
A pole 5 m high is fixed on the top of a tower. The angle of elevation of the top the pole observed from a point A on the ground is $ 60{}^\circ $ and the angle of depression of the point A from the top of the tower is $ 45{}^\circ $. Find the height of the tower.
Answer
602.1k+ views
Hint: First we draw a diagram by using the information given that a pole 5 m high is fixed on the top of a tower. The angle of elevation of the top the pole observed from a point A on the ground is $ 60{}^\circ $ and the angle of depression of the point A from the top of the tower is $ 45{}^\circ $ . Let us assume the height of the tower is $ x $. By using trigonometric ratio property we solve the question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have given that a pole 5 m high is fixed on the top of a tower. The angle of elevation of the top the pole observed from a point A on the ground is $ 60{}^\circ $ and the angle of depression of the point A from the top of the tower is $ 45{}^\circ $ .
We have to find the height of the tower.
First we draw a diagram assuming a point of observation A at the ground.
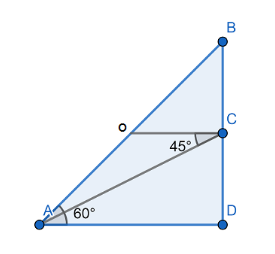
We have given that height of pole is $ 5\text{ m} $ . i.e. $ BC=5m $
Let us assume the height of tower is $ x $ , i.e. $ CD=x $.
Also, we have given angle of elevation $ \angle BAC=60{}^\circ $ and angle of depression $ \angle ACO=45{}^\circ $.
First let us consider right –angled triangle $ \Delta ADB $ ,
We know that $ \tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Base}} $
We have $ \theta =60{}^\circ $ as given in the question, angle of elevation.
When we substitute the values, we get
$ \begin{align}
& \tan 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{BD}{AD} \\
& \tan 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{x+5}{AD} \\
\end{align} $
We know that $ \tan 60{}^\circ =\sqrt{3} $ , so substitute the value we get
$ \begin{align}
& \sqrt{3}=\dfrac{x+5}{AD} \\
& \sqrt{3}AD=x+5 \\
& AD=\dfrac{x+5}{\sqrt{3}}................(i) \\
\end{align} $
Now, consider right –angled triangle $ \Delta ADC $ ,
We know that $ \tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Base}} $
Now, from the diagram we have $ \angle OCD=90{}^\circ $
Also,
$ \begin{align}
& \angle OCD=\angle ACD+\angle ACO \\
& 90{}^\circ =\angle ACD+45{}^\circ \\
& \angle ACD=45{}^\circ \\
\end{align} $
So, we have $ \theta =45{}^\circ $
When we substitute the values, we get
$ \begin{align}
& \tan 45{}^\circ =\dfrac{AD}{CD} \\
& \tan 45{}^\circ =\dfrac{AD}{x} \\
\end{align} $
We know that $ \tan 45{}^\circ =1 $
$ \begin{align}
& 1=\dfrac{AD}{x} \\
& AD=x.......(ii) \\
\end{align} $
When we put the value of $ AD $ from equation (i), we get
$ \begin{align}
& \dfrac{x+5}{\sqrt{3}}=x \\
& x+5=\sqrt{3}x \\
\end{align} $
We know that $ \left( \sqrt{3}=1.732 \right) $ ,
$ \begin{align}
& x+5=1.732x \\
& 5=1.732x-x \\
& 5=0.732x \\
& x=\dfrac{5}{0.732} \\
& x=6.83m \\
\end{align} $
Height of the tower is $ 6.83m $.
Note: The key concept to solve this type of questions is the use of trigonometric angle properties. Also, in this type of questions first draw a diagram using the information given in the question. Always assume the point of observation on the ground. These points help to solve the question easily and we will get the correct answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have given that a pole 5 m high is fixed on the top of a tower. The angle of elevation of the top the pole observed from a point A on the ground is $ 60{}^\circ $ and the angle of depression of the point A from the top of the tower is $ 45{}^\circ $ .
We have to find the height of the tower.
First we draw a diagram assuming a point of observation A at the ground.

We have given that height of pole is $ 5\text{ m} $ . i.e. $ BC=5m $
Let us assume the height of tower is $ x $ , i.e. $ CD=x $.
Also, we have given angle of elevation $ \angle BAC=60{}^\circ $ and angle of depression $ \angle ACO=45{}^\circ $.
First let us consider right –angled triangle $ \Delta ADB $ ,
We know that $ \tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Base}} $
We have $ \theta =60{}^\circ $ as given in the question, angle of elevation.
When we substitute the values, we get
$ \begin{align}
& \tan 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{BD}{AD} \\
& \tan 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{x+5}{AD} \\
\end{align} $
We know that $ \tan 60{}^\circ =\sqrt{3} $ , so substitute the value we get
$ \begin{align}
& \sqrt{3}=\dfrac{x+5}{AD} \\
& \sqrt{3}AD=x+5 \\
& AD=\dfrac{x+5}{\sqrt{3}}................(i) \\
\end{align} $
Now, consider right –angled triangle $ \Delta ADC $ ,
We know that $ \tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Base}} $
Now, from the diagram we have $ \angle OCD=90{}^\circ $
Also,
$ \begin{align}
& \angle OCD=\angle ACD+\angle ACO \\
& 90{}^\circ =\angle ACD+45{}^\circ \\
& \angle ACD=45{}^\circ \\
\end{align} $
So, we have $ \theta =45{}^\circ $
When we substitute the values, we get
$ \begin{align}
& \tan 45{}^\circ =\dfrac{AD}{CD} \\
& \tan 45{}^\circ =\dfrac{AD}{x} \\
\end{align} $
We know that $ \tan 45{}^\circ =1 $
$ \begin{align}
& 1=\dfrac{AD}{x} \\
& AD=x.......(ii) \\
\end{align} $
When we put the value of $ AD $ from equation (i), we get
$ \begin{align}
& \dfrac{x+5}{\sqrt{3}}=x \\
& x+5=\sqrt{3}x \\
\end{align} $
We know that $ \left( \sqrt{3}=1.732 \right) $ ,
$ \begin{align}
& x+5=1.732x \\
& 5=1.732x-x \\
& 5=0.732x \\
& x=\dfrac{5}{0.732} \\
& x=6.83m \\
\end{align} $
Height of the tower is $ 6.83m $.
Note: The key concept to solve this type of questions is the use of trigonometric angle properties. Also, in this type of questions first draw a diagram using the information given in the question. Always assume the point of observation on the ground. These points help to solve the question easily and we will get the correct answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




