
A proton of mass m collides elastically with a particle of unknown mass at rest. After the collision, the proton and the unknown particle are seen moving at an angle of ${ 90 }^{ 0 }$ with respect to each other. The mass of unknown particle is:
$A. \dfrac { m }{ \sqrt { 3 } }$
$B. \dfrac{ m }{ \ { 2 } }$
$C.2m$
$D.m$
Answer
600.6k+ views
Hint: Since it is an elastic collision, the conservation of momentum and conservation of kinetic energy will be needed. We also need to remember which are vector quantities and which are scalar quantities.
Step by step solution:
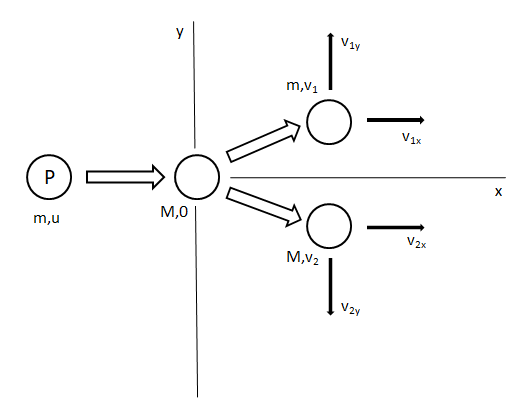
We know the proton’s mass is m having initial velocity u. Let’s consider the unknown mass as M and since it is at rest, its velocity is zero. After the collision the proton moves with velocity${ v }_{ 1 }$, making an angle ${ \theta }_{ 1 }$ with the horizontal. Similarly, M moves with velocity ${ v }_{ 2 }$ making an angle ${ \theta }_{ 2 }$ with the horizontal.
After collision, the velocity component of mass m will be divided into 2 components along the x and y axes, since it’s a vector quantity. We will call them ${ v }_{ 1x }$ and ${ v }_{ 1y }$ respectively.
${ v }_{ 1x }={ v }_{ 1 }\cos { { \theta }_{ 1 } }$ and ${ v }_{ 1y }={ v }_{ 1 }\sin { { \theta }_{ 1 } }$.
Similarly, the velocity components of ${ v }_{ 2 }$ will be divided into ${ v }_{ 2x }$ and ${ v }_{ 2y }$, for velocity components along x and y axes respectively.
${ v }_{ 2x }={ v }_{ 2 }\cos { { \theta }_{ 2 } }$ and ${ v }_{ 2y }={- v }_{ 2 }\sin { { \theta }_{ 2 } }$.
Let’s consider, both the masses are equal and try and see if we are getting the condition of ${ \theta }_{ 1 }$+${ \theta }_{ 2 }$=${ 90 }^{ 0 }$.
${ p }_{ x }$initial = ${ p }_{ x}$ final using conservation of momentum along the x axis.
$mu=m{ v }_{ 1 }\cos { { \theta }_{ 1 }+m{ v }_{ 2 }\cos { { \theta }_{ 2 } } }$
$u={{v}_{1}}\cos {{\theta }_{1}}+{{v}_{2}}\cos {{\theta }_{2}}\to (1)$
${ p }_{ y }$initial = ${ p }_{ y}$ final using conservation of momentum along the x axis.
