
A point source of light at the surface of a sphere causes a parallel beam of light to emerge from the opposite surface of the sphere. The refractive index of the material of the sphere is:
A) 5
B) $\dfrac{5}{3}$
C) 2
D) 2.5
Answer
579k+ views
Hint: As the beams were parallel therefore the image will be formed at infinity the distance of the source is 2R as the source is on the opposite side of the sphere. The outer environment has air therefore the refractive index will be equal to 1.
Formula used:
The formula for the mirror having different refractive index on both the sides is given by,
$\dfrac{{{\mu _2}}}{v} - \dfrac{{{\mu _1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2} - {\mu _1}}}{R}$
Where $u$is the object distance $v$ is the image distance ${\mu _1}$ is the refractive index of the mirror and ${\mu _2}$ is the refractive index of the other material.
Complete step by step answer:
It is given that there is a point source of light at the surface of a sphere that causes a parallel beam of light to emerge from the opposite surface of the sphere and we need to find the refractive index of the sphere.
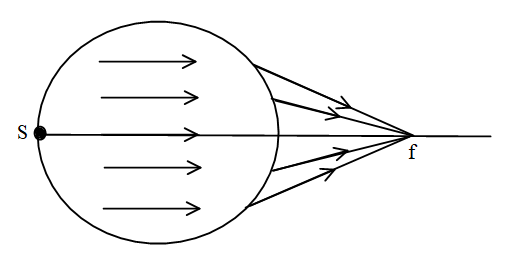
The source is represented as S and the focus is represented by f.
As the formula of the refractive index involving different refractive index is given by,
$\dfrac{{{\mu _2}}}{v} - \dfrac{{{\mu _1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2} - {\mu _1}}}{R}$
Where $u$ is the object distance $v$ is the image distance ${\mu _1}$ is the refractive index of the mirror and ${\mu _2}$ is the refractive index of the other material.
Here as the source is coming from the other side of the sphere therefore the object distance will be,
$u = - 2R$.
Since the beam has parallel rays therefore the image will be formed at the infinity that means that the image distance is equal to,
$v = \infty $.
The radius of the sphere is equal to $ - R$.
Applying the formula we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\mu _2}}}{v} - \dfrac{{{\mu _1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2} - {\mu _1}}}{R}$
The image distance is infinity also the refractive index of air is 1 and the refractive index of the sphere is ${\mu _1} = \mu $.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{\infty } - \dfrac{\mu }{{ - 2R}} = \dfrac{{1 - \mu }}{{ - R}}$
On simplification,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\mu }{{2R}} = \dfrac{{1 - \mu }}{{ - R}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\mu }{{2R}} = \dfrac{{\mu - 1}}{R}$
On further simplification,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\mu }{2} = \mu - 1$
$ \Rightarrow \mu = 2\left( {\mu - 1} \right)$
Solving for $\mu $
$ \Rightarrow \mu = 2\mu - 2$
$ \Rightarrow \mu = 2$.
The refractive index of the sphere is $\mu = 2$. The correct option is option C.
Note:
The object source is on the other side of the sphere therefore the sign of the object distance is negative also the radius of the sphere is taken as negative as the source is on the other side of the surface.
Formula used:
The formula for the mirror having different refractive index on both the sides is given by,
$\dfrac{{{\mu _2}}}{v} - \dfrac{{{\mu _1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2} - {\mu _1}}}{R}$
Where $u$is the object distance $v$ is the image distance ${\mu _1}$ is the refractive index of the mirror and ${\mu _2}$ is the refractive index of the other material.
Complete step by step answer:
It is given that there is a point source of light at the surface of a sphere that causes a parallel beam of light to emerge from the opposite surface of the sphere and we need to find the refractive index of the sphere.

The source is represented as S and the focus is represented by f.
As the formula of the refractive index involving different refractive index is given by,
$\dfrac{{{\mu _2}}}{v} - \dfrac{{{\mu _1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2} - {\mu _1}}}{R}$
Where $u$ is the object distance $v$ is the image distance ${\mu _1}$ is the refractive index of the mirror and ${\mu _2}$ is the refractive index of the other material.
Here as the source is coming from the other side of the sphere therefore the object distance will be,
$u = - 2R$.
Since the beam has parallel rays therefore the image will be formed at the infinity that means that the image distance is equal to,
$v = \infty $.
The radius of the sphere is equal to $ - R$.
Applying the formula we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\mu _2}}}{v} - \dfrac{{{\mu _1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2} - {\mu _1}}}{R}$
The image distance is infinity also the refractive index of air is 1 and the refractive index of the sphere is ${\mu _1} = \mu $.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{\infty } - \dfrac{\mu }{{ - 2R}} = \dfrac{{1 - \mu }}{{ - R}}$
On simplification,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\mu }{{2R}} = \dfrac{{1 - \mu }}{{ - R}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\mu }{{2R}} = \dfrac{{\mu - 1}}{R}$
On further simplification,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\mu }{2} = \mu - 1$
$ \Rightarrow \mu = 2\left( {\mu - 1} \right)$
Solving for $\mu $
$ \Rightarrow \mu = 2\mu - 2$
$ \Rightarrow \mu = 2$.
The refractive index of the sphere is $\mu = 2$. The correct option is option C.
Note:
The object source is on the other side of the sphere therefore the sign of the object distance is negative also the radius of the sphere is taken as negative as the source is on the other side of the surface.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




