
A point object of mass m is kept at (a,0) along x-axis. What mass should be kept at (-3a,0), so that center of mass lies at origin?
Answer
516.9k+ views
Hint: Given that a point object of mass m is kept at (a,0) along x-axis. Then using the equation of centre of mass equate that the centre of mass along the x-axis equal to zero. Then substitute the distance a, 3a and mass m in the equation of centre of mass we will get mass ${{m}_{1}}$such that the center of mass lies at origin.
Formula used:
The centre of mass is given by the equation,
${{x}_{CM}}=\sum\limits_{i}{\dfrac{{{m}_{i}}{{x}_{i}}}{M}}$
Where, M is the total mass of the system.
${{m}_{i}}$is the mass of an individual particle and ${{x}_{i}}$is the corresponding distance.
Complete step-by-step solution: -
A point object of mass m is kept at (a,0). Let the new mass be kept at (-3a,0) be \[{{m}_{1}}\].
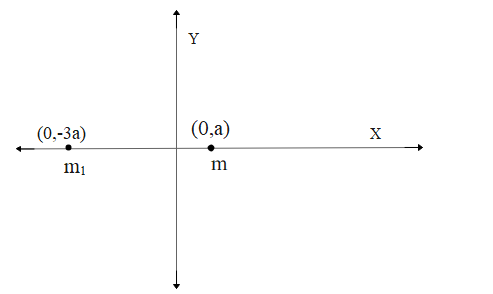
Then the centre of mass at origin is,
$\begin{align}
& {{x}_{CM}}=0 \\
& {{y}_{CM}}=0 \\
\end{align}$
${{x}_{CM}}=0=\dfrac{{{m}_{1}}{{x}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{x}_{2}}}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}$
${{m}_{1}}{{x}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{x}_{2}}=0$
$m\times a+{{m}_{1}}\times \left( -3a \right)=0$
$ma=3{{m}_{1}}a$
${{m}_{1}}=\dfrac{m}{3}$
Therefore to lie the center of mass lies at origin the mass $\dfrac{m}{3}$ should be kept at
(-3a,0).
Note: The centre of mass of a body can be defined as the point in which the whole mass of the body is concentrated. Thus for a system of particles this point where whole mass is concentrated is called the centre of mass. For calculation in mechanics which involve masses the concept of centre of mass is very useful. And also in orbital mechanics the point mass which is located in the centre of mass is used for forming the equations of motion.
Formula used:
The centre of mass is given by the equation,
${{x}_{CM}}=\sum\limits_{i}{\dfrac{{{m}_{i}}{{x}_{i}}}{M}}$
Where, M is the total mass of the system.
${{m}_{i}}$is the mass of an individual particle and ${{x}_{i}}$is the corresponding distance.
Complete step-by-step solution: -
A point object of mass m is kept at (a,0). Let the new mass be kept at (-3a,0) be \[{{m}_{1}}\].

Then the centre of mass at origin is,
$\begin{align}
& {{x}_{CM}}=0 \\
& {{y}_{CM}}=0 \\
\end{align}$
${{x}_{CM}}=0=\dfrac{{{m}_{1}}{{x}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{x}_{2}}}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}$
${{m}_{1}}{{x}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{x}_{2}}=0$
$m\times a+{{m}_{1}}\times \left( -3a \right)=0$
$ma=3{{m}_{1}}a$
${{m}_{1}}=\dfrac{m}{3}$
Therefore to lie the center of mass lies at origin the mass $\dfrac{m}{3}$ should be kept at
(-3a,0).
Note: The centre of mass of a body can be defined as the point in which the whole mass of the body is concentrated. Thus for a system of particles this point where whole mass is concentrated is called the centre of mass. For calculation in mechanics which involve masses the concept of centre of mass is very useful. And also in orbital mechanics the point mass which is located in the centre of mass is used for forming the equations of motion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