$0+0={ v }_{ 1 }\sin { { \theta }_{ 1 }-{ v }_{ 2 }\sin { { \theta }_{ 2 } } }$
$0={{v}_{1}}\sin {{\theta }_{1}}-{{v}_{2}}\sin {{\theta }_{2}}\to (2)$
${ (1) }^{ 2 }+{ (2) }^{ 2 }$ gives us,
${ u }^{ 2 }={ ({ v }_{ 1 }\cos { { \theta }_{ 1 }+{ v }_{ 2 }\cos { { \theta }_{ 2 } } } ) }^{ 2 }+{ ({ v }_{ 1 }\sin{ { \theta }_{ 1 }-{ v }_{ 2 }\sin { { \theta }_{ 2 } } } ) }^{ 2 }$
${ u }^{ 2 }={ v }_{ 1 }^{ 2 }\cos ^{ 2 }{ { \theta }_{ 1 } } +{ v }_{ 2 }^{ 2 }\cos ^{ 2 }{ { \theta }_{ 2 } } +2{ v }_{ 1 }{ v }_{ 2 }\cos { { \theta }_{ 1 }\cos { { \theta }_{ 2 } } +{ v }_{ 1 }^{ 2 }\sin ^{ 2 }{ { \theta }_{ 1 } } +{ v }_{ 2 }^{ 2 }\sin ^{ 2 }{ { \theta }_{ 2 } } } -2{ v }_{ 1 }{ v }_{ 2 }\sin { { \theta }_{ 1 }\sin { { \theta }_{ 2 } } }$
${ u }^{ 2 }={ v }_{ 1 }^{ 2 }(\cos ^{ 2 }{ { \theta }_{ 1 } } +\sin ^{ 2 }{ { \theta }_{ 1 } } )+{ v }_{ 2 }^{ 2 }(\cos ^{ 2 }{ { \theta }_{ 2 } } \sin ^{ 2 }{ { \theta }_{ 2 } } )+2{ v }_{ 1 }{ v }_{ 2 }(\cos { { \theta }_{ 1 }\cos { { \theta }_{ 2 } } } -\sin { { \theta }_{ 1 }\sin { { \theta }_{ 2 }) } }$
${{u}^{2}}=v_{1}^{2}+v_{2}^{2}+2{{v}_{1}}{{v}_{2}}\cos ({{\theta }_{1}}+{{\theta }_{2}})\to (3)$
Now, using the conservation of kinetic energy formula:
${ \dfrac { 1 }{ 2 } mu }^{ 2 }=\dfrac { 1 }{ 2 } m{ v }_{ 1 }^{ 2 }+\dfrac { 1 }{ 2 } m{ v }_{ 2 }^{ 2 }$
Here, we don’t use the velocity components along each axis as Energy is a scalar quantity and direction component isn’t required.
${{u}^{2}}=v_{1}^{2}+_{2}^{2}\to (4)$
Comparing the equations (3) and (4), we get:
$2{ v }_{ 1 }{ v }_{ 2 }\cos { { (\theta }_{ 1 }+{ \theta }_{ 2 }) } =0$
$\cos { { (\theta }_{ 1 }+{ \theta }_{ 2 }) } =0$
As we know that $\cos { (\dfrac { n\pi }{ 2 } ) } =0$ for n= any integer except zero.
Considering the case for n=1, we get, ${ \theta }_{ 1 }+{ \theta }_{ 2 }=\dfrac { \pi }{ 2 }$
This is the same condition as given in the question; hence our consideration of both the masses having the same mass is correct. Hence, unknown mass is $m$.
Note:
Here we need to remember to break the velocity to its components.
The velocity component along the axis needs to be considered as per the axis, hence the y component of velocity for unknown mass is negative.
Step by step solution:

We know the proton’s mass is m having initial velocity u. Let’s consider the unknown mass as M and since it is at rest, its velocity is zero. After the collision the proton moves with velocity${ v }_{ 1 }$, making an angle ${ \theta }_{ 1 }$ with the horizontal. Similarly, M moves with velocity ${ v }_{ 2 }$ making an angle ${ \theta }_{ 2 }$ with the horizontal.
After collision, the velocity component of mass m will be divided into 2 components along the x and y axes, since it’s a vector quantity. We will call them ${ v }_{ 1x }$ and ${ v }_{ 1y }$ respectively.
${ v }_{ 1x }={ v }_{ 1 }\cos { { \theta }_{ 1 } }$ and ${ v }_{ 1y }={ v }_{ 1 }\sin { { \theta }_{ 1 } }$.
Similarly, the velocity components of ${ v }_{ 2 }$ will be divided into ${ v }_{ 2x }$ and ${ v }_{ 2y }$, for velocity components along x and y axes respectively.
${ v }_{ 2x }={ v }_{ 2 }\cos { { \theta }_{ 2 } }$ and ${ v }_{ 2y }={- v }_{ 2 }\sin { { \theta }_{ 2 } }$.
Let’s consider, both the masses are equal and try and see if we are getting the condition of ${ \theta }_{ 1 }$+${ \theta }_{ 2 }$=${ 90 }^{ 0 }$.
