
A pole 6m high casts a shadow \[2\sqrt{3}\text{ m}\] long on the ground then finds the sun’s elevation.
Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: First of all, we should illustrate the situation in the form of a diagram. Let us assume that the length of the pole is AB. We know that a pole will be vertical. Let us assume the length of the pole is AC. The angle \[\theta \] represents the elevation of the sun. We know that according to Pythagora's theorem is “In a right-angle triangle, the sum of squares of lengths of two sides is equal to hypotenuse of that triangle”. So, by applying this theorem we will get the value of BC. We know that the \[\sin \theta \] is the ratio of opposite side and hypotenuse. Now by using this concept, we will find \[\sin \theta \]. By using this \[\sin \theta \], we will get the value of \[\theta \].
Complete step-by-step answer:
Before solving the problem, we should illustrate the situation. In the question, it was given that a pole 6m high casts a shadow \[2\sqrt{3}\text{ m}\]long on the ground. Let us assume that the length of the pole is AB. We know that a pole will be vertical. Let us assume the length of the pole is AC. The angle \[\theta \] represents the elevation of the sun.
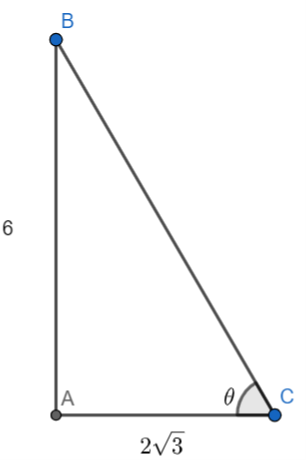
From the \[\Delta ABC\], we can say that
\[\begin{align}
& AC=2\sqrt{3}....(1) \\
& AB=6....(2) \\
\end{align}\]
We know that according to Pythagoras theorem is “In a right-angle triangle, the sum of squares of lengths of two sides is equal to hypotenuse of that triangle”.
So, by applying Pythagoras theorem, we get
\[A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}}=B{{C}^{2}}.....(3)\]
Now we will substitute equation (1) and equation (2) in equation (3).
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow B{{C}^{2}}=12+36 \\
& \Rightarrow B{{C}^{2}}=48 \\
& \Rightarrow BC=4\sqrt{3}....(4) \\
\end{align}\]
From the \[\Delta ABC\], we get
\[\Rightarrow \sin \theta =\dfrac{AB}{BC}....(5)\]
Now we will substitute equation (1) and equation (4) in equation (5), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \sin \theta =\dfrac{6}{4\sqrt{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow \sin \theta =\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \theta =60 \\
\end{align}\]
So, the angle of elevation of the sun is equal to 60.
Note: Students may undergo calculation mistakes while solving this question.
If we write
\[\Rightarrow \sin \theta =\dfrac{AC}{BC}.....(1)\]
From the diagram, we get
\[\begin{align}
& AC=2\sqrt{3}....(2) \\
& AB=6....(3) \\
\end{align}\]
Now we will substitute equation (2) and equation (3) in equation (1).
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \sin \theta =\dfrac{2\sqrt{3}}{4\sqrt{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow \sin \theta =\dfrac{1}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \theta =30 \\
\end{align}\]
So, we get the angle of elevation of the sun is equal to 30.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Before solving the problem, we should illustrate the situation. In the question, it was given that a pole 6m high casts a shadow \[2\sqrt{3}\text{ m}\]long on the ground. Let us assume that the length of the pole is AB. We know that a pole will be vertical. Let us assume the length of the pole is AC. The angle \[\theta \] represents the elevation of the sun.

From the \[\Delta ABC\], we can say that
\[\begin{align}
& AC=2\sqrt{3}....(1) \\
& AB=6....(2) \\
\end{align}\]
We know that according to Pythagoras theorem is “In a right-angle triangle, the sum of squares of lengths of two sides is equal to hypotenuse of that triangle”.
So, by applying Pythagoras theorem, we get
\[A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}}=B{{C}^{2}}.....(3)\]
Now we will substitute equation (1) and equation (2) in equation (3).
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow B{{C}^{2}}=12+36 \\
& \Rightarrow B{{C}^{2}}=48 \\
& \Rightarrow BC=4\sqrt{3}....(4) \\
\end{align}\]
From the \[\Delta ABC\], we get
\[\Rightarrow \sin \theta =\dfrac{AB}{BC}....(5)\]
Now we will substitute equation (1) and equation (4) in equation (5), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \sin \theta =\dfrac{6}{4\sqrt{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow \sin \theta =\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \theta =60 \\
\end{align}\]
So, the angle of elevation of the sun is equal to 60.
Note: Students may undergo calculation mistakes while solving this question.
If we write
\[\Rightarrow \sin \theta =\dfrac{AC}{BC}.....(1)\]
From the diagram, we get
\[\begin{align}
& AC=2\sqrt{3}....(2) \\
& AB=6....(3) \\
\end{align}\]
Now we will substitute equation (2) and equation (3) in equation (1).
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \sin \theta =\dfrac{2\sqrt{3}}{4\sqrt{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow \sin \theta =\dfrac{1}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \theta =30 \\
\end{align}\]
So, we get the angle of elevation of the sun is equal to 30.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




