
A person stands at a point A due South of a tower and observes elevation is \[{60^ \circ }\] . He then walks westward towards B where the elevation is \[{45^ \circ }\] . At a point C on AB produced he finds it to be \[{30^ \circ }\]. Prove that AB=BC.
Answer
534.3k+ views
Hint: In order to find the solution to the above question, we will be drawing a diagram to guide us while finding the answer. To solve the question, you need to keep in mind the property of a right-angled triangle, \[{\left( {hypotenuse} \right)^2} = {\left( {perpendicular} \right)^2} + {\left( {base} \right)^2}\] , we will be using this property.
Formula used:
In a right-angled triangle: \[{\left( {hypotenuse} \right)^2} = {\left( {perpendicular} \right)^2} + {\left( {base} \right)^2}\] .
Complete step by step solution:
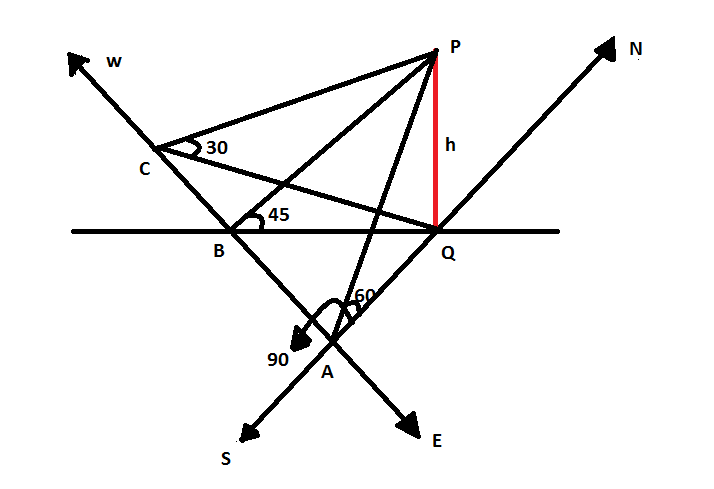
In the diagram given below, PQ is the tower which is standing on the paper. PQ is perpendicular to every line in the plane, therefore, PQ is perpendicular to AQ, BQ and CQ.
Also, we are given that the angles at the point A, B and C are \[{60^ \circ }\], \[{45^ \circ }\] and \[{30^ \circ }\] respectively.
We can see that \[\angle QAB = \angle QAC = {90^ \circ }\] and PQ is equal to h.
So, AQ\[ = h\cot {60^ \circ }\], BQ\[ = h\cot {45^ \circ }\] and CQ\[ = h\cot {30^ \circ }\] .
We can also write this as, AQ\[ = \dfrac{h}{{\sqrt 3 }}\], BQ\[ = h\] and CQ\[ = h\sqrt 3 \].
Now, from the right-angled triangle \[\vartriangle QAB\] , we get that,
\[AB = \sqrt {B{Q^2} - A{Q^2}} \]
\[ = \sqrt {\left( {{h^2} - \dfrac{{{h^2}}}{3}} \right)} \]
\[ = h\sqrt {\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}} \right)} \] .
Now from \[\vartriangle QAC\] , we get that,
\[AC = \sqrt {C{Q^2} - A{Q^2}} \]
\[
= \sqrt {\left( {3{h^2} - \dfrac{{{h^2}}}{3}} \right)} \\
= 2h\sqrt {\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}} \right)} \\
\]
We get that, \[AC = 2AB\] (Using \[AB = h\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{3}} \] )
We can write this as
\[
AB + BC = 2AB \\
\Rightarrow AB = BC \\
\].
Hence proved.
Note: while solving questions similar to the one given above, always try to make a diagram following the statements given in the question. This will help you in solving the question easily in a very less amount of time. Also, in the above question we have used the property of right-angled triangle where \[{\left( {hypotenuse} \right)^2} = {\left( {perpendicular} \right)^2} + {\left( {base} \right)^2}\]. Remember this property while solving these questions.
Formula used:
In a right-angled triangle: \[{\left( {hypotenuse} \right)^2} = {\left( {perpendicular} \right)^2} + {\left( {base} \right)^2}\] .
Complete step by step solution:
In the diagram given below, PQ is the tower which is standing on the paper. PQ is perpendicular to every line in the plane, therefore, PQ is perpendicular to AQ, BQ and CQ.
Also, we are given that the angles at the point A, B and C are \[{60^ \circ }\], \[{45^ \circ }\] and \[{30^ \circ }\] respectively.
We can see that \[\angle QAB = \angle QAC = {90^ \circ }\] and PQ is equal to h.
So, AQ\[ = h\cot {60^ \circ }\], BQ\[ = h\cot {45^ \circ }\] and CQ\[ = h\cot {30^ \circ }\] .
We can also write this as, AQ\[ = \dfrac{h}{{\sqrt 3 }}\], BQ\[ = h\] and CQ\[ = h\sqrt 3 \].
Now, from the right-angled triangle \[\vartriangle QAB\] , we get that,
\[AB = \sqrt {B{Q^2} - A{Q^2}} \]
\[ = \sqrt {\left( {{h^2} - \dfrac{{{h^2}}}{3}} \right)} \]
\[ = h\sqrt {\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}} \right)} \] .
Now from \[\vartriangle QAC\] , we get that,
\[AC = \sqrt {C{Q^2} - A{Q^2}} \]
\[
= \sqrt {\left( {3{h^2} - \dfrac{{{h^2}}}{3}} \right)} \\
= 2h\sqrt {\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}} \right)} \\
\]
We get that, \[AC = 2AB\] (Using \[AB = h\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{3}} \] )
We can write this as
\[
AB + BC = 2AB \\
\Rightarrow AB = BC \\
\].
Hence proved.

Note: while solving questions similar to the one given above, always try to make a diagram following the statements given in the question. This will help you in solving the question easily in a very less amount of time. Also, in the above question we have used the property of right-angled triangle where \[{\left( {hypotenuse} \right)^2} = {\left( {perpendicular} \right)^2} + {\left( {base} \right)^2}\]. Remember this property while solving these questions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