${ p }_{ x }$initial = ${ p }_{ x}$ final using conservation of momentum along the x axis.
$mu=m{ v }_{ 1 }\cos { { \theta }_{ 1 }+m{ v }_{ 2 }\cos { { \theta }_{ 2 } } }$
$u={{v}_{1}}\cos {{\theta }_{1}}+{{v}_{2}}\cos {{\theta }_{2}}\to (1)$
${ p }_{ y }$initial = ${ p }_{ y}$ final using conservation of momentum along the x axis.
$0+0={ v }_{ 1 }\sin { { \theta }_{ 1 }-{ v }_{ 2 }\sin { { \theta }_{ 2 } } }$
$0={{v}_{1}}\sin {{\theta }_{1}}-{{v}_{2}}\sin {{\theta }_{2}}\to (2)$
${ (1) }^{ 2 }+{ (2) }^{ 2 }$ gives us,
${ u }^{ 2 }={ ({ v }_{ 1 }\cos { { \theta }_{ 1 }+{ v }_{ 2 }\cos { { \theta }_{ 2 } } } ) }^{ 2 }+{ ({ v }_{ 1 }\sin{ { \theta }_{ 1 }-{ v }_{ 2 }\sin { { \theta }_{ 2 } } } ) }^{ 2 }$
${ u }^{ 2 }={ v }_{ 1 }^{ 2 }\cos ^{ 2 }{ { \theta }_{ 1 } } +{ v }_{ 2 }^{ 2 }\cos ^{ 2 }{ { \theta }_{ 2 } } +2{ v }_{ 1 }{ v }_{ 2 }\cos { { \theta }_{ 1 }\cos { { \theta }_{ 2 } } +{ v }_{ 1 }^{ 2 }\sin ^{ 2 }{ { \theta }_{ 1 } } +{ v }_{ 2 }^{ 2 }\sin ^{ 2 }{ { \theta }_{ 2 } } } -2{ v }_{ 1 }{ v }_{ 2 }\sin { { \theta }_{ 1 }\sin { { \theta }_{ 2 } } }$
${ u }^{ 2 }={ v }_{ 1 }^{ 2 }(\cos ^{ 2 }{ { \theta }_{ 1 } } +\sin ^{ 2 }{ { \theta }_{ 1 } } )+{ v }_{ 2 }^{ 2 }(\cos ^{ 2 }{ { \theta }_{ 2 } } \sin ^{ 2 }{ { \theta }_{ 2 } } )+2{ v }_{ 1 }{ v }_{ 2 }(\cos { { \theta }_{ 1 }\cos { { \theta }_{ 2 } } } -\sin { { \theta }_{ 1 }\sin { { \theta }_{ 2 }) } }$
${{u}^{2}}=v_{1}^{2}+v_{2}^{2}+2{{v}_{1}}{{v}_{2}}\cos ({{\theta }_{1}}+{{\theta }_{2}})\to (3)$
Now, using the conservation of kinetic energy formula:
${ \dfrac { 1 }{ 2 } mu }^{ 2 }=\dfrac { 1 }{ 2 } m{ v }_{ 1 }^{ 2 }+\dfrac { 1 }{ 2 } m{ v }_{ 2 }^{ 2 }$
Here, we don’t use the velocity components along each axis as Energy is a scalar quantity and direction component isn’t required.
${{u}^{2}}=v_{1}^{2}+_{2}^{2}\to (4)$
Comparing the equations (3) and (4), we get:
$2{ v }_{ 1 }{ v }_{ 2 }\cos { { (\theta }_{ 1 }+{ \theta }_{ 2 }) } =0$
$\cos { { (\theta }_{ 1 }+{ \theta }_{ 2 }) } =0$
As we know that $\cos { (\dfrac { n\pi }{ 2 } ) } =0$ for n= any integer except zero.
Considering the case for n=1, we get, ${ \theta }_{ 1 }+{ \theta }_{ 2 }=\dfrac { \pi }{ 2 }$
This is the same condition as given in the question; hence our consideration of both the masses having the same mass is correct. Hence, unknown mass is $m$.
Note:
Here we need to remember to break the velocity to its components.
The velocity component along the axis needs to be considered as per the axis, hence the y component of velocity for unknown mass is negative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




