
A ray is reflected in turn by three plain mirrors mutually at right angles to each other. The angle between the incident and the reflected ray is
Answer
508.2k+ views
Hint: The answer to the above question lies in the question itself. In the question it is given to us that the ray is reflected in turn by three plain mirrors mutually at right angles to each other. There is no need to draw the diagram nor any calculation involved in the above question. It is just the case of understanding the direction of light which is reflected by the above system of mirrors.
Complete step-by-step solution:
In the question we are given three plane mirrors which are mutually perpendicular to each other. After some reflection of the incident ray from the above system, it is given to us that the ray is reflected in turn by three plain mirrors. The meaning of this statement basically means that the incident ray and the reflected ray are in the same sense but in opposite directions. More precisely the incident ray and the reflected ray are in opposite directions with respect to each other.
Since the rays of light are opposite to each other, we can say the angle between the incident and the reflected ray is 180 degrees.
Given figure below consists of three plane mirrors M(1), M(2) and M(3) which are mutually perpendicular to each other. The incident ray is denoted by ‘i’ and the reflected ray by ‘r’.
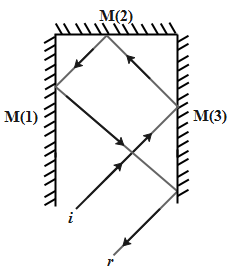
The above figure is one among the many possible outcomes, by which the above scenario can be explained.
Note: When two rays travel along the same path or parallel paths irrespective of their direction, we say the two rays travel in the same sense. It is also to be noted that in the above problem, we cannot say the ray got reflected just three times or how many times as we wish to consider it. There can be finitely many examples where in the above system of plane mirrors the incident ray is in the opposite direction of itself.
Complete step-by-step solution:
In the question we are given three plane mirrors which are mutually perpendicular to each other. After some reflection of the incident ray from the above system, it is given to us that the ray is reflected in turn by three plain mirrors. The meaning of this statement basically means that the incident ray and the reflected ray are in the same sense but in opposite directions. More precisely the incident ray and the reflected ray are in opposite directions with respect to each other.
Since the rays of light are opposite to each other, we can say the angle between the incident and the reflected ray is 180 degrees.
Given figure below consists of three plane mirrors M(1), M(2) and M(3) which are mutually perpendicular to each other. The incident ray is denoted by ‘i’ and the reflected ray by ‘r’.

The above figure is one among the many possible outcomes, by which the above scenario can be explained.
Note: When two rays travel along the same path or parallel paths irrespective of their direction, we say the two rays travel in the same sense. It is also to be noted that in the above problem, we cannot say the ray got reflected just three times or how many times as we wish to consider it. There can be finitely many examples where in the above system of plane mirrors the incident ray is in the opposite direction of itself.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




