
A point source of light is placed at a distance of $2f$ from a converging lens of focal length $f$. The intensity on the other side of the lens is maximum at a distance _ _ _ _ _ _.
A. $f$
B. Between $f$ and $2f$
C. $2f$
D. More than $2f$
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: Draw the proper diagram and use a mirror formula to calculate the answer. Also we have to remember the mirror formula.
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{u} + \dfrac{1}{v}$ where f is the focal length, u is the object distance and v is the image distance.
Complete step by step answer:
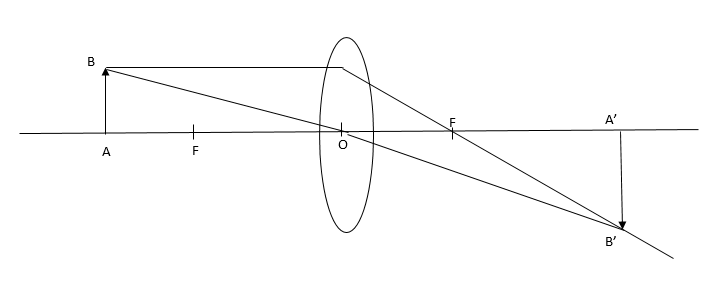
Converging lens is formed by joining two convex lenses of the same force length.
Converging lens helps to sharpen images close to the total length. If the object and the image are on the same side, then image is ritual. And if the object image is on the opposite side, then the image is red.
Sign conversion of converging lens. For converging lenses, focal length is always positive.
If the object and image are on the same side, then image distance is negative.
If the object and image are on the opposite side, then image distance is positive.
$\therefore $In the given diagram.
Object distance $ = + 2f$
Focal length$ = + f$
New, according to minor formula,
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{u} + \dfrac{1}{v}$
Where, $f$is the focal length
$u$is the object distance
$v$is image distance
By substituting the values in the above equation, we get
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{{2f}} + \dfrac{1}{v}$
By rearranging the above equation, we get
$\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{f} - \dfrac{1}{{2f}}$
$ = \dfrac{{2 - 1}}{{2f}}$ (By taking LCM and cross multiplying)
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{{2f}}$
By taking reciprocal, we get
$v = 2f$
Therefore, the image will be formed at $0$ distance $2f$ from the converging lens.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
The sign conversion for convex lens, converging lens and diverging lens differ a little. You should be careful while applying sign conversion. Do not mix them up.
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{u} + \dfrac{1}{v}$ where f is the focal length, u is the object distance and v is the image distance.
Complete step by step answer:

Converging lens is formed by joining two convex lenses of the same force length.
Converging lens helps to sharpen images close to the total length. If the object and the image are on the same side, then image is ritual. And if the object image is on the opposite side, then the image is red.
Sign conversion of converging lens. For converging lenses, focal length is always positive.
If the object and image are on the same side, then image distance is negative.
If the object and image are on the opposite side, then image distance is positive.
$\therefore $In the given diagram.
Object distance $ = + 2f$
Focal length$ = + f$
New, according to minor formula,
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{u} + \dfrac{1}{v}$
Where, $f$is the focal length
$u$is the object distance
$v$is image distance
By substituting the values in the above equation, we get
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{{2f}} + \dfrac{1}{v}$
By rearranging the above equation, we get
$\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{f} - \dfrac{1}{{2f}}$
$ = \dfrac{{2 - 1}}{{2f}}$ (By taking LCM and cross multiplying)
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{{2f}}$
By taking reciprocal, we get
$v = 2f$
Therefore, the image will be formed at $0$ distance $2f$ from the converging lens.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
The sign conversion for convex lens, converging lens and diverging lens differ a little. You should be careful while applying sign conversion. Do not mix them up.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




