted line.
(Angle on a straight line is 180°, a perpendicular line divides it into two equal halves.)
⟹∠P + ∠r = 90° --- (1)
Now from the figure we can say the angle P is corresponding to the angle of the prism. Therefore using the property of corresponding angle we get ∠P = 60°.
Using this in equation (1) we get,
⟹∠P + ∠r = 90°
⟹60° + ∠r = 90°
⟹∠r = 30° -- (2)
Therefore the angle of refraction is 30°.
Snell’s law gives us the relation between the angles of incidence and refraction when a ray of light passes from one medium to the other such as air, water and glass etc.
Refractive index of a medium is defined as the ratio of velocity of light in vacuum to the velocity of light in the specific medium.
Applying Snell’s law using the figure
${\mu _{\text{1}}}{\text{Sin}}{\theta _1} = {\mu _2}{\text{Sin}}{\theta _2}$
Here angle of incidence is i, angle of refraction is ∠r = 30°,${\mu _{\text{1}}}$ is refractive index of air\[\left( {{\mu _{\text{a}}} = 1} \right)\] and ${\mu _2}$ is the refractive index of glass\[\left( {{\mu _{\text{g}}} = \sqrt 3 } \right)\]given.
Therefore according to Snell’s law:
$
\Rightarrow {\mu _{\text{a}}}{\text{Sin}}\left( {\text{i}} \right) = {\mu _{\text{g}}}{\text{Sin}}\left( {\text{r}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow 1 \times {\text{Sin}}\left( {\text{i}} \right) = \sqrt 3 \times {\text{Sin}}\left( {30^\circ } \right) \\
$
From the trigonometric table of Sin function we know ${\text{Sin}}\left( {30^\circ } \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}$.
Therefore,
$
\Rightarrow 1 \times {\text{Sin}}\left( {\text{i}} \right) = \sqrt 3 \times \dfrac{1}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{Sin}}\left( {\text{i}} \right) = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{i = Si}}{{\text{n}}^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow {\text{i = 60}}^\circ \\
$
From the trigonometric table of Sin function we get, ${\text{Si}}{{\text{n}}^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right) = 60^\circ $
Hence the angle of incidence of the ray is 60°.
Note – In order to answer this type of question the key is to know the properties of a prism like corresponding angles and minimum deviation.
Corresponding angles are the angles which are in the same relative position on two parallel lines intersecting the same traversal. Corresponding angles are congruent.
At minimum deviation, if the refracted ray inside the prism becomes parallel to the base of the prism the angle of refraction becomes $\angle {\text{r = }}\dfrac{{\angle {\text{A}}}}{2}$, where A is the angle of the prism.
The angle of refraction depends on the refractive index of a medium, the greater the refractive index the smaller the angle of refraction, i.e. the refracted ray is closer to the normal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




