
A person of mass \[50kg\] stands on a weighing scale oil a lift if the lift is descending with a downward acceleration of $9m{s^{ - 2}}$ . What would be the reading of the weighing scale?
Answer
510.6k+ views
Hint: To answer this issue, we must first rewrite the supplied facts, and because we have the acceleration value and also know the gravitational (acceleration due to gravity), we must first get the apparent weight, and then we can determine the weighing scale reading using the apparent weight.
Formula used:
$N = mg - ma$
Here, $N$ = normal force acting upward along the body , $m$ = the mass of the person , $a$ = acceleration of the lift and $g$= acceleration due to gravity.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Here, we are given that;
Mass of the person is = \[50kg\]
Acceleration of the lift = \[a\] = $9m{s^{ - 2}}$
For the following question, if the lift descends with an acceleration the apparent weight on the weighing scale will decrease.
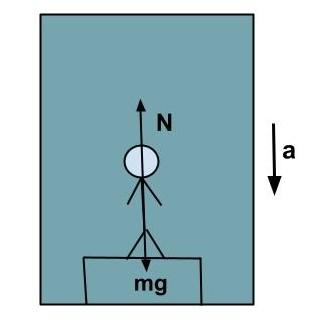
When a person steps on the weighing scale, the person experiences a normal reaction. The magnitude of a normal reaction is determined using a calibrated weighing scale reading.
It is possible to assume that the weighing scale reading corresponds to the person's visible weight.
Normal reaction acts upward along the upward direction of the individual, while gravitational force acts downward on the person.
Thus,
$
W' = N = \left( {mg - ma} \right) \\
\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,N = m\left( {g - a} \right) \\
$
The apparent weight of the lift on the weighing scale would now be; due to reaction force.
$
W' = 50\left( {10 - 9} \right) \\
W' = 50N \\
$
Thus, the reading of the weighing scale would be
$\dfrac{R}{g} = \dfrac{{50}}{{10}} = 5kg$
Therefore, the reading of the weighing scale would be $5kg$.
Note:During a free fall of a body under gravity in an elevator, the apparent weight of the body reaches zero. As the force of reaction between the individual and the plane with which he is in contact vanishes, the body might be said to become weightless.
Formula used:
$N = mg - ma$
Here, $N$ = normal force acting upward along the body , $m$ = the mass of the person , $a$ = acceleration of the lift and $g$= acceleration due to gravity.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Here, we are given that;
Mass of the person is = \[50kg\]
Acceleration of the lift = \[a\] = $9m{s^{ - 2}}$
For the following question, if the lift descends with an acceleration the apparent weight on the weighing scale will decrease.

When a person steps on the weighing scale, the person experiences a normal reaction. The magnitude of a normal reaction is determined using a calibrated weighing scale reading.
It is possible to assume that the weighing scale reading corresponds to the person's visible weight.
Normal reaction acts upward along the upward direction of the individual, while gravitational force acts downward on the person.
Thus,
$
W' = N = \left( {mg - ma} \right) \\
\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,N = m\left( {g - a} \right) \\
$
The apparent weight of the lift on the weighing scale would now be; due to reaction force.
$
W' = 50\left( {10 - 9} \right) \\
W' = 50N \\
$
Thus, the reading of the weighing scale would be
$\dfrac{R}{g} = \dfrac{{50}}{{10}} = 5kg$
Therefore, the reading of the weighing scale would be $5kg$.
Note:During a free fall of a body under gravity in an elevator, the apparent weight of the body reaches zero. As the force of reaction between the individual and the plane with which he is in contact vanishes, the body might be said to become weightless.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




