
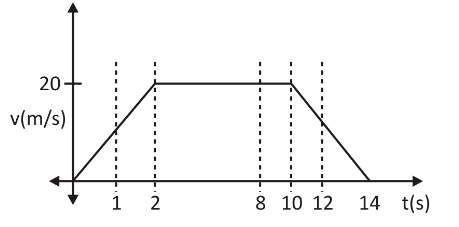
A person of mass M standing on a lift. The lift is moving upwards according to given V-t graph then find out the weight of man at the following instant
(I) \[t=1\] second
(II) \[t=8\] second
(III) \[t=10,12\] and 14 second

Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint: Human weight is just the normal reaction force that earth applies to us so. The slope of the Velocity vs time graph gives the resultant acceleration of the lift. After finding the acceleration of the lift we can apply Newton law of motion to find the normal reaction force.
Complete step by step solution:
Given: \[g=10m{{s}^{-2}}\]
(I) weight at instant \[t=1\] second
slope ${m_1}$ of given graph from \[t=0\] to \[t=2\] second is given as
\[{{m}_{1}}=\dfrac{20}{2}=10\]
This value of slope is equal to acceleration of the lift from \[t=0\] to \[t=2\] second then apply newton law lift has upward acceleration of \[10m/{{s}^{2}}\]
\[
N-Mg=M\times 10 \\
\Rightarrow N=M\left( 10+g \right) \\
\Rightarrow N=M\text{ }\left( 10+10 \right) \\
\]
\[\mathbf{N}=\mathbf{20M}\] newton at \[t=1\] seconds.
(II) weight at instant \[t=8\] second
slope (\[{{m}_{2}}\]) of given graph from \[t=2\]to \[t=10\] second is given as \[{{m}_{2}}\text{ =}\dfrac{0}{8}=0\]
slope is zero so lift acceleration during \[t=2\]to \[t=10\] second is zero
then applying newton's law
\[
N-Mg=M\times 0 \\
\Rightarrow N=Mg \\
\]
\[\mathbf{N}=\mathbf{10M}\text{ }\] newton at \[t=8\] second.
(III) weight at instant \[t=10,12,14\]second
slope (\[{{m}_{3}}\]) of given graph from \[t=10\] to \[t=14\] second is given as
\[{{m}_{3}}=\dfrac{-20}{4}=-5m/{{s}^{2}}\]
This time the acceleration is negative means in downward direction applying Newton's law of motion.
\[
Mg-N=M\times 5 \\
\Rightarrow N=10M-5M \\
\]
\[\mathbf{N}=\mathbf{5M}\]newton at \[t=10,12,14\] second.
Note:While solving this problem, most of the students tend to make mistakes in finding the slope of the curve at various instants. It should be remembered that when the lift is accelerating upwards the weight acting downward increases. This is because the floor of the lift presses harder to our feet while ascending upwards. When the lift moves with constant velocity, the net acceleration of the lift is zero, as we know acceleration is nothing but rate of change of velocity.
Complete step by step solution:
Given: \[g=10m{{s}^{-2}}\]
(I) weight at instant \[t=1\] second
slope ${m_1}$ of given graph from \[t=0\] to \[t=2\] second is given as
\[{{m}_{1}}=\dfrac{20}{2}=10\]
This value of slope is equal to acceleration of the lift from \[t=0\] to \[t=2\] second then apply newton law lift has upward acceleration of \[10m/{{s}^{2}}\]
\[
N-Mg=M\times 10 \\
\Rightarrow N=M\left( 10+g \right) \\
\Rightarrow N=M\text{ }\left( 10+10 \right) \\
\]
\[\mathbf{N}=\mathbf{20M}\] newton at \[t=1\] seconds.
(II) weight at instant \[t=8\] second
slope (\[{{m}_{2}}\]) of given graph from \[t=2\]to \[t=10\] second is given as \[{{m}_{2}}\text{ =}\dfrac{0}{8}=0\]
slope is zero so lift acceleration during \[t=2\]to \[t=10\] second is zero
then applying newton's law
\[
N-Mg=M\times 0 \\
\Rightarrow N=Mg \\
\]
\[\mathbf{N}=\mathbf{10M}\text{ }\] newton at \[t=8\] second.
(III) weight at instant \[t=10,12,14\]second
slope (\[{{m}_{3}}\]) of given graph from \[t=10\] to \[t=14\] second is given as
\[{{m}_{3}}=\dfrac{-20}{4}=-5m/{{s}^{2}}\]
This time the acceleration is negative means in downward direction applying Newton's law of motion.
\[
Mg-N=M\times 5 \\
\Rightarrow N=10M-5M \\
\]
\[\mathbf{N}=\mathbf{5M}\]newton at \[t=10,12,14\] second.
Note:While solving this problem, most of the students tend to make mistakes in finding the slope of the curve at various instants. It should be remembered that when the lift is accelerating upwards the weight acting downward increases. This is because the floor of the lift presses harder to our feet while ascending upwards. When the lift moves with constant velocity, the net acceleration of the lift is zero, as we know acceleration is nothing but rate of change of velocity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




