
A ray is incident at an angle of incidence on one surface of a prism of small-angle A and emerges normally from the opposite surface. If the refractive index of the material of the prism is $\mu $, the angle of incident i is nearly equal to:
A. $\dfrac{A}{\mu }$
B. $\dfrac{A}{2\mu }$
C. $\dfrac{\mu }{A}$
D. $\mu A$
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: First, draw the diagram for the given small angle prism indicating the angle of incidence, the angle of emergence and the angle of prism. Use the relation between the angle of deviation and the angle of prism for small angle prism. Use the relation between the angle of prism, the angle of emergence, the angle of incidence and the angle of deviation. Using these two relations find out the angle of incidence in terms of the angle of prism and refractive index of prism.
Complete step by step solution:
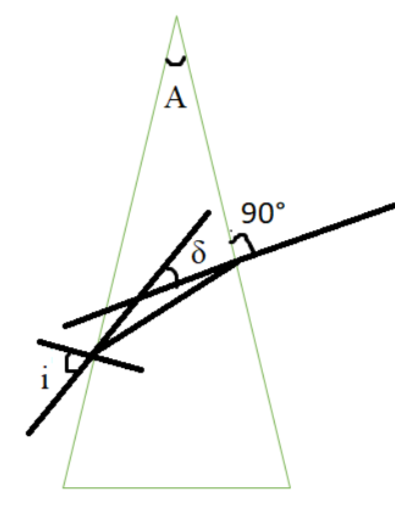
Let
i be the angle of incidence
A be the angle of prism
e be the angle of emergence
$\mu $ be the refractive index of prism
Given that ray emerges normally to the surface. Therefore, e=0.
For small angle prism angle of deviation is given as
$\delta =(\mu -1)A$
Also we have the relation,
$A+\delta =i+e$
Thus,
$\begin{align}
& A+(\mu -1)A=i+0 \\
& \therefore A\mu =i \\
& i.e.\text{ }i=A\mu \\
\end{align}$
So, The answer is D. $\mu A$.
Note: Note that this relation is valid only for small angle prisms. The angle of incidence and the angle of emergence are always measured with respect to the normal to surface. Since ray emerges normally to the surface, the angle made by it with normal is zero. Do not take angle with respect to the surface. The angle of deviation is the angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray. This angle can be found by extending incident ray in forward direction and emergent ray in backward direction.
Complete step by step solution:

Let
i be the angle of incidence
A be the angle of prism
e be the angle of emergence
$\mu $ be the refractive index of prism
Given that ray emerges normally to the surface. Therefore, e=0.
For small angle prism angle of deviation is given as
$\delta =(\mu -1)A$
Also we have the relation,
$A+\delta =i+e$
Thus,
$\begin{align}
& A+(\mu -1)A=i+0 \\
& \therefore A\mu =i \\
& i.e.\text{ }i=A\mu \\
\end{align}$
So, The answer is D. $\mu A$.
Note: Note that this relation is valid only for small angle prisms. The angle of incidence and the angle of emergence are always measured with respect to the normal to surface. Since ray emerges normally to the surface, the angle made by it with normal is zero. Do not take angle with respect to the surface. The angle of deviation is the angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray. This angle can be found by extending incident ray in forward direction and emergent ray in backward direction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




