
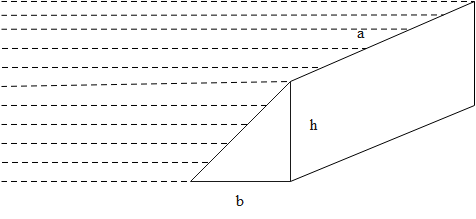
A prismatic bar of a given dimension is kept in water. Find the hydrostatic forces on the slant face.
\[\begin{align}
& (1)\,\rho gha\sqrt{{{b}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}} \\
& (2)\,\dfrac{\rho gh}{2}a\sqrt{{{b}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}} \\
& (3)\,\dfrac{\rho gh}{2}ah \\
& (4)\,\rho ghab \\
\end{align}\]

Answer
534.9k+ views
Hint: The pressure of a fluid exerts a force on the surface which comes in contact with the fluid. The force that gets distributed over the area will have the resultant magnitude and the direction. Thus, the force will be the product of pressure and area.
Formula used:
\[F=P\times A\]
Complete answer:
The pressure of a fluid exerts a force on the surface which comes in contact with the fluid. The force that gets distributed over the area will have the resultant magnitude and the direction.
The pressure of a fluid exerts thrust on each part of a surface with which the fluid made contact. Each force distributed over the area has a resultant magnitude and direction that is very crucial. In the case of a horizontal surface, over the plane, the pressure does not vary. So, the total force will be the product of the pressure and the area and its direction will be perpendicular to the plane. In the case of a surface that is not horizontal, the pressure will vary at each point of the surface. So, the calculation of the total thrust will be different.
\[\begin{align}
& F=P\times A \\
& \therefore F=\dfrac{\rho gh}{2}(ah) \\
\end{align}\]
Where \[\rho \]is the density of the liquid, h is the height, a and h are the sides of a rectangle.
\[\therefore \] The hydrostatic force on the slant face is \[\dfrac{\rho gh}{2}(ah)\].
Thus, option (3) is correct.
Note:
In the case of a horizontal surface, over the plane, the pressure does not vary. So, the total force will be the product of the pressure and the area and its direction will be perpendicular to the plane. In the case of a surface that is not horizontal, the pressure will vary at each point of the surface. So, the calculation of the total thrust will be different.
Formula used:
\[F=P\times A\]
Complete answer:
The pressure of a fluid exerts a force on the surface which comes in contact with the fluid. The force that gets distributed over the area will have the resultant magnitude and the direction.
The pressure of a fluid exerts thrust on each part of a surface with which the fluid made contact. Each force distributed over the area has a resultant magnitude and direction that is very crucial. In the case of a horizontal surface, over the plane, the pressure does not vary. So, the total force will be the product of the pressure and the area and its direction will be perpendicular to the plane. In the case of a surface that is not horizontal, the pressure will vary at each point of the surface. So, the calculation of the total thrust will be different.
\[\begin{align}
& F=P\times A \\
& \therefore F=\dfrac{\rho gh}{2}(ah) \\
\end{align}\]
Where \[\rho \]is the density of the liquid, h is the height, a and h are the sides of a rectangle.
\[\therefore \] The hydrostatic force on the slant face is \[\dfrac{\rho gh}{2}(ah)\].
Thus, option (3) is correct.
Note:
In the case of a horizontal surface, over the plane, the pressure does not vary. So, the total force will be the product of the pressure and the area and its direction will be perpendicular to the plane. In the case of a surface that is not horizontal, the pressure will vary at each point of the surface. So, the calculation of the total thrust will be different.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




