
A point object is enclosed in a glass sphere of 8 cm radius. It is situated 2 cm from centre and is viewed from the side to which it is nearer. Where will it appear to be if μ of glass = 1.5?
A. 6 cm from the centre.
B. 4 cm from the nearer surface.
C.16/3 cm from the nearer surface.
D. 11/3 cm from the centre.
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: When light travels from one medium to the other medium, it changes its path due to the difference of densities in the two mediums. A convention term called refractive index relates the refraction of light from one medium to the other medium.
Complete step by step answer:
Refer to the figure given below.
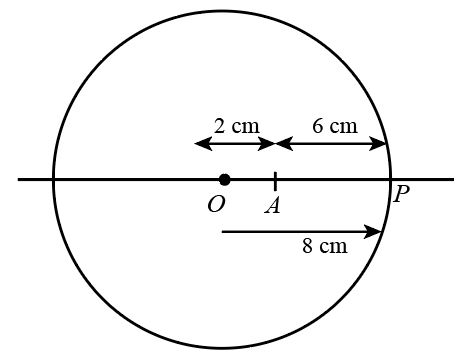
According to the sign convention the data are given as:
The refractive index of the glass is ${\mu _1} = 1.5$.
The refractive index of the air is ${\mu _2} = 1$.
The radius of the sphere is $R = - 8\;{\rm{cm}}$.
The object distance is $u = - 6\;{\rm{cm}}$
The object is situated at point A which is 6cm from the nearby surface point P.
Express the relation for spherical lenses.
$\dfrac{{{\mu _2}}}{v} - \dfrac{{{\mu _1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2} - {\mu _1}}}{R}$
Here, v is the distance of image from the surface point P.
Substitute ${\mu _1} = 1.5$, ${\mu _2} = 1$, $R = - 8\;{\rm{cm}}$, $u = - 6\;{\rm{cm}}$ to find the value of v.
\[\begin{array}{l}
\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{{1.5}}{{6\;{\rm{cm}}}} = \dfrac{{1 - 1.5}}{{ - 8\,{\rm{cm}}}}\\
v = - \dfrac{{16}}{3}\;{\rm{cm}}
\end{array}\]
Note:
he definition of the refractive index can also be told as the ratio of the speed of light in vacuum to the speed of light in another medium may be water, glass etc. and it is represented as:
$\mu = \dfrac{c}{v}$
Here, $\mu $ is the refractive index, c is the speed of light in vacuum and v is the speed of light in the medium.
Complete step by step answer:
Refer to the figure given below.

According to the sign convention the data are given as:
The refractive index of the glass is ${\mu _1} = 1.5$.
The refractive index of the air is ${\mu _2} = 1$.
The radius of the sphere is $R = - 8\;{\rm{cm}}$.
The object distance is $u = - 6\;{\rm{cm}}$
The object is situated at point A which is 6cm from the nearby surface point P.
Express the relation for spherical lenses.
$\dfrac{{{\mu _2}}}{v} - \dfrac{{{\mu _1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2} - {\mu _1}}}{R}$
Here, v is the distance of image from the surface point P.
Substitute ${\mu _1} = 1.5$, ${\mu _2} = 1$, $R = - 8\;{\rm{cm}}$, $u = - 6\;{\rm{cm}}$ to find the value of v.
\[\begin{array}{l}
\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{{1.5}}{{6\;{\rm{cm}}}} = \dfrac{{1 - 1.5}}{{ - 8\,{\rm{cm}}}}\\
v = - \dfrac{{16}}{3}\;{\rm{cm}}
\end{array}\]
Note:
he definition of the refractive index can also be told as the ratio of the speed of light in vacuum to the speed of light in another medium may be water, glass etc. and it is represented as:
$\mu = \dfrac{c}{v}$
Here, $\mu $ is the refractive index, c is the speed of light in vacuum and v is the speed of light in the medium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




