
A prism of refracting angle ${{60}^{\circ }}$ and refractive index 1.5 is immersed in water $\left( \mu =\dfrac{4}{3} \right)$. The angle of minimum deviation is
A. ${{8.6}^{\circ }}$
B. ${{4.2}^{\circ }}$
C. ${{30}^{\circ }}$
D. ${{4.8}^{\circ }}$
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: To solve the given problem, we must know the fact that the minimum deviation of a ray of light passing through a prism occurs when the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of emergence. We must also know that the formula for the angle of deviation. With this we can apply the Snell’s law and find the angle of minimum deviation.
Formula used:
$\delta =2i-A$
${{\mu }_{i}}\sin i={{\mu }_{r}}\sin r$
Complete step by step answer:
When a light ray passes through a prism, it gets deviated. The angle of deviation is given as $\delta =i+e-A$,
where ‘i’ is angle of incidence, ‘e’ is angle of emergence and A is the refracting angle of the prism.
When a light ray passes through a prism, the minimum deviation occurs if the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of emergence.
Angle of emergence is the angle that the emergent ray (light ray coming out of the prism) makes with the normal at the interface of the prism and the outer medium.
Let the.
Therefore, minimum deviation will occur when $i=e$. This is depicted in the figure given below.
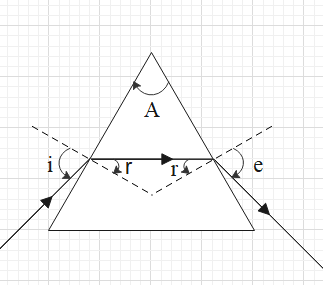
(self made)
This means that the minimum deviation is equal to $\delta =2i-A$ …. (i).
From the figure we get that $A=2r$.
And it is given that $A={{60}^{\circ }}$.
$\Rightarrow r=\dfrac{A}{2}=\dfrac{60}{2}={{30}^{\circ }}$
Now apply Snell’s law at the first interface. According to Snell’s law, ${{\mu }_{i}}\sin i={{\mu }_{r}}\sin r$ …..(ii),
where i, r are the angles of incidence and refraction, ${{\mu }_{i}}$ is the refractive index of the medium from which the light is incident and ${{\mu }_{r}}$ is the refractive index of the medium in which the light ray enters after refraction.
For the refraction at the first interface, ${{\mu }_{i}}=\dfrac{4}{3}$ and ${{\mu }_{r}}=1.5$.
Substitute the values of r, ${{\mu }_{i}}$ and ${{\mu }_{r}}$ in (ii).
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{3}\sin i=(1.5)\sin ({{30}^{\circ }})$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{3}\sin i=(1.5)(0.5)$
$\Rightarrow \sin i=\dfrac{9}{16}$
$\Rightarrow i={{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{9}{16} \right)={{34.3}^{\circ }}$.
Now, substitute the value of i and A in (i).
$\Rightarrow \delta =2({{34.3}^{\circ }})-{{60}^{\circ }}={{8.6}^{\circ }}$.
This means that the minimum deviation for the given prism is ${{8.6}^{\circ }}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
The above solution is the procedure to find the minimum deviation of a ray of light when it passes through a medium.
Other than this procedure, you can directly use the formula given below to find the minimum deviation.
i.e. $\mu =\dfrac{\sin \left( \dfrac{A+{{\delta }_{min}}}{2} \right)}{\sin \left( \dfrac{A}{2} \right)}$ .
Here, $\mu $ is the refractive index of the prism with respect to the surrounding medium (in this case, it is water).
Formula used:
$\delta =2i-A$
${{\mu }_{i}}\sin i={{\mu }_{r}}\sin r$
Complete step by step answer:
When a light ray passes through a prism, it gets deviated. The angle of deviation is given as $\delta =i+e-A$,
where ‘i’ is angle of incidence, ‘e’ is angle of emergence and A is the refracting angle of the prism.
When a light ray passes through a prism, the minimum deviation occurs if the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of emergence.
Angle of emergence is the angle that the emergent ray (light ray coming out of the prism) makes with the normal at the interface of the prism and the outer medium.
Let the.
Therefore, minimum deviation will occur when $i=e$. This is depicted in the figure given below.

(self made)
This means that the minimum deviation is equal to $\delta =2i-A$ …. (i).
From the figure we get that $A=2r$.
And it is given that $A={{60}^{\circ }}$.
$\Rightarrow r=\dfrac{A}{2}=\dfrac{60}{2}={{30}^{\circ }}$
Now apply Snell’s law at the first interface. According to Snell’s law, ${{\mu }_{i}}\sin i={{\mu }_{r}}\sin r$ …..(ii),
where i, r are the angles of incidence and refraction, ${{\mu }_{i}}$ is the refractive index of the medium from which the light is incident and ${{\mu }_{r}}$ is the refractive index of the medium in which the light ray enters after refraction.
For the refraction at the first interface, ${{\mu }_{i}}=\dfrac{4}{3}$ and ${{\mu }_{r}}=1.5$.
Substitute the values of r, ${{\mu }_{i}}$ and ${{\mu }_{r}}$ in (ii).
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{3}\sin i=(1.5)\sin ({{30}^{\circ }})$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{3}\sin i=(1.5)(0.5)$
$\Rightarrow \sin i=\dfrac{9}{16}$
$\Rightarrow i={{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{9}{16} \right)={{34.3}^{\circ }}$.
Now, substitute the value of i and A in (i).
$\Rightarrow \delta =2({{34.3}^{\circ }})-{{60}^{\circ }}={{8.6}^{\circ }}$.
This means that the minimum deviation for the given prism is ${{8.6}^{\circ }}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
The above solution is the procedure to find the minimum deviation of a ray of light when it passes through a medium.
Other than this procedure, you can directly use the formula given below to find the minimum deviation.
i.e. $\mu =\dfrac{\sin \left( \dfrac{A+{{\delta }_{min}}}{2} \right)}{\sin \left( \dfrac{A}{2} \right)}$ .
Here, $\mu $ is the refractive index of the prism with respect to the surrounding medium (in this case, it is water).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 12 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Complete reduction of benzene diazonium chloride with class 12 chemistry CBSE

How can you identify optical isomers class 12 chemistry CBSE

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE




