
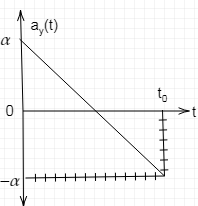
A person of mass ${{m}_{p}}$ stands on a scale in an elevator of mass ${{m}_{e}}$. The scale reads the magnitude of the force $F$ exerted on it from above in a downward direction. Starting at rest at $t=0$ the elevator moves upward,coming to rest again at $t={{t}_{0}}$. The downward acceleration of gravity is $g$. The acceleration of the elevator during this period is shown graphically above and is given analytically by
${{a}_{y}}(t)=\alpha -\dfrac{2\alpha }{{{t}_{0}}}t$.
a)Find the maximum speed of the elevator.
b)Find the total distance travelled by the elevator.

Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint: First we will calculate the maximum increase in velocity of the elevator from the acceleration-time graph. Then we will add it with the initial velocity of the elevator to get the maximum velocity. Then we will determine the average acceleration of the elevator for the time interval for which the acceleration is positive and negative separately. Then using the kinematics equations for uniform acceleration we will calculate the total distance travelled by the elevator.
Formula used:
Area enclosed by the $a-t$ graph with time axis gives $\vartriangle v$, $v=u+at$, $s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$.
Complete answer:
a) Now the acceleration of the elevator varies with the relation
${{a}_{y}}(t)=\alpha -\dfrac{2\alpha }{{{t}_{0}}}t$. Let at time $T$ the acceleration ${{a}_{y}}(t)$ becomes zero. Thus we have
$\begin{align}
& 0=\alpha -\dfrac{2\alpha }{{{t}_{0}}}T \\
& orT=\dfrac{{{t}_{0}}}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Thus we can draw the graph as follows
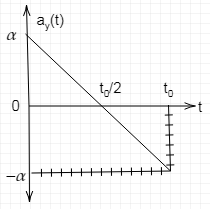
Now the maximum change in the velocity is given by the area of the triangle which is in the positive y side. So the graph we have the maximum change in velocity as
$\vartriangle v=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{{{t}_{0}}}{2}\times \alpha =\dfrac{\alpha {{t}_{0}}}{4}$.
Now as the elevator starts from rest, $\vartriangle v$ will be its maximum velocity.
So the maximum velocity of the elevator is $\dfrac{\alpha {{t}_{0}}}{4}$.
b) We can see from the $a-t$ graph the acceleration changes uniformly. Thus for the first $\dfrac{{{t}_{0}}}{2}$ time the average acceleration is given by
$\dfrac{\alpha +0}{2}=\dfrac{\alpha }{2}$.
So the distance travelled by in the first $\dfrac{{{t}_{0}}}{2}$time is given by
${{s}_{1}}=0\times \dfrac{{{t}_{0}}}{2}+\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\times {{(\dfrac{{{t}_{0}}}{2})}^{2}}=\dfrac{\alpha t_{0}^{2}}{16}$.
Now after $\dfrac{{{t}_{0}}}{2}$ time its velocity becomes
$v=0+\dfrac{\alpha }{2}\times \dfrac{{{t}_{0}}}{2}=\dfrac{\alpha {{t}_{0}}}{4}$.
For the next $\dfrac{{{t}_{0}}}{2}$ time the average acceleration is $-\dfrac{\alpha }{2}$. So the distance travelled in the next $\dfrac{{{t}_{0}}}{2}$ is given by
\[{{s}_{2}}=\dfrac{\alpha {{t}_{0}}}{4}\times \dfrac{{{t}_{0}}}{2}-\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\times {{(\dfrac{{{t}_{0}}}{2})}^{2}}=\dfrac{\alpha t_{0}^{2}}{16}\].
So the total distance travelled by the elevator is
\[{{s}_{1}}+{{s}_{2}}=\dfrac{\alpha t_{0}^{2}}{16}+\dfrac{\alpha t_{0}^{2}}{16}=\dfrac{\alpha t_{0}^{2}}{8}\].
Note:
In this question the first part i.e. the part in which the mass of the person and all that are given is given just to confuse us. They are immaterial. To solve the question we just need to have an idea for the acceleration of the elevator and it is clearly given in the question. We should remember that the area enclosed by the $a-t$ graph with the time axis gives the change in velocity in case of non uniform accelerations.
Formula used:
Area enclosed by the $a-t$ graph with time axis gives $\vartriangle v$, $v=u+at$, $s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$.
Complete answer:
a) Now the acceleration of the elevator varies with the relation
${{a}_{y}}(t)=\alpha -\dfrac{2\alpha }{{{t}_{0}}}t$. Let at time $T$ the acceleration ${{a}_{y}}(t)$ becomes zero. Thus we have
$\begin{align}
& 0=\alpha -\dfrac{2\alpha }{{{t}_{0}}}T \\
& orT=\dfrac{{{t}_{0}}}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Thus we can draw the graph as follows

Now the maximum change in the velocity is given by the area of the triangle which is in the positive y side. So the graph we have the maximum change in velocity as
$\vartriangle v=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{{{t}_{0}}}{2}\times \alpha =\dfrac{\alpha {{t}_{0}}}{4}$.
Now as the elevator starts from rest, $\vartriangle v$ will be its maximum velocity.
So the maximum velocity of the elevator is $\dfrac{\alpha {{t}_{0}}}{4}$.
b) We can see from the $a-t$ graph the acceleration changes uniformly. Thus for the first $\dfrac{{{t}_{0}}}{2}$ time the average acceleration is given by
$\dfrac{\alpha +0}{2}=\dfrac{\alpha }{2}$.
So the distance travelled by in the first $\dfrac{{{t}_{0}}}{2}$time is given by
${{s}_{1}}=0\times \dfrac{{{t}_{0}}}{2}+\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\times {{(\dfrac{{{t}_{0}}}{2})}^{2}}=\dfrac{\alpha t_{0}^{2}}{16}$.
Now after $\dfrac{{{t}_{0}}}{2}$ time its velocity becomes
$v=0+\dfrac{\alpha }{2}\times \dfrac{{{t}_{0}}}{2}=\dfrac{\alpha {{t}_{0}}}{4}$.
For the next $\dfrac{{{t}_{0}}}{2}$ time the average acceleration is $-\dfrac{\alpha }{2}$. So the distance travelled in the next $\dfrac{{{t}_{0}}}{2}$ is given by
\[{{s}_{2}}=\dfrac{\alpha {{t}_{0}}}{4}\times \dfrac{{{t}_{0}}}{2}-\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\times {{(\dfrac{{{t}_{0}}}{2})}^{2}}=\dfrac{\alpha t_{0}^{2}}{16}\].
So the total distance travelled by the elevator is
\[{{s}_{1}}+{{s}_{2}}=\dfrac{\alpha t_{0}^{2}}{16}+\dfrac{\alpha t_{0}^{2}}{16}=\dfrac{\alpha t_{0}^{2}}{8}\].
Note:
In this question the first part i.e. the part in which the mass of the person and all that are given is given just to confuse us. They are immaterial. To solve the question we just need to have an idea for the acceleration of the elevator and it is clearly given in the question. We should remember that the area enclosed by the $a-t$ graph with the time axis gives the change in velocity in case of non uniform accelerations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




