
A piece of wood of mass 0.03Kg is dropped from the top of a 100m height building. At the same time, a bullet of mass 0.02Kg is fired vertically upward, with a velocity \[100{\text{ m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\], from the ground. The bullet gets embedded in the wood. Then the maximum height to which the combined system reaches above the top of the building before falling below is: ($g = 10{\text{ m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}$).
A. 30 m
B. 10 m
C. 40 m
D. 20 m
Answer
599.1k+ views
Hint: This question is related to inelastic collision i.e. the law of conservation of momentum holds good but the kinetic energy is not conserved. First we need to find the time taken for the particles to collide and speeds of wood and bullet just before collision. Then we need to find the velocity using the law of conservation of momentum. Using this velocity we can now find the maximum height.
Complete step-by-step answer:
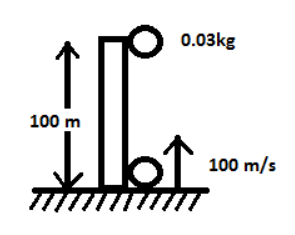
Time taken for the particles to collide,
${\text{t = }}\dfrac{{\text{d}}}{{{{\text{V}}_{{\text{rel}}}}}} = \dfrac{{100}}{{100}} = 1\sec $
Here, d= distance covered
And${{\text{V}}_{{\text{rel}}}}$is the relative velocity
Speed of wood just before collision$ = {\text{gt = 10 m/s}}$
Speed of bullet just before collision ${\text{v - gt}} = 100 - 10 = 90{\text{ m/s}}$
Now, conversation of linear momentum just before and after collision
Total momentum before collision = Total momentum after collision
That is, \[{m_1}{u_1} + {m_2}{u_2} = {m_1}{v_1} + {m_2}{v_2}\]
\[{m_{total}}{v_c} = {m_b}{v_b} + {m_w}{v_w}\]
Where \[{m_{total}}\] is combined mass of bullet and wood that is $0.02 + 0.03 = 0.05$,
\[{v_c}\] is the velocity combination,
\[{m_b}\] is the mass of bullet,
\[{v_b}\] is the velocity of bullet,
\[{m_w}\] is the mass of wooden block
\[{v_w}\] is the velocity of wooden block
$ \Rightarrow \left( {0.03} \right)\left( { - 10} \right) + \left( {0.02} \right)\left( {90} \right) = \left( {0.05} \right){{\text{v}}_c}$
$ \Rightarrow - \left( {0.03} \right)\left( {10} \right) + \left( {0.02} \right)\left( {90} \right) = \left( {0.05} \right){{\text{v}}_c}$
$ \Rightarrow 150 = 5{{\text{v}}_c}$
$ \Rightarrow {{\text{v}}_c}{\text{ = 30 m/s}}$
Maximum height reached by body ${{\text{h}}_{{\text{max}}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{{\text{v}}^2}}}{{2{\text{g}}}}$
Before collision: $0.03{\text{ kg}} \downarrow 10{\text{ m/s}}$
$0.02{\text{ kg}} \uparrow 90{\text{ m/s}}$
After collision: $30{\text{m/s }} \uparrow {\text{ 0}}{\text{.05kg}}$
$ \Rightarrow {{\text{h}}_{{\text{max}}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{30 \times 30}}{{2 \times 10}} = 40{\text{ m}}$
Therefore, the maximum height to which the combined system reaches above the top of the building before falling below is 40 m.
Note: In the above solution, to calculate the time taken for collision we used the distance covered to relative velocity. Instead of that we can also solve by distance covered by piece of wood from certain height in t sec using ${\text{S = ut + }}\dfrac{1}{2}{\text{a}}{{\text{t}}^2}$and then bullet covering distance using the same formula. This total distance now can be equal to the height of the building based on the given question. Solving the equation will give the time taken to collide.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Time taken for the particles to collide,
${\text{t = }}\dfrac{{\text{d}}}{{{{\text{V}}_{{\text{rel}}}}}} = \dfrac{{100}}{{100}} = 1\sec $
Here, d= distance covered
And${{\text{V}}_{{\text{rel}}}}$is the relative velocity
Speed of wood just before collision$ = {\text{gt = 10 m/s}}$
Speed of bullet just before collision ${\text{v - gt}} = 100 - 10 = 90{\text{ m/s}}$
Now, conversation of linear momentum just before and after collision
Total momentum before collision = Total momentum after collision
That is, \[{m_1}{u_1} + {m_2}{u_2} = {m_1}{v_1} + {m_2}{v_2}\]
\[{m_{total}}{v_c} = {m_b}{v_b} + {m_w}{v_w}\]
Where \[{m_{total}}\] is combined mass of bullet and wood that is $0.02 + 0.03 = 0.05$,
\[{v_c}\] is the velocity combination,
\[{m_b}\] is the mass of bullet,
\[{v_b}\] is the velocity of bullet,
\[{m_w}\] is the mass of wooden block
\[{v_w}\] is the velocity of wooden block
$ \Rightarrow \left( {0.03} \right)\left( { - 10} \right) + \left( {0.02} \right)\left( {90} \right) = \left( {0.05} \right){{\text{v}}_c}$
$ \Rightarrow - \left( {0.03} \right)\left( {10} \right) + \left( {0.02} \right)\left( {90} \right) = \left( {0.05} \right){{\text{v}}_c}$
$ \Rightarrow 150 = 5{{\text{v}}_c}$
$ \Rightarrow {{\text{v}}_c}{\text{ = 30 m/s}}$
Maximum height reached by body ${{\text{h}}_{{\text{max}}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{{\text{v}}^2}}}{{2{\text{g}}}}$
Before collision: $0.03{\text{ kg}} \downarrow 10{\text{ m/s}}$
$0.02{\text{ kg}} \uparrow 90{\text{ m/s}}$
After collision: $30{\text{m/s }} \uparrow {\text{ 0}}{\text{.05kg}}$
$ \Rightarrow {{\text{h}}_{{\text{max}}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{30 \times 30}}{{2 \times 10}} = 40{\text{ m}}$
Therefore, the maximum height to which the combined system reaches above the top of the building before falling below is 40 m.
Note: In the above solution, to calculate the time taken for collision we used the distance covered to relative velocity. Instead of that we can also solve by distance covered by piece of wood from certain height in t sec using ${\text{S = ut + }}\dfrac{1}{2}{\text{a}}{{\text{t}}^2}$and then bullet covering distance using the same formula. This total distance now can be equal to the height of the building based on the given question. Solving the equation will give the time taken to collide.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




