
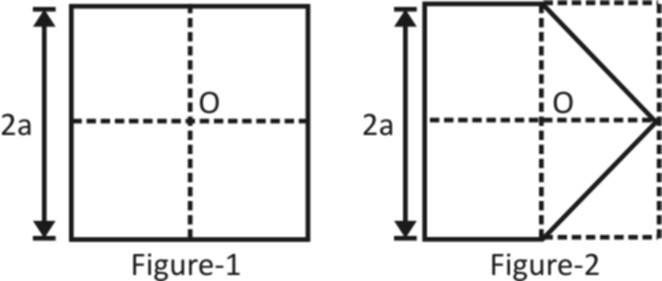
A piece of paper (shown in figure-1) is in the form of a square. Two corners of this square are folded to make it appear like figure-2. Both corners are put together at the centre of the square . If O is taken to be (0, 0), the centre of mass of the new system will be at Figure-1and Figure-2.
\[
(A)\;\;\;\left( {\dfrac{{ - a}}{8},0} \right) \\
(B)\;\;\;\left( {\dfrac{{ - a}}{6},0} \right) \\
(C)\;\;\;\left( {\dfrac{a}{{12}},0} \right) \\
(D)\;\;\;\left( {\dfrac{{ - a}}{{12}},0} \right) \\
\]
A piece of paper (shown in figure-1) is in the form of a square. Two corners of this square are folded to make it appear like figure-2. Both corners are put together at the centre of the square ‘O’.

Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Centre of mass of a regular body is the same as their centre. Like the centre of mass of the rectangle lies at the point where its diagonals interest each other.
Complete step by step answer:
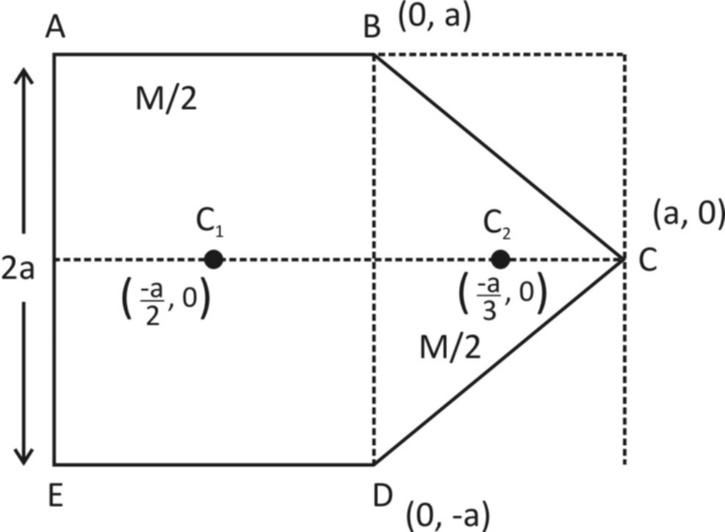
If the total mass of the square sheet is M, then the mass of the ABDE sheet will be $\dfrac{M}{2}$ and that of BCD will also be $\dfrac{M}{2}$.
The centre of mass of ABDE, will be its centre i.e. \[G\;\left( {\dfrac{{ - a}}{2},0} \right)\].
Now, BCD is an isosceles triangle.
Its centre of mass will be
\[
{C_2} = \left( {\dfrac{{o + a + o}}{3},\;\dfrac{{a + o - a}}{3}} \right) \\
{C_2} = \left( {\dfrac{a}{3},0} \right) \\
\]
Now, centre of mass of whole system will be
Centre of mass along redirection,
$
{(COM)_x} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{M}{2}\left( {\dfrac{{ - a}}{2}} \right) + \dfrac{M}{2}\;\left( {\dfrac{a}{3}} \right)}}{M} \\
= \dfrac{{\dfrac{M}{2}\;\left( {\dfrac{{ - a}}{2} + \dfrac{a}{3}} \right)}}{M} = \dfrac{{ - 9}}{{12}} \\
$
Along $y - axis,\;\;(COM){\;_y} = 0$
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
Centre of mass of the whole system is calculated by formula
$
{x_{cm}} = \dfrac{{{m_1}\,{x_1}\, + {m_2}\,{x_2}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}} \\
{y_{cm}} = \dfrac{{{m_1}\,{y_1} + {m_2}\,{y_2}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}} \\
$
Complete step by step answer:

If the total mass of the square sheet is M, then the mass of the ABDE sheet will be $\dfrac{M}{2}$ and that of BCD will also be $\dfrac{M}{2}$.
The centre of mass of ABDE, will be its centre i.e. \[G\;\left( {\dfrac{{ - a}}{2},0} \right)\].
Now, BCD is an isosceles triangle.
Its centre of mass will be
\[
{C_2} = \left( {\dfrac{{o + a + o}}{3},\;\dfrac{{a + o - a}}{3}} \right) \\
{C_2} = \left( {\dfrac{a}{3},0} \right) \\
\]
Now, centre of mass of whole system will be
Centre of mass along redirection,
$
{(COM)_x} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{M}{2}\left( {\dfrac{{ - a}}{2}} \right) + \dfrac{M}{2}\;\left( {\dfrac{a}{3}} \right)}}{M} \\
= \dfrac{{\dfrac{M}{2}\;\left( {\dfrac{{ - a}}{2} + \dfrac{a}{3}} \right)}}{M} = \dfrac{{ - 9}}{{12}} \\
$
Along $y - axis,\;\;(COM){\;_y} = 0$
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
Centre of mass of the whole system is calculated by formula
$
{x_{cm}} = \dfrac{{{m_1}\,{x_1}\, + {m_2}\,{x_2}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}} \\
{y_{cm}} = \dfrac{{{m_1}\,{y_1} + {m_2}\,{y_2}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}} \\
$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




