
A person moves towards East for $3\;{{m}}$, then towards North for $4\;{{m}}$ and then moves vertically up by $5\;{{m}}$. What is his distance now from the starting point?
Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint: To find the distance of the person, first describe the direction in terms of unit vectors, then write the final position vector of the particle. Finally use the concept of magnitude of the vector to find the required distance.
Complete step by step solution:
A vector in 3-D plane is described by the pair of its vector coordinates. The $x$ coordinate of a vector is known as $x$ component, $y$ coordinates of a vector is known as $y$ component, and $z$ coordinate of the vector is known as $z$ component of the vector.
The final position vector of the particle in this coordinate system is given by \[A = {{{a}}_1}{{\hat i}} + {{{a}}_2}{{\hat j}} + {{{a}}_3}{{\hat i}}\], here $\left( {{{{a}}_{{1}}}{{,}}{{{a}}_{{2}}}{{,}}{{{a}}_{{3}}}} \right)$ are the position of a point in $x$, $y$, and $z$ directions, respectively.
These components of the vectors are defined by the unit vectors $i$, $j$, and $k$. These vectors are the unit vectors in the positive $x$, $y$, and $z$ directions, respectively.
The magnitude of the vector is calculated as,
\[\left| {{A}} \right| = \sqrt {a_1^2 + a_2^2 + a_3^2} \]
In the given problem, a person moves towards East for $3\;{{m}}$, then towards North for $4\;{{m}}$ and then moves vertically up by $5\;{{m}}$.
Let the East direction be along ${{\hat i}}$ and the North direction be along ${{\hat j}}$ and the person be initially at the origin. Then ${{\hat k}}$ point will be in the vertically upward direction.
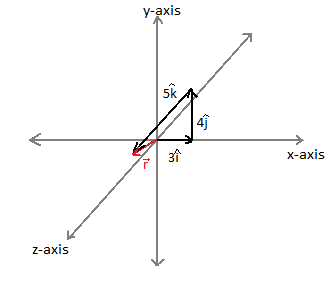
The above diagram shows the point in three dimensional view moreover the vector representation.
Now, write the final position vector of the particle as follows.
$\overrightarrow {{r}} = 3{{\hat i}} + 4{{\hat j}} + 5{{\hat k}}$
The distance of the person from the origin is calculated by finding the magnitude of the position vector as,
$ \left| {\overrightarrow {{r}} } \right| = \sqrt {{3^2} + {4^2} + {5^2}} \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt {9 + 16 + 25} \\
\Rightarrow 5\sqrt 2 \\ $
Therefore, the distance of the person from the starting point is $5\sqrt 2 $.
Note: Assume the unit vector according to the given direction and use the magnitude formula carefully to get the required distance. Do the calculation carefully and avoid silly mistakes. Most students can make mistakes and consider the north direction and the vertically upward direction as the same direction. This problem needs three axes for representation of the given state.
Complete step by step solution:
A vector in 3-D plane is described by the pair of its vector coordinates. The $x$ coordinate of a vector is known as $x$ component, $y$ coordinates of a vector is known as $y$ component, and $z$ coordinate of the vector is known as $z$ component of the vector.
The final position vector of the particle in this coordinate system is given by \[A = {{{a}}_1}{{\hat i}} + {{{a}}_2}{{\hat j}} + {{{a}}_3}{{\hat i}}\], here $\left( {{{{a}}_{{1}}}{{,}}{{{a}}_{{2}}}{{,}}{{{a}}_{{3}}}} \right)$ are the position of a point in $x$, $y$, and $z$ directions, respectively.
These components of the vectors are defined by the unit vectors $i$, $j$, and $k$. These vectors are the unit vectors in the positive $x$, $y$, and $z$ directions, respectively.
The magnitude of the vector is calculated as,
\[\left| {{A}} \right| = \sqrt {a_1^2 + a_2^2 + a_3^2} \]
In the given problem, a person moves towards East for $3\;{{m}}$, then towards North for $4\;{{m}}$ and then moves vertically up by $5\;{{m}}$.
Let the East direction be along ${{\hat i}}$ and the North direction be along ${{\hat j}}$ and the person be initially at the origin. Then ${{\hat k}}$ point will be in the vertically upward direction.

The above diagram shows the point in three dimensional view moreover the vector representation.
Now, write the final position vector of the particle as follows.
$\overrightarrow {{r}} = 3{{\hat i}} + 4{{\hat j}} + 5{{\hat k}}$
The distance of the person from the origin is calculated by finding the magnitude of the position vector as,
$ \left| {\overrightarrow {{r}} } \right| = \sqrt {{3^2} + {4^2} + {5^2}} \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt {9 + 16 + 25} \\
\Rightarrow 5\sqrt 2 \\ $
Therefore, the distance of the person from the starting point is $5\sqrt 2 $.
Note: Assume the unit vector according to the given direction and use the magnitude formula carefully to get the required distance. Do the calculation carefully and avoid silly mistakes. Most students can make mistakes and consider the north direction and the vertically upward direction as the same direction. This problem needs three axes for representation of the given state.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




