
A pole has to be erected at a point on the boundary of a circular park of diameter 17 metre in such a way that the difference of its distance from two diametrically opposite in fixed gates A and B on the boundary is 7 metres. Is it possible to do so? Yes, at what distance from the two gates should the pole be erected?
Answer
615k+ views
Hint- Here we will proceed by assuming the position of pole, opposite fixed gates as variables. Then we will use Pythagoras theorem i.e. ${\left( {hypotenuse} \right)^2} = {\left( {base} \right)^2} + {\left( {perpendicular} \right)^2}$ such that we get the distance from both the gates to pole.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Formula of Pythagoras theorem- ${\left( {hypotenuse} \right)^2} = {\left( {base} \right)^2} + {\left( {perpendicular} \right)^2}$
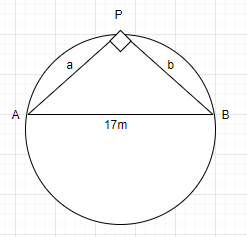
Let us assume,
P be the position of the pole, A and B be the opposite fixed gates.
Also we are given that the difference from two diametrically opposite in fixed gates is 7 metres
$ \Rightarrow $ PA-PB=7m
Or a-b=7
Or a=7+b ……………… (1)
Now in PAB,
$ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = A{P^2} + B{P^2}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {17} \right) = {\left( a \right)^2} + \left( {{b^2}} \right)$
Or ${a^2} + {b^2} = 289$
Putting the value of a=7 + b in the above,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {7 + b} \right)^2} + {b^2} = 289$
Or $49 + 14b + 2{b^2} = 289$
Or $2{b^2} + 14b + 49 - 289 = 0$
Or $2{b^2} + 14b - 240 = 0$
Dividing the above by 2, we get
$ \Rightarrow {b^2} + 7b - 120 = 0$
Or ${b^2} + 15b - 8b - 120 = 0$
Or $b\left( {b + 15} \right) - 8\left( {b + 15} \right) = 0$
Or $\left( {b - 8} \right)\left( {b + 15} \right) = 0$
Either b = 8 or b = -15
Since this value cannot be negative, so b = 8 is the correct value.
Now putting b = 8 in equation 1,
We get
a = 7 + 8
a = 15
Hence PA = 15m and PB = 8m
So, the distance from gate A to pole is 15m and from gate B to the pole is 8m.
Note – We can also verify this answer using the Pythagoras theorem i.e. $A{B^2} = A{P^2} + B{P^2}$where we will put the values of AB, AP and BP so that LHS=RHS. This implies that the above calculated answer is right.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Formula of Pythagoras theorem- ${\left( {hypotenuse} \right)^2} = {\left( {base} \right)^2} + {\left( {perpendicular} \right)^2}$

Let us assume,
P be the position of the pole, A and B be the opposite fixed gates.
Also we are given that the difference from two diametrically opposite in fixed gates is 7 metres
$ \Rightarrow $ PA-PB=7m
Or a-b=7
Or a=7+b ……………… (1)
Now in PAB,
$ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = A{P^2} + B{P^2}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {17} \right) = {\left( a \right)^2} + \left( {{b^2}} \right)$
Or ${a^2} + {b^2} = 289$
Putting the value of a=7 + b in the above,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {7 + b} \right)^2} + {b^2} = 289$
Or $49 + 14b + 2{b^2} = 289$
Or $2{b^2} + 14b + 49 - 289 = 0$
Or $2{b^2} + 14b - 240 = 0$
Dividing the above by 2, we get
$ \Rightarrow {b^2} + 7b - 120 = 0$
Or ${b^2} + 15b - 8b - 120 = 0$
Or $b\left( {b + 15} \right) - 8\left( {b + 15} \right) = 0$
Or $\left( {b - 8} \right)\left( {b + 15} \right) = 0$
Either b = 8 or b = -15
Since this value cannot be negative, so b = 8 is the correct value.
Now putting b = 8 in equation 1,
We get
a = 7 + 8
a = 15
Hence PA = 15m and PB = 8m
So, the distance from gate A to pole is 15m and from gate B to the pole is 8m.
Note – We can also verify this answer using the Pythagoras theorem i.e. $A{B^2} = A{P^2} + B{P^2}$where we will put the values of AB, AP and BP so that LHS=RHS. This implies that the above calculated answer is right.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




