
A pipe open at both ends has a fundamental frequency ‘f’ in air. The pipe is dipped vertically in water so that half of it is water. The fundamental frequency of the air column is now:
A. f/2
B. 3f/4
C. 2f
D. f
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: A transverse wave is the one which travels through a medium, making crests and troughs. Wave on a string is an example of a transverse wave. A longitudinal wave is the one which travels through the medium making compressions and rarefactions. Sound waves are an example of longitudinal waves. When two waves approach each other in the same place, on the same line, standing waves are formed. Organ pipe is an example of the situation in which standing waves are formed.
Complete answer:
Organ pipe is related to the experiments on sound waves. It is of two types. Open organ pipe is the one in which both ends are opened and then sound is passed through it. Closed organ pipe is the one in which only one end is open and the other is closed and then sound is passed.
Now, given: $f = \dfrac{\nu}{2L}$
But when the pipe is dipped in water to half of its length, the length of the pipe becomes halved and the pipe starts acting as closed organ pipe, having fundamental frequency $\nu = \dfrac{v}{4L}$ (Since water is a denser medium and sound will be reflected).
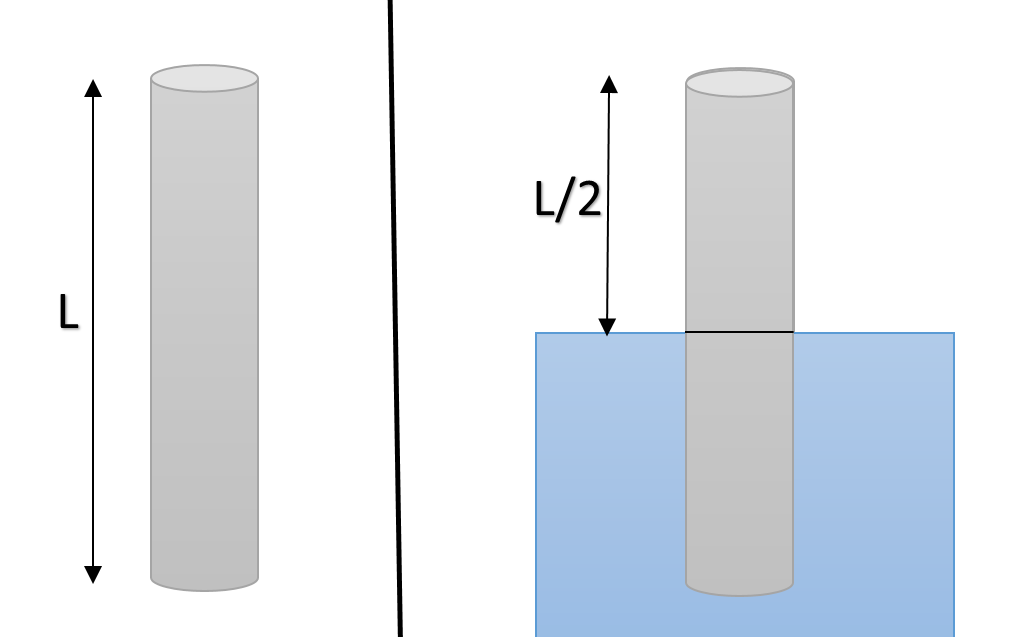
Hence $f^\prime = \dfrac{v}{4(L/2)} = \dfrac{v}{2L} = f$
Thus, there will be no technical difference between the fundamentals of pipe after being dipped into the water.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
Closed organ pipe is not really only that pipe which is blocked by a solid object at one end. It could be assumed closed id any medium denser than air is present on the other end. One must know that sound waves create standing waves inside the tube so that we can analyze the situation and know the parameters like frequency and conduct the experiment. Students are advised to derive these expressions once by their own.
Complete answer:
Organ pipe is related to the experiments on sound waves. It is of two types. Open organ pipe is the one in which both ends are opened and then sound is passed through it. Closed organ pipe is the one in which only one end is open and the other is closed and then sound is passed.
Now, given: $f = \dfrac{\nu}{2L}$
But when the pipe is dipped in water to half of its length, the length of the pipe becomes halved and the pipe starts acting as closed organ pipe, having fundamental frequency $\nu = \dfrac{v}{4L}$ (Since water is a denser medium and sound will be reflected).

Hence $f^\prime = \dfrac{v}{4(L/2)} = \dfrac{v}{2L} = f$
Thus, there will be no technical difference between the fundamentals of pipe after being dipped into the water.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
Closed organ pipe is not really only that pipe which is blocked by a solid object at one end. It could be assumed closed id any medium denser than air is present on the other end. One must know that sound waves create standing waves inside the tube so that we can analyze the situation and know the parameters like frequency and conduct the experiment. Students are advised to derive these expressions once by their own.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




