
A person walking along a straight road towards a hill observes at two points distance \[\sqrt{3}\]km, the angle of elevation of the hill to be ${{30}^{\circ }}$ and ${{60}^{\circ }}$. The height of the hill is:
A. $\dfrac{3}{2}\text{ km}$
B. $\sqrt{\dfrac{21}{32}}\text{ km}$
C. $\dfrac{\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)}{2}\text{ km}$
D. $\sqrt{3}\text{ km}$
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: First we will analyze the question and draw the diagram according to the conditions given in the question and then we will see that two right angled triangle will form we will then take the triangle one by one and find out the tan of the given by $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Base}}$ such that we will get two equations in $h\text{ and }x$ and then solve them to find the height of the hill.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given that the person observes the point from two points and the angle of elevation be ${{30}^{\circ }}$ and ${{60}^{\circ }}$ respectively,
Let the point observed be $D$ from $A$ and $B$ at an angle of ${{30}^{\circ }}$ and ${{60}^{\circ }}$ respectively, it is given the distance between the two points that is $AB=\sqrt{3}\text{ km}$
Now let the height of the hill be $h$ that is the distance $CD$ and the distance from point $B$ to the foot of the hill that is the point $C$ be $x\text{ km}$. Then we will have the following figure according to the condition given in the question:
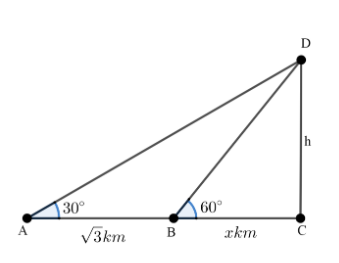
Let’s take the triangle $\Delta DBC$ ,
Now as we see that it a right angled triangle now we know that $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Base}}$ :
Therefore, $\tan {{60}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{h}{x}\text{ }$ , we know that the value of $\tan {{60}^{\circ }}=\sqrt{3}$ , therefore:
$\sqrt{3}=\dfrac{h}{x}\text{ }\Rightarrow h=\sqrt{3}x\text{ }........\text{Equation 1}\text{.}$
Similarly, Let’s take the triangle $\Delta DAC$,
$\tan {{30}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{h}{\sqrt{3}+x}\text{ }$ , we know that the value of $\tan {{30}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$ , therefore:
$\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{h}{\sqrt{3}+x}\text{ }.......\text{Equation 2}\text{.}$
We will now put the value of $h$ from equation 1 into equation 2:
So, we will have:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{h}{\sqrt{3}+x}\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}x}{\sqrt{3}+x}\Rightarrow \sqrt{3}+x=3x \\
& \Rightarrow 3x-x=\sqrt{3}\Rightarrow 2x=\sqrt{3} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Now we will put this value in equation 1 to find the value of $h$ :
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow h=\sqrt{3}x\Rightarrow h=\left( \sqrt{3}\times \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow h=\dfrac{3}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: Student can make the mistake while writing down the values of $\tan {{60}^{\circ }}\text{ and }\tan {{30}^{\circ }}$ because there values are reciprocal of each other. It is always better to draw diagrams in questions like this as it will cause less mistakes and will help the examiner to better the solution and variables that you have assumed.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given that the person observes the point from two points and the angle of elevation be ${{30}^{\circ }}$ and ${{60}^{\circ }}$ respectively,
Let the point observed be $D$ from $A$ and $B$ at an angle of ${{30}^{\circ }}$ and ${{60}^{\circ }}$ respectively, it is given the distance between the two points that is $AB=\sqrt{3}\text{ km}$
Now let the height of the hill be $h$ that is the distance $CD$ and the distance from point $B$ to the foot of the hill that is the point $C$ be $x\text{ km}$. Then we will have the following figure according to the condition given in the question:

Let’s take the triangle $\Delta DBC$ ,
Now as we see that it a right angled triangle now we know that $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Base}}$ :
Therefore, $\tan {{60}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{h}{x}\text{ }$ , we know that the value of $\tan {{60}^{\circ }}=\sqrt{3}$ , therefore:
$\sqrt{3}=\dfrac{h}{x}\text{ }\Rightarrow h=\sqrt{3}x\text{ }........\text{Equation 1}\text{.}$
Similarly, Let’s take the triangle $\Delta DAC$,
$\tan {{30}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{h}{\sqrt{3}+x}\text{ }$ , we know that the value of $\tan {{30}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$ , therefore:
$\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{h}{\sqrt{3}+x}\text{ }.......\text{Equation 2}\text{.}$
We will now put the value of $h$ from equation 1 into equation 2:
So, we will have:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{h}{\sqrt{3}+x}\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}x}{\sqrt{3}+x}\Rightarrow \sqrt{3}+x=3x \\
& \Rightarrow 3x-x=\sqrt{3}\Rightarrow 2x=\sqrt{3} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Now we will put this value in equation 1 to find the value of $h$ :
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow h=\sqrt{3}x\Rightarrow h=\left( \sqrt{3}\times \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow h=\dfrac{3}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: Student can make the mistake while writing down the values of $\tan {{60}^{\circ }}\text{ and }\tan {{30}^{\circ }}$ because there values are reciprocal of each other. It is always better to draw diagrams in questions like this as it will cause less mistakes and will help the examiner to better the solution and variables that you have assumed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




