
A point charge q is placed at a distance of r from the center of an uncharged conducting sphere of radius R(< r). The potential at any point on the sphere is
A.Zero
B.$\dfrac {1}{4 \pi {\epsilon}_{0}}.\dfrac {q}{r}$
C.$\dfrac {1}{4 \pi {\epsilon}_{0}}. \dfrac{qR}{{r}^{2}}$
D.$\dfrac {1}{4 \pi {\epsilon}_{0}}. \dfrac {q {r}^{2}}{R}$
Answer
583.5k+ views
Hint: To solve this problem, find the electric field inside the conducting sphere. Then, substitute that value in the formula giving relation between the electric field and electric potential. Next, find the electric potential at the center. But, the potential due to induced charge at the center is zero. Substitute this value in the equation for the electric potential at the center. The obtained equation will be the potential at any point in the sphere.
Formula used:
$\nabla . V=-E$
Complete answer:
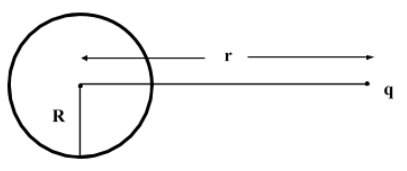
Electric field inside the spherical conductor is zero.
$E=0$ …(1)
Relation between electric field and electric potential is given by,
$\nabla . V=-E$
Substituting equation. (1) in above equation we get,
$\nabla . V=0$
$\Rightarrow V= constant$
Thus, the potential throughout the sphere will be constant.
Electric potential at the center is given by,
$ V= \dfrac {1}{4 \pi {\epsilon}_{0}}.\dfrac {q}{r} + {V}_{c}$ …(2)
Where, ${V}_{c}$ is the potential at center due to induced charge.
But, the potential due to net induced charge is zero.
Substituting this value in the equation. (2) we get,
$ V= \dfrac {1}{4 \pi {\epsilon}_{0}}.\dfrac {q}{r}$
Thus, the potential at any point on the surface is $\dfrac {1}{4 \pi {\epsilon}_{0}}.\dfrac {q}{r}$.
Hence, the correct answer is option B i.e. $\dfrac {1}{4 \pi {\epsilon}_{0}}.\dfrac {q}{r}$.
Note:
It is important for the students to remember the characteristic property of a conductor, electric field and electric potential. Students should know that when we say the electric field is zero, we mean electric field lines do not exist in that region. Electric fields have definite magnitude and specific direction. As no electric field lines pass from inside the conductor, the electric field inside the conductor is zero.
Formula used:
$\nabla . V=-E$
Complete answer:

Electric field inside the spherical conductor is zero.
$E=0$ …(1)
Relation between electric field and electric potential is given by,
$\nabla . V=-E$
Substituting equation. (1) in above equation we get,
$\nabla . V=0$
$\Rightarrow V= constant$
Thus, the potential throughout the sphere will be constant.
Electric potential at the center is given by,
$ V= \dfrac {1}{4 \pi {\epsilon}_{0}}.\dfrac {q}{r} + {V}_{c}$ …(2)
Where, ${V}_{c}$ is the potential at center due to induced charge.
But, the potential due to net induced charge is zero.
Substituting this value in the equation. (2) we get,
$ V= \dfrac {1}{4 \pi {\epsilon}_{0}}.\dfrac {q}{r}$
Thus, the potential at any point on the surface is $\dfrac {1}{4 \pi {\epsilon}_{0}}.\dfrac {q}{r}$.
Hence, the correct answer is option B i.e. $\dfrac {1}{4 \pi {\epsilon}_{0}}.\dfrac {q}{r}$.
Note:
It is important for the students to remember the characteristic property of a conductor, electric field and electric potential. Students should know that when we say the electric field is zero, we mean electric field lines do not exist in that region. Electric fields have definite magnitude and specific direction. As no electric field lines pass from inside the conductor, the electric field inside the conductor is zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




