
What is a periodic table? What is periodic classification?
Answer
499.5k+ views
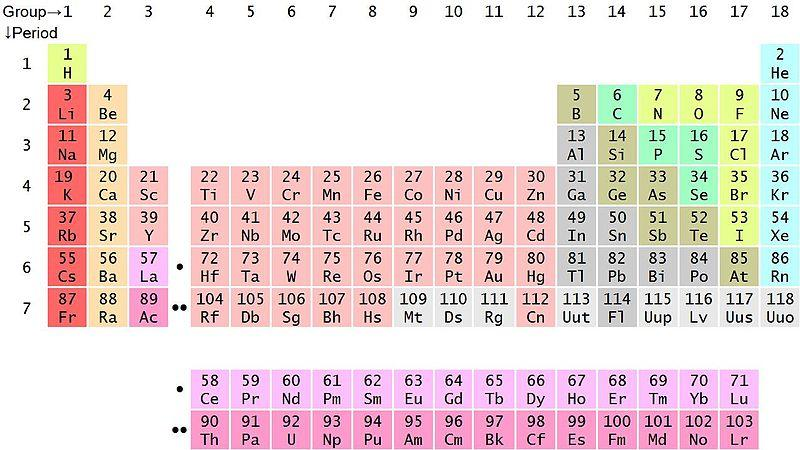
Hint: As we know that in chemistry, periodic tables play a vital role. Now we are using a modern periodic table. This modern periodic table consists of totally \[118\] elements. In the periodic table there are totally \[18\] columns and \[7\] rows. The columns are called groups. Hence, \[18\] groups in the periodic table. The rows are called periods. Hence, totally \[7\] period in the table.
Complete answer:
We have to know that in the world there are a lot of elements in various forms. For study and developing purposes, classification happens. Periodic table used to study the elements in easy form. If one new element is discovered, it means, based on the physical and chemical property we placed in the periodic table.
In general, modern periodic table ordering is based on the atomic number of the atoms. The lowest atomic number starting from the first and followed by a higher atomic number.
Depending on the energy level of the outermost shell in the atoms, periods are classified and place the atom in respect period. Depending on the electrons shielding and size and physical behaviour of the atom, groups are coming.
In the modern periodic table, metallic atoms are placed on the left side of the table and non-metallic atoms are placed on the right side of the table. Metalloids and transition elements are placed in between metal and non-metal elements. Below the two rows are there. There are nothing but lanthanides and actinides. These are f-block elements.
Note:
We must have to remember that the atomic number of the element is nothing but the number of electrons or number of protons. The mass number of the atom is nothing but the sum of the number of protons and number of neutrons. In general we move left to right metallic property of the atom decreases. We move right to left and non-metallic property decreases.
Complete answer:
We have to know that in the world there are a lot of elements in various forms. For study and developing purposes, classification happens. Periodic table used to study the elements in easy form. If one new element is discovered, it means, based on the physical and chemical property we placed in the periodic table.
In general, modern periodic table ordering is based on the atomic number of the atoms. The lowest atomic number starting from the first and followed by a higher atomic number.
Depending on the energy level of the outermost shell in the atoms, periods are classified and place the atom in respect period. Depending on the electrons shielding and size and physical behaviour of the atom, groups are coming.
In the modern periodic table, metallic atoms are placed on the left side of the table and non-metallic atoms are placed on the right side of the table. Metalloids and transition elements are placed in between metal and non-metal elements. Below the two rows are there. There are nothing but lanthanides and actinides. These are f-block elements.

Note:
We must have to remember that the atomic number of the element is nothing but the number of electrons or number of protons. The mass number of the atom is nothing but the sum of the number of protons and number of neutrons. In general we move left to right metallic property of the atom decreases. We move right to left and non-metallic property decreases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




