
A point on the line $3x + 5y = 15$and equidistant from the coordinate axis, lies in:
A) None of the quadrants
B) Quadrants I and II only
C) Quadrant I only
D) Quadrants I, II and III only
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint:
A point on the line $3x + 5y = 15$ which is equidistant from the coordinate axis, which means the values of $x$ and $y$ are equal regardless of its sign, i.e. $\left| x \right| = \left| y \right|$, there can be two possible quadrants in which both the point and line justifies the question.
Complete step by step solution:
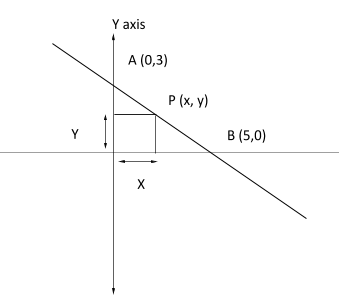
Now, as per the question a point on the line $3x + 5y = 15$which is equidistant from the coordinate axis (X axis and Y axis are called coordinate axis), The line cuts the coordinate axis at $A(0,3)$and $B(5,0)$, and a point $p(x,y)$which is equidistant from the coordinate axis.
As per the diagram above there is no chance that the point will be in the IIIrd quadrant
So, the point $p(x,y)$ are, for $\left| x \right| = \left| y \right|$
When, $x = y$
$
\Rightarrow 3x + 5y = 15 \\
\Rightarrow 3x + 5x = 15 \\
\Rightarrow 8x = 15 \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{15}}{8} \\
So,p(x,y) = p\left( {\dfrac{{15}}{8},\dfrac{{15}}{8}} \right).........(1) \\
$
And when $x = - y\left( {or} \right) - x = y$
$
\Rightarrow 3x + 5y = 15 \\
\Rightarrow 3x + 5( - x) = 15 \\
\Rightarrow 3x - 5x = 15 \\
\Rightarrow - 2x = 15 \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{ - 15}}{2} \\
so, p(x,y) = p\left( {\dfrac{{ - 15}}{2},\dfrac{{15}}{2}} \right).........\left( 2 \right) \\
$
So, from (1) and (2) we can conclude that point $p(x,y)$ lies in quadrant I and II.
Hence, option (B) is correct.
Note:
Before starting the question, draw a graph of the line and at which points it cuts the coordinate axis, you will get a clear idea in which quadrant the points may lie.
A point on the line $3x + 5y = 15$ which is equidistant from the coordinate axis, which means the values of $x$ and $y$ are equal regardless of its sign, i.e. $\left| x \right| = \left| y \right|$, there can be two possible quadrants in which both the point and line justifies the question.
Complete step by step solution:

Now, as per the question a point on the line $3x + 5y = 15$which is equidistant from the coordinate axis (X axis and Y axis are called coordinate axis), The line cuts the coordinate axis at $A(0,3)$and $B(5,0)$, and a point $p(x,y)$which is equidistant from the coordinate axis.
As per the diagram above there is no chance that the point will be in the IIIrd quadrant
So, the point $p(x,y)$ are, for $\left| x \right| = \left| y \right|$
When, $x = y$
$
\Rightarrow 3x + 5y = 15 \\
\Rightarrow 3x + 5x = 15 \\
\Rightarrow 8x = 15 \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{15}}{8} \\
So,p(x,y) = p\left( {\dfrac{{15}}{8},\dfrac{{15}}{8}} \right).........(1) \\
$
And when $x = - y\left( {or} \right) - x = y$
$
\Rightarrow 3x + 5y = 15 \\
\Rightarrow 3x + 5( - x) = 15 \\
\Rightarrow 3x - 5x = 15 \\
\Rightarrow - 2x = 15 \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{ - 15}}{2} \\
so, p(x,y) = p\left( {\dfrac{{ - 15}}{2},\dfrac{{15}}{2}} \right).........\left( 2 \right) \\
$
So, from (1) and (2) we can conclude that point $p(x,y)$ lies in quadrant I and II.
Hence, option (B) is correct.
Note:
Before starting the question, draw a graph of the line and at which points it cuts the coordinate axis, you will get a clear idea in which quadrant the points may lie.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




