
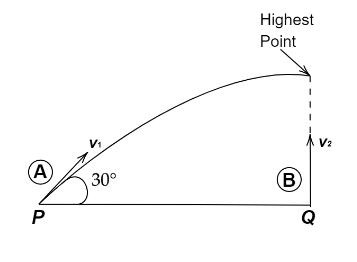
A projectile A is thrown at an angle of $30^\circ $ to the horizontal from point P. At the same time, another projectile B is thrown with velocity $v_2$ upwards from the point Q vertically below the highest point. For B to collide with A, $\dfrac{{v_2}}{{v_1}}$ should be
A. $1$
B. $2$
C. $\dfrac{1}{2}$
D. $4$

Answer
495k+ views
Hint:The projectile A is thrown at an angle hence we will get two compnet after rev;oving. Now as per the problem statement for A and B to collide the vertical velocity of the two particles initial vertical component must be equals so as to meet at a point at a particular time. After solving two step we can get the required ratio.
Complete step by step answer:
As per the given problem a projectile A is thrown at an angle of $30^\circ $ to the horizontal from point P. At the same time, another projectile B is thrown with velocity $v_2$ upwards from the point Q vertically below the highest point.We need to calculate the $\dfrac{{v_2}}{{v_1}}$ if the B collides with A.
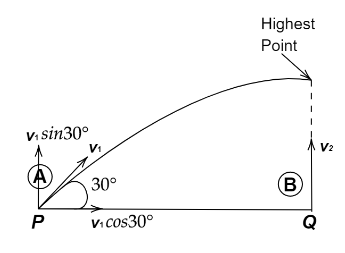
As the A is projected at an angle of $30^\circ $ then the velocity must be slipped into two compnet one is vertical and another is horizontal. $v_1$ is the velocity of A.
$v_1H = v_1\cos 30^\circ $
Where, $v_1H$ is the horizontal component of A.
$v_1V = v_1\sin 30^\circ $
Where, $v_1V$ is the vertical component of B.
And B is thrown with velocity $v_2$ upwards.Hence vertical velocity is the same as the projected velocity.
For A and B to collide , the initial vertical components of the velocities must be equal.
Equation velocities along the vertical we will get,
Vertical velocity of A= Vertical velocity of B
$v_1V = v_2$
Now putting the vertical component of A we will get,
$v_1\sin 30^\circ = v_2$
We know the value of $sin30 = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Now,
$v_1 \times \dfrac{1}{2} = v_2$
Now rearranging the equation we will get,
$\therefore \dfrac{{v_2}}{{v_1}} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Therefore the correct option is $\left( C \right)$.
Note:When two or more bodies collide then an event called collision takes place where these bodies exert force on each other in a short period of time. Remember that the horizontal component remains the same throughout the flight and hence the horizontal motion of a projectile is independent of its vertical motion.
Complete step by step answer:
As per the given problem a projectile A is thrown at an angle of $30^\circ $ to the horizontal from point P. At the same time, another projectile B is thrown with velocity $v_2$ upwards from the point Q vertically below the highest point.We need to calculate the $\dfrac{{v_2}}{{v_1}}$ if the B collides with A.

As the A is projected at an angle of $30^\circ $ then the velocity must be slipped into two compnet one is vertical and another is horizontal. $v_1$ is the velocity of A.
$v_1H = v_1\cos 30^\circ $
Where, $v_1H$ is the horizontal component of A.
$v_1V = v_1\sin 30^\circ $
Where, $v_1V$ is the vertical component of B.
And B is thrown with velocity $v_2$ upwards.Hence vertical velocity is the same as the projected velocity.
For A and B to collide , the initial vertical components of the velocities must be equal.
Equation velocities along the vertical we will get,
Vertical velocity of A= Vertical velocity of B
$v_1V = v_2$
Now putting the vertical component of A we will get,
$v_1\sin 30^\circ = v_2$
We know the value of $sin30 = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Now,
$v_1 \times \dfrac{1}{2} = v_2$
Now rearranging the equation we will get,
$\therefore \dfrac{{v_2}}{{v_1}} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Therefore the correct option is $\left( C \right)$.
Note:When two or more bodies collide then an event called collision takes place where these bodies exert force on each other in a short period of time. Remember that the horizontal component remains the same throughout the flight and hence the horizontal motion of a projectile is independent of its vertical motion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




