
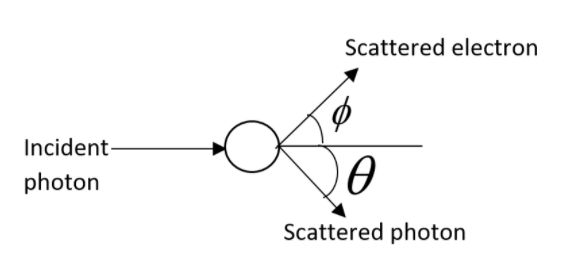
A photon of wavelength $\lambda $ is scattered from an electron, which is at rest. The shift in wavelength $\Delta \lambda $ be three times of $\lambda $ and the angle of scattering $\theta $ will be $60{}^\circ $. The angle at which the electron comes back is $\phi $. What will be the value of $\tan \phi $? Let us assume that electron speed is much smaller than the speed of light.
$\begin{align}
& A.0.28 \\
& B.0.22 \\
& C.0.25 \\
& D.0.16 \\
\end{align}$
Answer
576k+ views
Hint: Find the initial momentum of photon, scattered momentum of the photon, initial momentum of electron and Final momentum of electron. The momentum conservation says that the initial momentum of the particle will be equivalent to its final momentum. Apply this in both horizontal and vertical direction and reach at the answer.
Complete answer:
First of all let us find the initial momentum of the photon. That is,
${{P}_{initial}}=\dfrac{h}{{{\lambda }_{i}}}$
Where ${{\lambda }_{i}}$ be the initial wavelength of the photon.
The scattered momentum of the photon will be given as,
${{P}_{scattered}}=\dfrac{h}{{{\lambda }_{f}}}$
Where ${{\lambda }_{f}}$ be the final momentum of the photon.
Let us take that the initial momentum of the electron is zero.
${{P}_{1}}=0$
Final momentum of the electron is $P$.
${{P}_{2}}=P$
According to conservation of momentum, for the horizontal component, we can write that,
$\dfrac{h}{{{\lambda }_{i}}}+0=\dfrac{h}{{{\lambda }_{f}}}\cos \theta +P\cos \phi $ …………….. (1)
In accordance with the momentum conservation, for the vertical component we can write that,
$0=\dfrac{h}{{{\lambda }_{f}}}\sin \theta -P\sin \phi $………….. (2)
It has been already mentioned in the question that the angle of scattering be,
$\theta =60{}^\circ $
And also,
$\begin{align}
& \Delta \lambda =3{{\lambda }_{i}}={{\lambda }_{f}}-{{\lambda }_{i}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\lambda }_{f}}=4{{\lambda }_{i}} \\
\end{align}$
From the equation (1) and (2) we can write that,
$\begin{align}
& P\cos \phi =\dfrac{7h}{8{{\lambda }_{i}}} \\
& P\sin \phi =\dfrac{\sqrt{3}h}{8{{\lambda }_{i}}} \\
\end{align}$
Dividing both the equations will give the tangent of the angle. That is,
$\tan \phi =\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{7}=0.25$
Therefore the value mentioned in the question has been calculated.
The answer is given as option C.
Note:
The conservation of momentum is derived from Newton's third law of motion. When a collision occurs the forces on the colliding objects will be always equivalent and opposite at each moment. Hence the momentum has been conserved.
Complete answer:
First of all let us find the initial momentum of the photon. That is,
${{P}_{initial}}=\dfrac{h}{{{\lambda }_{i}}}$
Where ${{\lambda }_{i}}$ be the initial wavelength of the photon.
The scattered momentum of the photon will be given as,
${{P}_{scattered}}=\dfrac{h}{{{\lambda }_{f}}}$
Where ${{\lambda }_{f}}$ be the final momentum of the photon.
Let us take that the initial momentum of the electron is zero.
${{P}_{1}}=0$
Final momentum of the electron is $P$.
${{P}_{2}}=P$
According to conservation of momentum, for the horizontal component, we can write that,
$\dfrac{h}{{{\lambda }_{i}}}+0=\dfrac{h}{{{\lambda }_{f}}}\cos \theta +P\cos \phi $ …………….. (1)
In accordance with the momentum conservation, for the vertical component we can write that,
$0=\dfrac{h}{{{\lambda }_{f}}}\sin \theta -P\sin \phi $………….. (2)
It has been already mentioned in the question that the angle of scattering be,
$\theta =60{}^\circ $
And also,
$\begin{align}
& \Delta \lambda =3{{\lambda }_{i}}={{\lambda }_{f}}-{{\lambda }_{i}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\lambda }_{f}}=4{{\lambda }_{i}} \\
\end{align}$
From the equation (1) and (2) we can write that,
$\begin{align}
& P\cos \phi =\dfrac{7h}{8{{\lambda }_{i}}} \\
& P\sin \phi =\dfrac{\sqrt{3}h}{8{{\lambda }_{i}}} \\
\end{align}$
Dividing both the equations will give the tangent of the angle. That is,
$\tan \phi =\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{7}=0.25$
Therefore the value mentioned in the question has been calculated.
The answer is given as option C.

Note:
The conservation of momentum is derived from Newton's third law of motion. When a collision occurs the forces on the colliding objects will be always equivalent and opposite at each moment. Hence the momentum has been conserved.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




