
A point charge \[5\times {{10}^{-6}}\]is at a distance of 5 cm directly above the centre of the square of the side 10 cm. What is the magnitude of the flux?
Answer
535.2k+ views
Hint: The electric flux is the rate of flow of the electric field through a given area/surface. So, while computing the electric flux due to the charges enclosed by the surface, we have to take into consideration the charges that are present only inside that surface.
Complete answer:
According to Gauss law, closed surfaces of various shapes can surround the charge. The net flux through closed surface equals \[\dfrac{1}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\]times the net charge enclosed by that surface. The product of the closed integral of the electric field and a small area is also the net electric flux. The mathematical representation of the same is given as follows.
\[\Phi =\oint{E.dA}=\dfrac{{{q}_{net}}}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\]
Consider the figure.
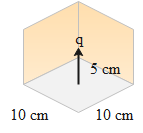
Consider the square to be a side of a cube.
From the figure, we can notice that the charges enclosed by the cube is \[q=5\times {{10}^{-6}}C\]. So, while computing the flux of the electric field through the cube, we should consider only the charge.
Now, we will compute the magnitude of the flux.
Consider the formula for computing the electric flux through a cube.
\[\Phi =\dfrac{1}{6}\dfrac{{{q}_{net}}}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\]
Substitute the value of the net charge enclosed by the cube obtained in the above equation.
\[\begin{align}
& \Phi =\dfrac{1}{6}\times \dfrac{5\times {{10}^{-6}}}{8.854\times {{10}^{-12}}} \\
& \therefore \Phi =9.4\times {{10}^{4}}N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-1}} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore \] The flux of the electric field due to the charge enclosed by the cube is \[9.4\times {{10}^{4}}N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-1}}\].
Note:
Gauss law connects the electric field with its source. The net flux will be independent of the shape and size of the closed surface (Gaussian surface) surrounding the charge. As the electric field due to many changes is the vector sum of the electric fields produced by the individual charges, the flux through any closed surface can be expressed as the sum of charges by \[{{\varepsilon }_{0}}\].
Complete answer:
According to Gauss law, closed surfaces of various shapes can surround the charge. The net flux through closed surface equals \[\dfrac{1}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\]times the net charge enclosed by that surface. The product of the closed integral of the electric field and a small area is also the net electric flux. The mathematical representation of the same is given as follows.
\[\Phi =\oint{E.dA}=\dfrac{{{q}_{net}}}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\]
Consider the figure.

Consider the square to be a side of a cube.
From the figure, we can notice that the charges enclosed by the cube is \[q=5\times {{10}^{-6}}C\]. So, while computing the flux of the electric field through the cube, we should consider only the charge.
Now, we will compute the magnitude of the flux.
Consider the formula for computing the electric flux through a cube.
\[\Phi =\dfrac{1}{6}\dfrac{{{q}_{net}}}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\]
Substitute the value of the net charge enclosed by the cube obtained in the above equation.
\[\begin{align}
& \Phi =\dfrac{1}{6}\times \dfrac{5\times {{10}^{-6}}}{8.854\times {{10}^{-12}}} \\
& \therefore \Phi =9.4\times {{10}^{4}}N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-1}} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore \] The flux of the electric field due to the charge enclosed by the cube is \[9.4\times {{10}^{4}}N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-1}}\].
Note:
Gauss law connects the electric field with its source. The net flux will be independent of the shape and size of the closed surface (Gaussian surface) surrounding the charge. As the electric field due to many changes is the vector sum of the electric fields produced by the individual charges, the flux through any closed surface can be expressed as the sum of charges by \[{{\varepsilon }_{0}}\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




